AWS Autodiscovery
Device42's AWS Autodiscovery ensures you have full visibility into your AWS environments. This visibility gives you insights into your total AWS consumption - allowing you optimize on spend and services consumed. We are adding new discoveries all the time, specifically based on customer need.
Discovery Items List Page
You can view the discovered AWS items by navigating to the list page under Resources > Cloud Resources. Use the search bar on the left or click on one of the column dropdown menus to filter for specific AWS discovery item fields.
For example, click on the Vendor Resource Type dropdown menu and start typing a discovery item type in the search bar. Filter by a segment of the item field name using the advanced Contains search bar or use the Not Contains criteria to filter by exclusion.
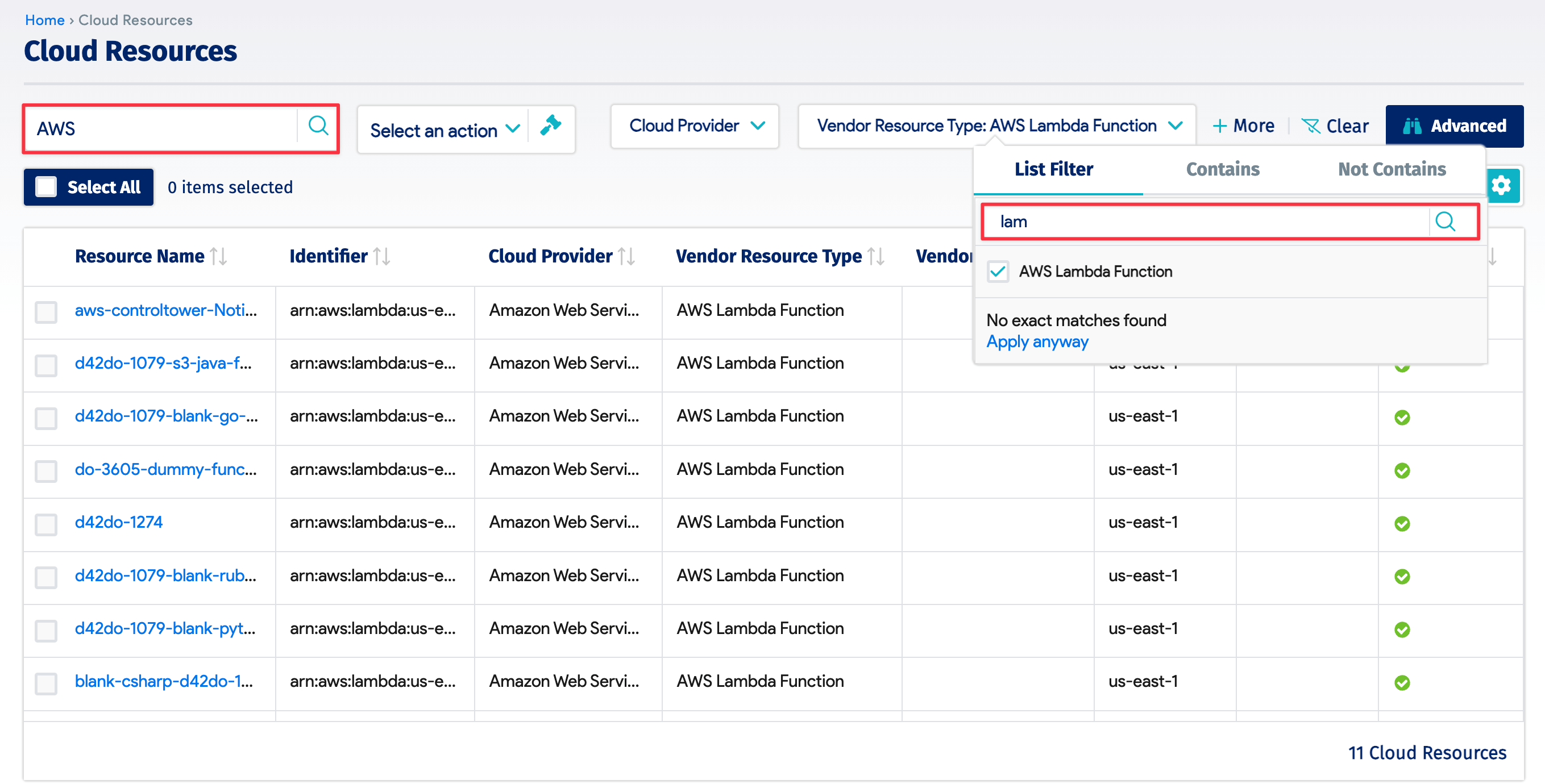
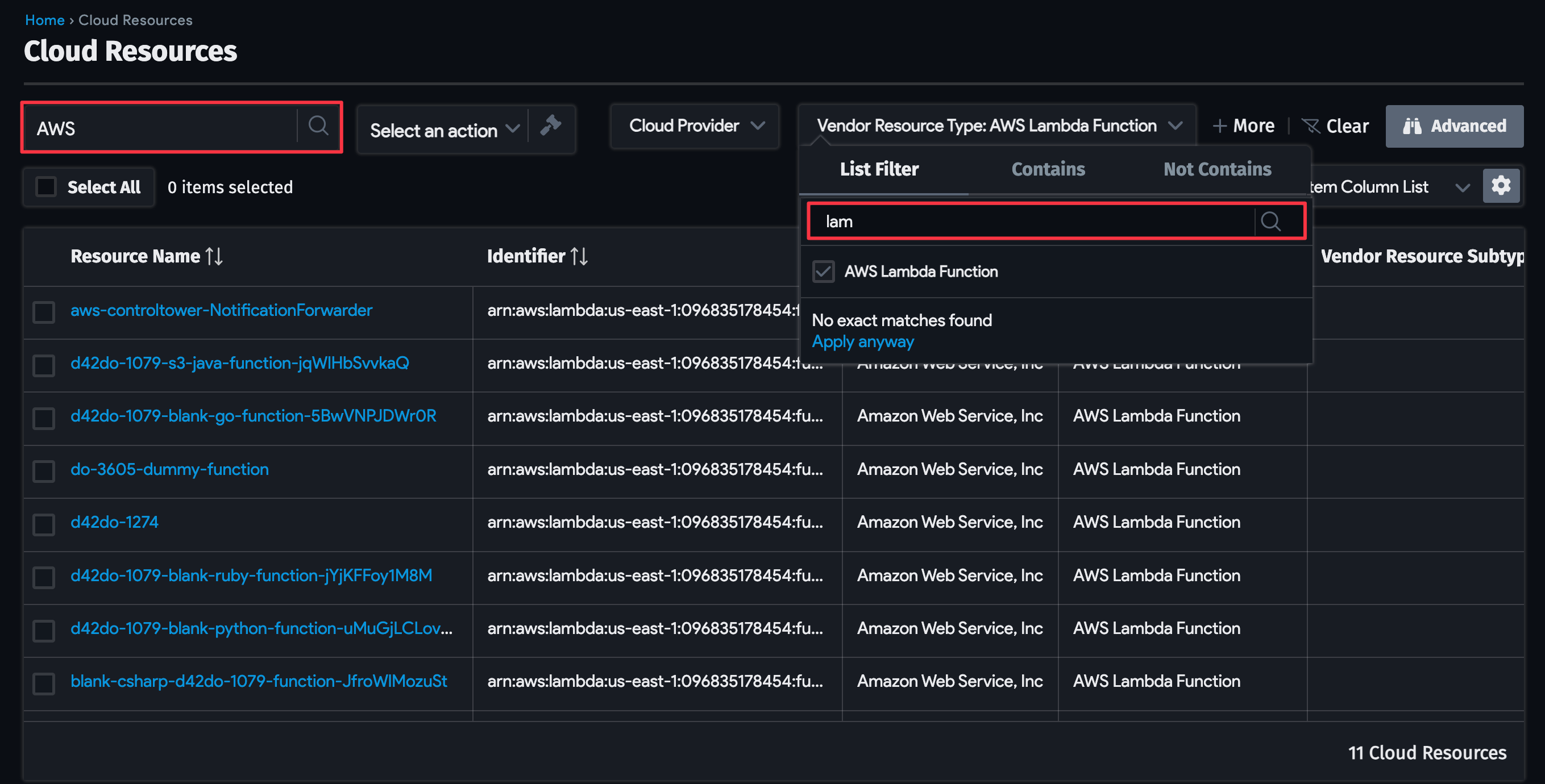
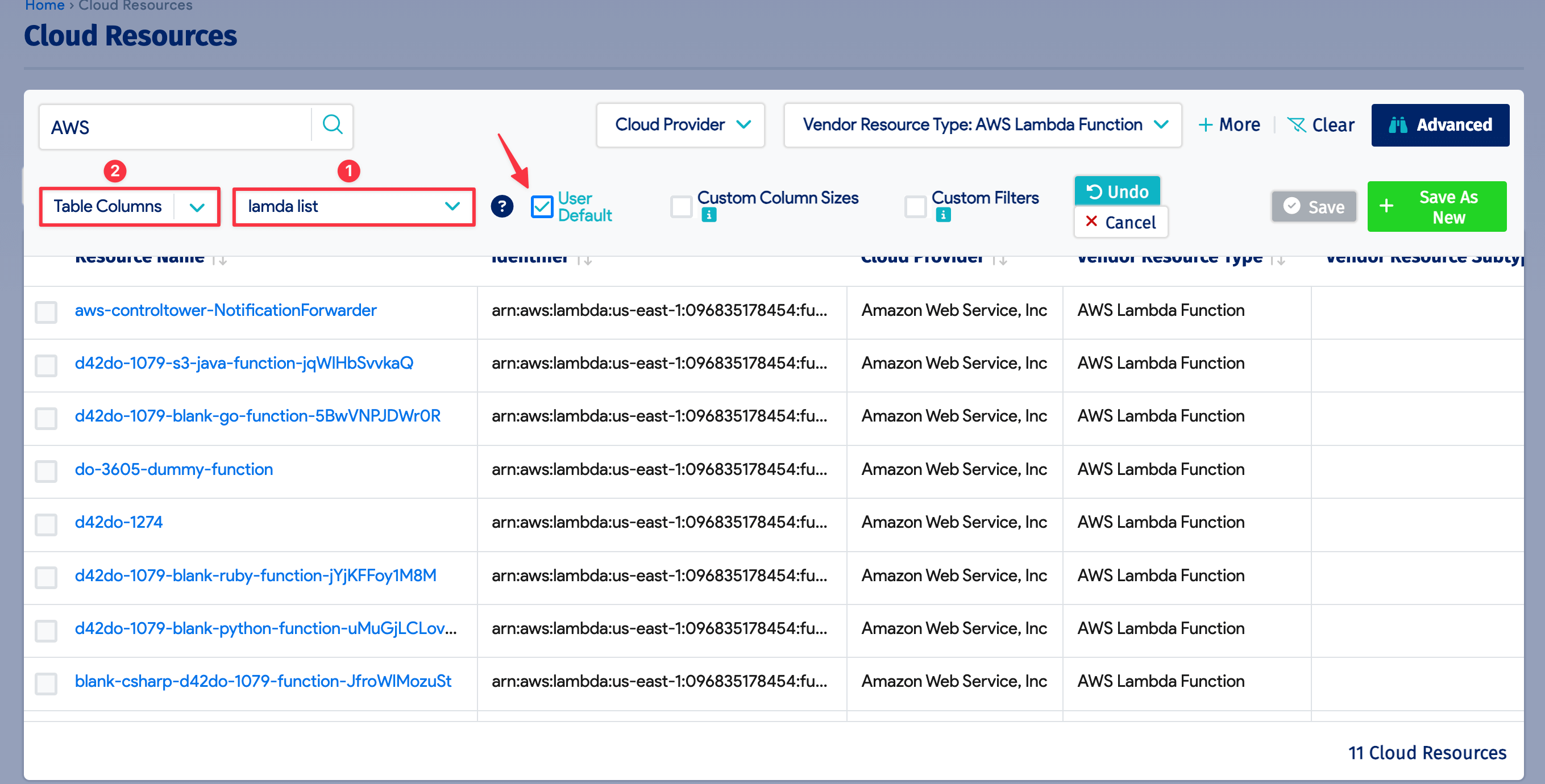
You can save your search to apply it later without repeating the search steps. Click on the gear icon on the left, name your search (1), and click on the green + Save As New button.
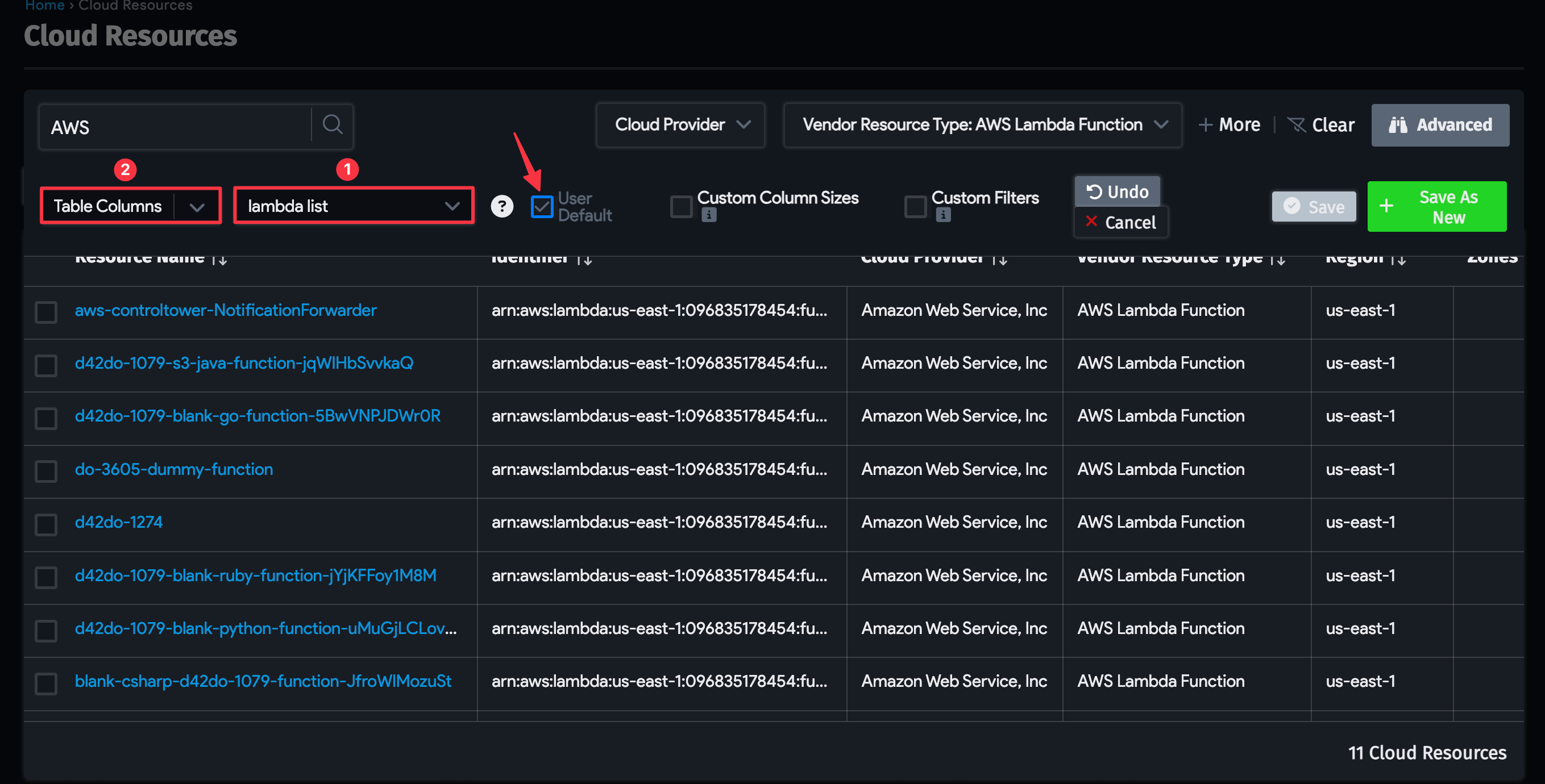
To change which columns are displayed, click on Table Columns (2) and select and deselect the columns from the list.
If you want to keep this list page setup as the default view, select the User Default box.
Getting Started with AWS Autodiscovery
To create an AWS Autodiscovery job, you will need to:
- Prepare your AWS Account - you can use the policy example shown below.
- Device42 utilizes your AWS Access Key and Secret Key to perform discovery; please have these handy.
Note: Device42 encourages customers to follow AWS best practices for managing your IAM credentials, including using strong passwords, regular password rotation, applying the principle of least privilege to users and their passwords, etc.
For more information, see the article Best Practices for Managing AWS Access Keys at https://docs.aws.amazon.com/accounts/latest/reference/best-practices.html.
Initiating an AWS Discovery
- Select Discovery > Cloud from the main menu and then click Add Cloud Autodiscovery at the top right of the Cloud Autodiscovery list page.
- Enter a Name for the job.
- Select the Cloud Type > Amazon AWS from the drop-down menu.


- Select the Remote Collector for the job.
- Add your Amazon Access Key ID and your Secret Key for the account(s) to be discovered. (Do this by clicking the magnifying glass, and then clicking Add Password in the upper right corner. Enter your Access Key ID or Secret Key in the field labeled Password. Device42 will store the keys encrypted_._)
- Select Discover Main Account to have the job discover the main AWS account in addition to any AWS Roles accounts you select.
- Select the Available AWS Roles whose account(s) you want to discover and use the arrow to add them to the Chosen AWS Roles list.
Note: See Defining AWS Roles below for instruction for creating the AWS Roles that Devices42 displays for AWS cloud autodiscovery jobs.
- Choose one or more Amazon regions to search.
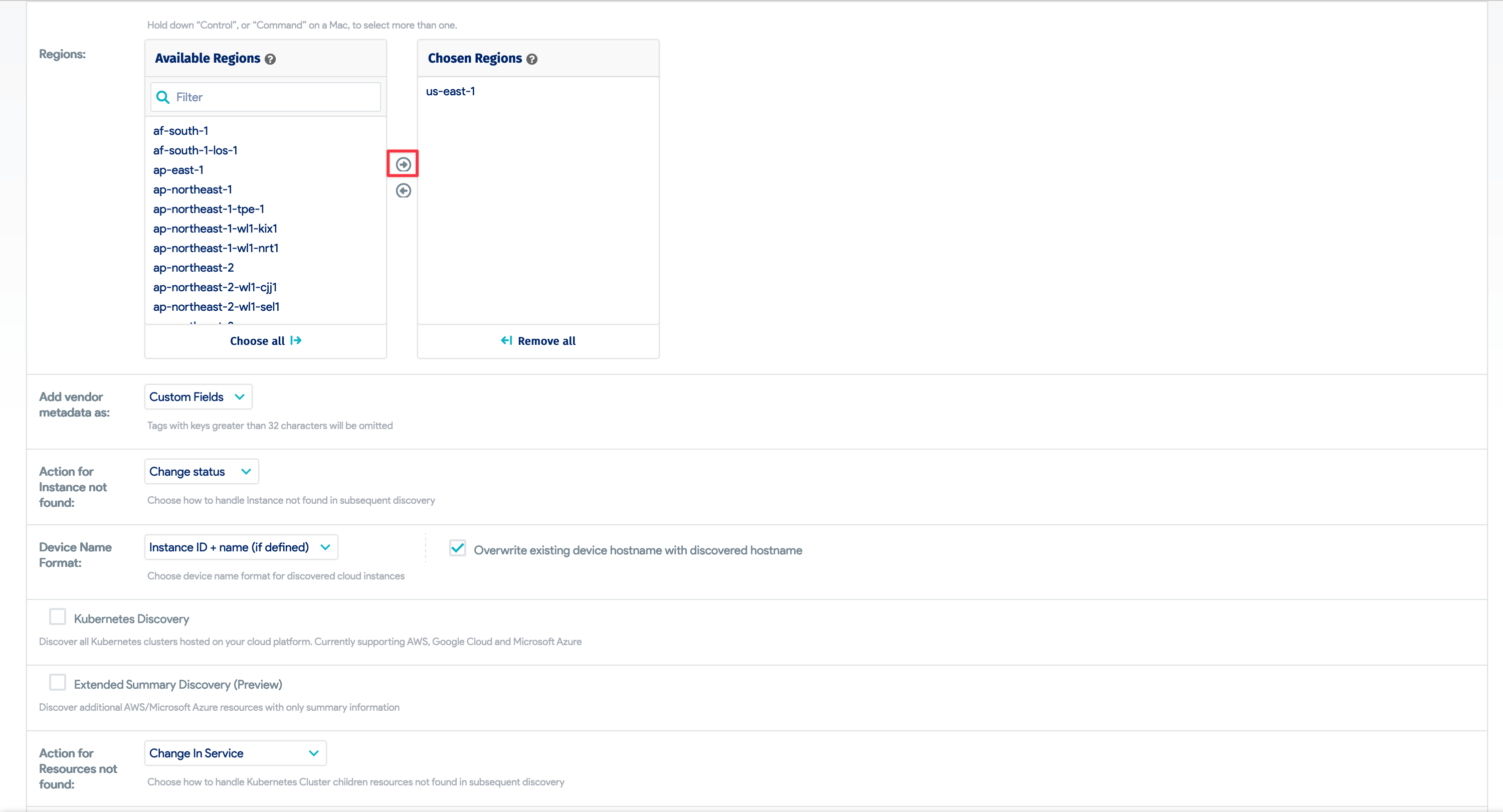

- You can also select options for adding vendor metadata, choose how to handle instances not found in subsequent discovery vendor, select device name format options, add tags for discovered devices, etc.
- Check Kubernetes Discovery to discover Kubernetes clusters hosted on your cloud platform.
- Check Extended Summary Discovery to discover the full breadth of resources within your AWS Environment. These resources will display in the Cloud Resources section with a limited dataset.
- Optionally, you can set the Service Level of the job to be applied to the discovered items.
- Add object categories, tags, and a customer for discovered devices, etc.
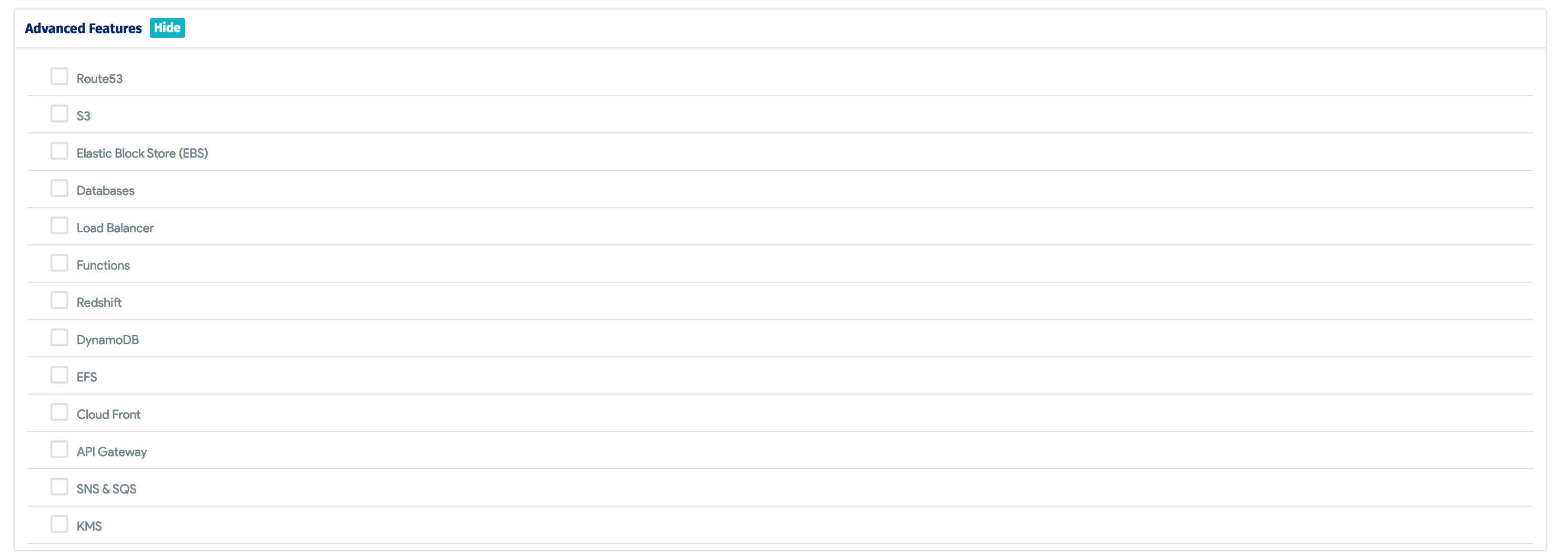
- Scroll down the page and click the Advanced Features (Show) tab to select the different types of resources you want the job to discover (Route53, S3, EBS, Databases, etc.).

- Add an Autodiscovery Schedule to schedule the job if wanted or add Admin Groups for the job.
- Click Save or Save and continue editing to save the discovery job.
- When you return to the Cloud Discovery list page, you can click Run Now to run the job immediately.
AWS Discovery Items
Note that some Discovery items require enabling the feature and cannot be discovered otherwise.
| Cloud Service/Object Name | Where in D42 | Accessed API | Information Generated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamo DB | Resources --> All Resources | dynamodb.region.amazonaws.com | Backup details, contributor insights, tables, limits, etc. |
| EC2 Instances | Resources --> All Resources | ec2.region.amazonaws.com | Service name, instance id, status, location, etc. |
| Elastic Block Storage (EBS) | Resources --> All Resources | ec2.region.amazonaws.com | Lists, rules, tags, etc. |
| ElastiCache Nodes | Resources --> All Resources | elasticache.region.amazonaws.com | Account info, status, location |
| Elastic File System (EFS) | Resources --> All Resources | elasticfilesystemr_egion.amazonaws.com | File system, access points, mount targets |
| Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) | Resources --> All Resources | elasticloadbalancing.region.amazonaws.com | Attributes, description, rules, tags, target groups |
| Lambda | Resources --> All Resources | lambda.region.com | Name, ARN, code size, memory, runtime |
| KMS | Resources --> All Resources | kms.region.amazonaws.com | Region, categories, access points, ACLs, notes, tags, custom fields |
| Kubernetes (EKS) | Resources --> All Resources | eks.region.amazonaws.com | Containers, nodes, clusters |
| RDS Instances | Resources --> All Resources | rds.region.amazonaws.com | Account info, status, location |
| Redshift | Resources --> All Resources | redshift.region.amazonaws.com | Backup details, contributor insights, tables, limits |
| Route 53 | Resources --> All Resources | route53.amazonaws.com | Type, content, tags |
| S3 | Resources --> Storage --> Cloud Storage | *.s3.region.amazonaws.com s3.region.amazonaws.com *.s3.amazonaws.com s3.amazonaws.com | Storage utilization, bucket, bucket policies |
| Security Group (AWS) | Resources --> Cloud Resources | ec2.region.amazonaws.com | Region, identifier, owner ID, Vpc Id, etc. |
| SNS | Resources --> All Resources | sns.region.amazon.aws.com | Topic, endpoints, attributes, subscriptions |
| SQS | Resources --> All Resources | sqs.region.amazon.aws.com | Queues, tags, queue attributes |
| Subnets | Network --> Subnets | Subnets | |
| VPCs | Resources --> VPC | vpc.aws-region.amazonaws.com | Attributes, AZs, Auth rules, etc. |
Additional Endpoint Information
Regular Discovery
- sts.amazonaws.com
https://organizations.us-east-1.amazonaws.com(Only if one of any of the available features is enabled.)
K8s cluster endpoints access per K8s RBAC setup
- /api/v1/namespaces/kube-system
- /api/v1/nodes?watch=False
- /api/v1/services?watch=False
- /apis/apps/v1/deployments?watch=False OR /apis/extensions/v1beta1/deployments?watch=False (depends on k8s version)
- /apis/networking.k8s.io/v1beta1/ingresses?watch=False OR /apis/extensions/v1beta1/ingresses?watch=False (depends on k8s version)
Example IAM Policy (except for K8s cluster endpoints, since it is controlled by K8s RBAC).
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"acm:DescribeCertificate",
"acm:List*",
"apigateway:GET",
"autoscaling:Describe*",
"cloudfront:ListDistributions",
"cloudfront:ListTagsForResource",
"cloudsearch:DescribeDomains",
"cloudwatch:Describe*",
"cloudwatch:GetMetricData",
"cloudwatch:GetMetricStatistics",
"cloudwatch:ListMetrics",
"config:SelectResourceConfig",
"dynamodb:DescribeGlobalTable",
"dynamodb:DescribeLimits",
"dynamodb:DescribeTable",
"dynamodb:ListGlobalTables",
"dynamodb:ListTables",
"ec2:Describe*",
"eks:DescribeCluster",
"eks:DescribeNodegroup",
"eks:DescribeUpdate",
"eks:ListClusters",
"eks:ListNodegroups",
"eks:ListUpdates",
"elasticache:Describe*",
"elasticfilesystem:DescribeAccessPoints",
"elasticfilesystem:DescribeAccountPreferences",
"elasticfilesystem:DescribeFileSystems",
"elasticfilesystem:DescribeMountTargets",
"elasticloadbalancing:Describe*",
"kms:DescribeKey",
"kms:ListKeys",
"kms:ListResourceTags",
"lambda:GetAccountSettings",
"lambda:GetFunction",
"lambda:GetPolicy",
"lambda:List*",
"logs:DescribeLogStreams",
"logs:GetLogEvents",
"organizations:DescribeAccount",
"organizations:ListAccountsForParent",
"organizations:ListOrganizationalUnitsForParent",
"organizations:ListRoots",
"organizations:ListTagsForResource",
"rds:Describe*",
"rds:ListTagsForResource",
"redshift:DescribeClusters",
"redshift:DescribeReservedNodes",
"route53:ListHostedZones",
"route53:ListResourceRecordSets",
"route53:ListTagsForResource",
"route53domains:ListDomains",
"s3:GetAccessPointPolicyStatus",
"s3:GetBucketAcl",
"s3:GetBucketLocation",
"s3:GetBucketPolicyStatus",
"s3:GetBucketPublicAccessBlock",
"s3:GetBucketTagging",
"s3:GetEncryptionConfiguration",
"s3:ListAccessPoints",
"s3:ListAllMyBuckets",
"sns:GetTopicAttributes",
"sns:ListTagsForResource",
"sns:ListTopics",
"sqs:GetQueueAttributes",
"sqs:ListQueues",
"sqs:ListQueueTags"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
AWS Tags
Organizations that use AWS tags can retrieve tags associated with each cloud account within AWS. Discovered tags are located under the Vendor Custom Fields field.

Amazon S3 Fields and Access Control
Device42 can discover information on the following S3 fields:
- Has Public Access Point
- Has Public ACL
- Has Public Policy
- Public ACLs Blocked
- Public Policies Blocked
A bucket can be public if it has Public Access Point, Public ACL or Public Policy. The Public ACLs Blocked and Public Policies Blocked flags can be independently controlled with settings in the AWS S3 console. When these flags are checked off, a user with the correct permissions can access the bucket.
Additional resources:
- See S3 Bucket policy examples for more details.
- Visit the block public access settings section for S3 access control options.
Add/Edit AWS Roles
Device42 includes an editor you can use to define or edit the AWS Roles displayed for Amazon AWS cloud autodiscovery jobs. Follow the steps below to view and add AWS Roles.
- Select Resources > Secrets > AWS Roles from the main menu.

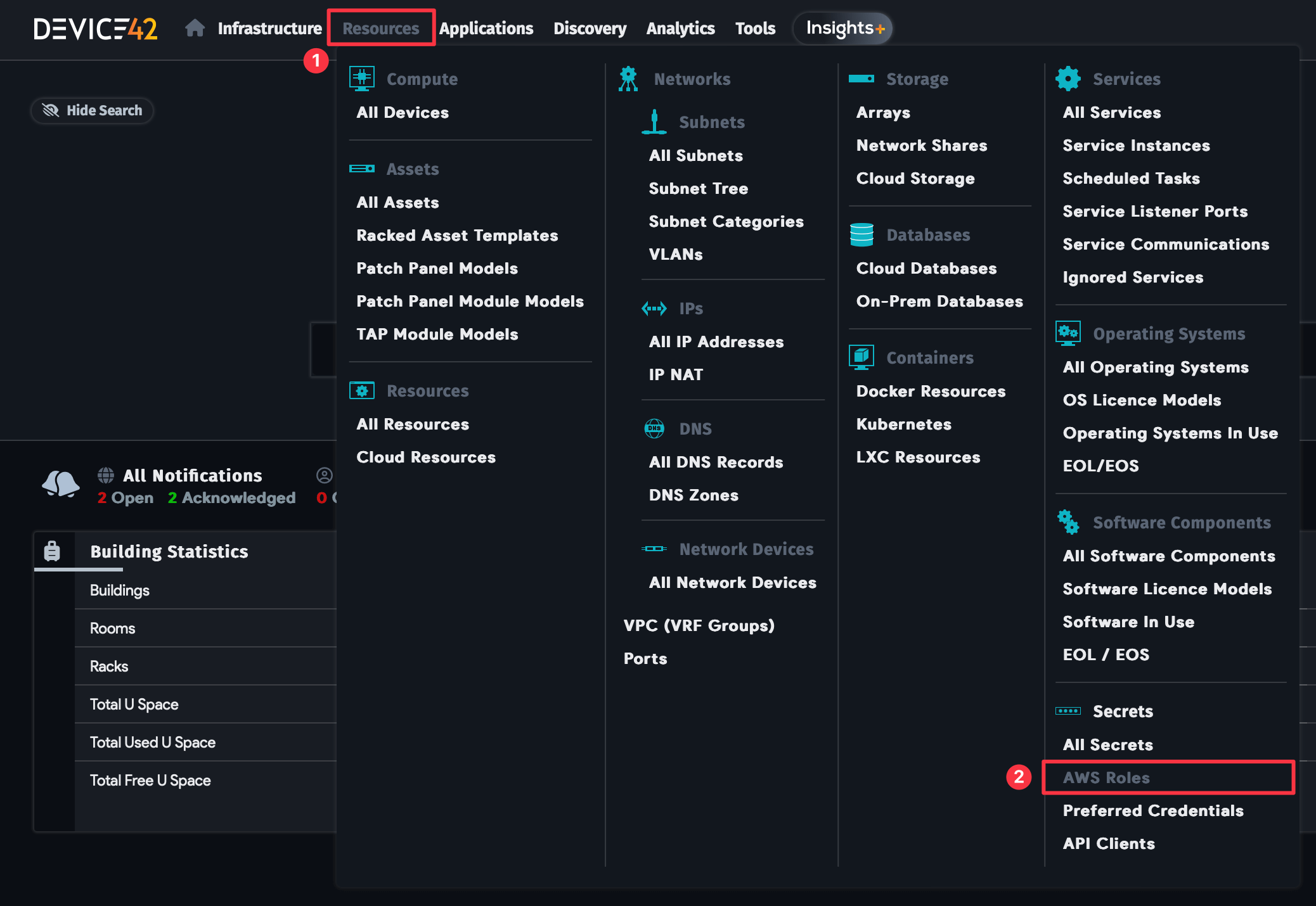
- Device42 displays the AWS Roles list page. Use the AWS Role drop-down to select a role to display or click Advanced to construct more specific searches. See the Advanced Search Feature documentation page for instructions.


- Click Add at the top right to add a new role – click a role Name to view or edit that role.


- Enter a Name for the role.
- Enter the AWS Role label and an optional AWS Role Description.
- In the Account ID and External ID section, click + Add More.
- Add the role Account ID and the External ID – click the eye icon to show or hide the field. Click the trash can icon to remove the entries.
- Click Save at the top right of the page to save the role.
Device42 adds the new AWS Role to the roles list; it will also appear in the Available AWS Roles list when you create or edit an Amazon AWS cloud autodiscovery job.
Note: The following steps are required if you are looking to leverage the AWS switch (Assume) Role on the API calls to scan other AWS accounts
-
From the Main Account:
-
Create a role within IAM -> This should be using the "Another AWS Account" option
-
We would need an account that uses just accountID and one that would be with the Require ExternalID option - Note no requirement for MFA option at this time
-
Policy to be added - use the example policy needed for discovery from our docs site here
-
-
From the Sub (or separate)-account
Have a user that is assigned the assumerole from Step 2 "Grant Access to the Role" here in the AWS IAM case IAM Tutorial
Setting up Dynamic Account Discovery Roles
In 18.11.03, you can now discover all sub accounts and add them to the discovery by using Dynamic Account Discovery. There are a few prerequisite steps that we'll cover first and then get into how to appropriately set up the roles.
- Create a role with no accounts associated with it
- Use the role in the discovery with the key/pair associated with it.
Set Up
Option 1:
- Key/pair user must be deployed into the org’s root account.
- This user policy must have at a minimum the following rights:
sts:assumeroleorganizations:listaccounts
- A role must be added to all accounts where discovery is desired, with the same role name used in every account where discovery is desired.
- The Device42 discovery policy must be granted to the role.
- For role config within Device42, do not add any accounts to the role.
- At this time, we cannot use dynamic account discovery to discover roles which use external ID values
Option 2:
- If you don't want to follow the steps above, you can either:
- make the assumable role available in the main account (dynamic discovery will pull it in if no accounts are listed, or if the main account is included in the manually added list of ID’s),
- or also attach the Device42 discovery policy to the user directly (requires selection of the “discover main account” box on the job).
Using AWS Roles To Discover Accounts Within Discovery Jobs
AWS Cloud Discovery Jobs can use AWS roles to discover accounts. When the job includes the AWS role, the discovery job will dynamically grab multiple accounts from AWS. We previously (before v18.13) aimed to maintain a 1:1 relationship between roles and accounts. Now, a single role can discover multiple accounts. This enables AWS users to set up discovery and specify the precise account to create, or leave the account empty to have the discovery job create Cloud accounts as a result of the discovery.
Setting up Environment Credentials using EC2 Instance Profiles
In 18.14, you can now perform AWS discovery without the need to supply any form of long-term, programmatic credentials by leveraging Instance Profiles / IAM roles for Amazon EC2 instances.
Support for this comes in the form of a new discovery option called 'Use Environment Credentials', which when enabled, allows the discovery job to be saved without selecting an Access Key ID or Secret Key in the job configuration.

Note: This is only possible when using a AWS hosted Main Appliance or Remote Collector for discovery as it relies on internal AWS mechanisms.
Configuration
-
Deploy a Main Appliance or Remote Collector within AWS
-
Create a new IAM Policy
- 2.1. On the IAM Policy creation screen, click on 'JSON' in the policy editor and copy/paste one of the policies below based on your desired discovery configuration:
-
Option 1: Single Account Discovery
Please refer to the example discovery policy above.
-
Option 2: Role Assumption Using Static Account Discovery
This option is good if you have a need to specify External IDs when assuming roles, as Dynamic Account Discovery does not support role assumption using External IDs.
Example IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"sts:assumerole"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
} -
Option 3: Role Assumption Using Dynamic Account Discovery
This option is good if you want to discover resources in all member accounts without the need to specify individual Account IDs.
Note: This requires the associated Remote Collector or Main Appliance to be deployed within the organization's root (management) account.
See: Setting Up Dynamic Account Discovery Roles for more details on configuring Dynamic Account Discovery.
Example IAM Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"sts:assumerole",
"organizations:listaccounts"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
-
- 2.2. Once you've confirmed you have the appropriate permission set selected, click on next, give the policy a name and description and then click on 'Create Policy'.
- 2.1. On the IAM Policy creation screen, click on 'JSON' in the policy editor and copy/paste one of the policies below based on your desired discovery configuration:
-
Create a new IAM Role
-
3.1. On the IAM Role creation screen, select 'AWS service' as the trusted entity type and 'EC2' as the Service or use case. Click Next.
-
3.2. On the add permissions screen, search for and select the policy created in step 2. Click on next, give the role a name and description and then click on 'Create Role'.
For those that may be looking to do the role preparation via the AWS CLI and not within the AWS Management Console, you can reference the trust policy below.
Example Trust Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"sts:AssumeRole"
],
"Principal": {
"Service": [
"ec2.amazonaws.com"
]
}
}
]
}
-
-
Attach the role
- 4.1. From the EC2 Instances list page, select the EC2 instance created in step 1. Then click on 'Actions' -> 'Security' -> 'Modify IAM role'.
- 4.2. From the 'Modify IAM role' page, select the IAM Role created in step 3 and then click 'Update IAM role'.
-
Additional Member Account Configuration for Role Assumption Using Static / Dynamic Account Discovery
Note: If you're configuring Single Account Discovery, then there are no remaining steps to be done. If you've opted instead for Role Assumption using static or dynamic account discovery, then continue following the steps below:
-
5.1 Create the discovery policy in each member account to be discovered.
Follow step 2 again but this time use the example discovery policy above.
-
5.2 Create the discovery role in each member account to be discovered.
Follow step 3 again but this time select 'Custom trust policy' instead of 'AWS service'. Copy/paste the trust policy below and then at the add permissions screen, search for and select the discovery policy created in the previous step.
Example Trust Policy
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::ROOT_ACCOUNT_ID:role/EC2_D42_RC_ROLE"
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}Note: Be sure to replace
ROOT_ACCOUNT_IDandEC2_D42_RC_ROLEwith your own values.- ROOT_ACCOUNT_ID: This is the root account ID where the role configured in step 3 resides
- EC2_D42_RC_ROLE: This is the name of the role in the root account to establish a trust with
-