Windows and Hyper-V Autodiscovery
Windows and Hyper-V discovery collects detailed host information, operating systems, services, software, and virtual machine data from Windows-based targets. Device42 can use either WinRM or WMI to communicate with target devices, with WMI as the default.
This page covers prerequisites, how to create and run Windows and Hyper-V discovery jobs, device naming options, and the minimum permissions required for WMI and WinRM.
Prerequisites
When using WMI, install the Windows Discovery Service (WDS) and connect to your Remote Collectors (RCs) before setting up your Windows discovery job. For WDS installation instructions and information, visit the Windows Discovery Service Installation documentation.
WinRM Network Requirements
WinRM uses port 5985 (HTTP) or 5986 (HTTPS), depending on the configuration of the target host. These connections come from the RC selected at the top of the jobs page. For configuration within your environment, refer to the Microsoft documentation. You must enable WinRM on your Windows machines, which can be configured through a Group Policy Object (GPO).
WMI Network Requirements
WMI is based on DCOM/RPC. This means a connection is first initiated on port 135 to determine what dynamic port to use. The connection then proceeds to use the dynamic port negotiated. The following Microsoft documentation can be used for configuring WMI.
Network Issues
The Device42 support team can provide best-effort assistance in resolving issues. However, for both protocols, reach out to your network or system admin to resolve connection issues.
Discovered Information
With a properly configured discovery account, Device42 gathers the following information:
|
|
Within the Parts section of device details, the CPU, RAM, and storage entries for the device will be displayed. You may also see additional information such as model number, slot, and location.
Create a Windows or Hyper-V Discovery Job
Navigate to Discovery > HyperVisors / *Nix / Windows to set up and save multiple discovery jobs for Windows, Hyper-V, and other platforms.
-
Click the Create button to set up a new Windows or Hyper-V discovery job.
-
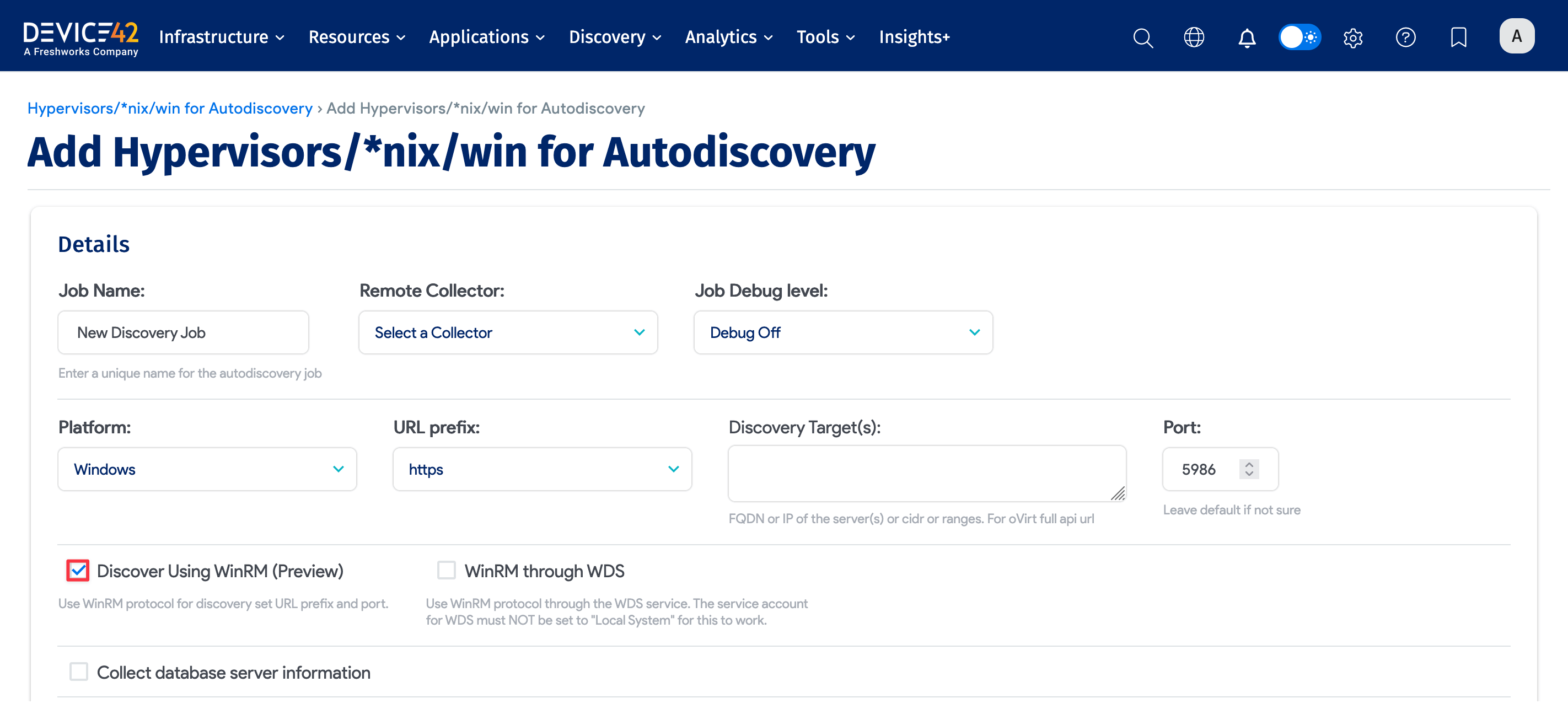
For Windows or Hyper-V discovery, select Windows as the Platform.
- Select Discover Using WinRM to use the WinRM protocol for discovery, which is fast and Microsoft's preferred protocol. The URL prefix and Port fields will default accordingly.
noteIt is not necessary to update existing jobs to use WinRM, as Device42 currently uses NTLM, which Microsoft is in the process of deprecating. Kerberos support is planned for a future release.
- If you're using WinRM, select the WinRM through WDS option to run the discovery using the local WDS. Ensure that your WDS service account operates under a domain account and is not set to Local System, as it doesn't support remote authentication.
-
Click Add another Username/Password to add one or more sets of credentials for the discovery targets.

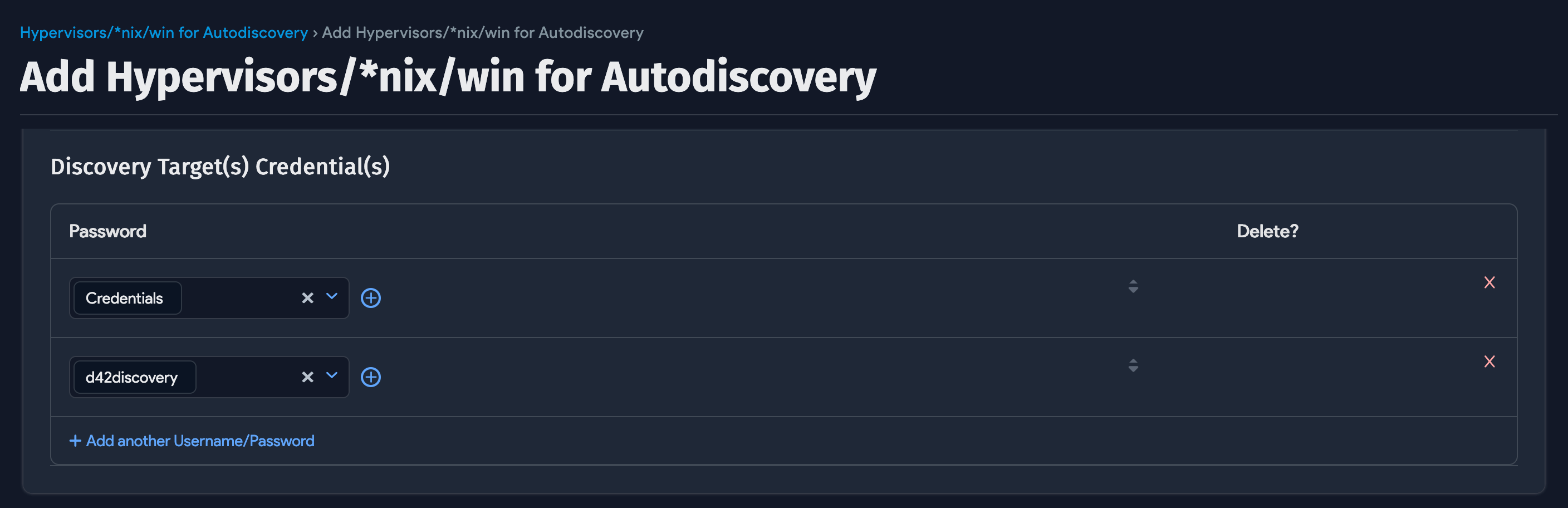
Classic WinRM is no longer a Platform type as of 18.08.00. Existing Classic WinRM jobs will continue to function.
Windows and Hyper-V Discovery Job Options
The following options are available when configuring a Windows or Hyper-V discovery job.
-
Job Name: Provide a unique name for the job.
-
Remote Collector: Select which RC you’d like to run the discovery job from.
-
Job Debug Level: Select Debug On to collect extra debug info that's useful for support tickets.
-
Discovery Target(s): Specify the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) or IP of the discovery target(s). If using FQDN, Device42 must be configured to resolve the DNS.
-
Use Service Account Credentials: Use the currently logged-in user of the system running WDS to perform WMI discovery.
-
Query domain controller to obtain a list of discovery devices: Select this to hide the Discovery Target(s) field. Targets discovered in this mode are instead defined by the result of the chosen LDAP Criteria, as returned by the specified Microsoft Windows Active Directory Domain or Domain Directory Server. See the Query Domain Controller section below.
-
Collect database server information: Select this option to discover Oracle, MSSQL, DB2, and Postgres database servers. Displays a Database Username/Password(s) field.
-
ADM Sampling Interval: Turn Off or set the sampling interval in minutes or hours.
-
Enable Resource Utilization Tracking for Device(s): Enable the collection of resource utilization metrics from discovered devices.
-
Resource Utilization Sampling Interval: Set the interval for resource utilization data collection. Only takes effect if resource utilization tracking is enabled.
-
Autodiscovery Schedule: Schedule the discovery to run at specific times.
Options to Ignore IPs and MAC Addresses
You can ignore IP and MAC addresses to exclude them from the database during discovery. Devices with these addresses will still be discovered, but the detailed information that is typically stored and collected will be ignored.
When creating or editing a job, you can configure rules to ignore IP and MAC addresses for that specific job.
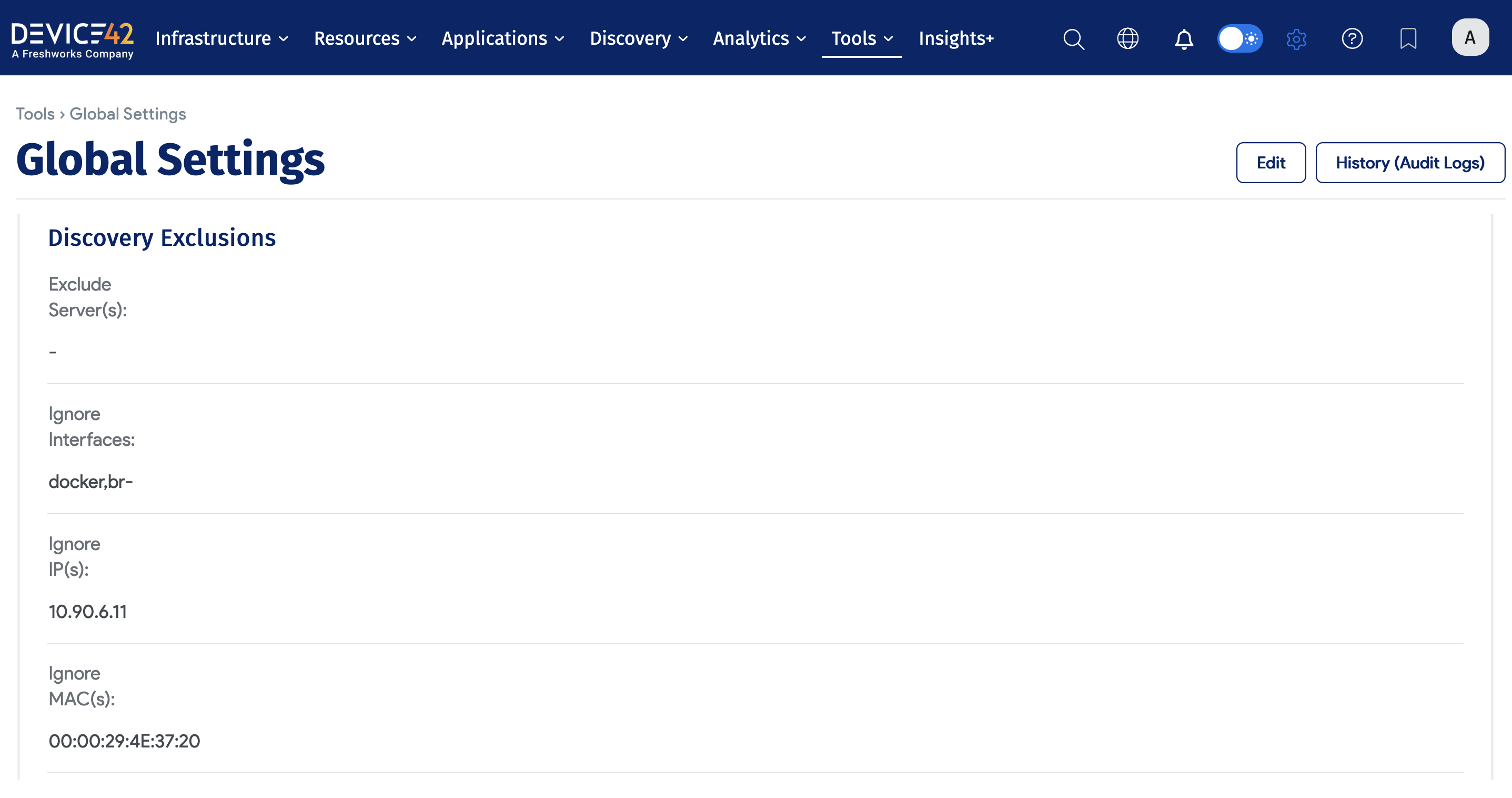
Globally, you can add an Exclusion to ignore IP and MAC addresses for all jobs by navigating to Tools > Settings > Global Settings on the Main Appliance (MA).
The “Query domain controller to obtain list of discovery devices” Option
Selecting the Query domain controller to obtain list of discovery devices option hides the Server(s): field. Target(s) discovered in this mode are instead defined by the result of the chosen LDAP Criteria, as returned by the specified Microsoft Windows Active Directory Domain or Domain Directory Server.
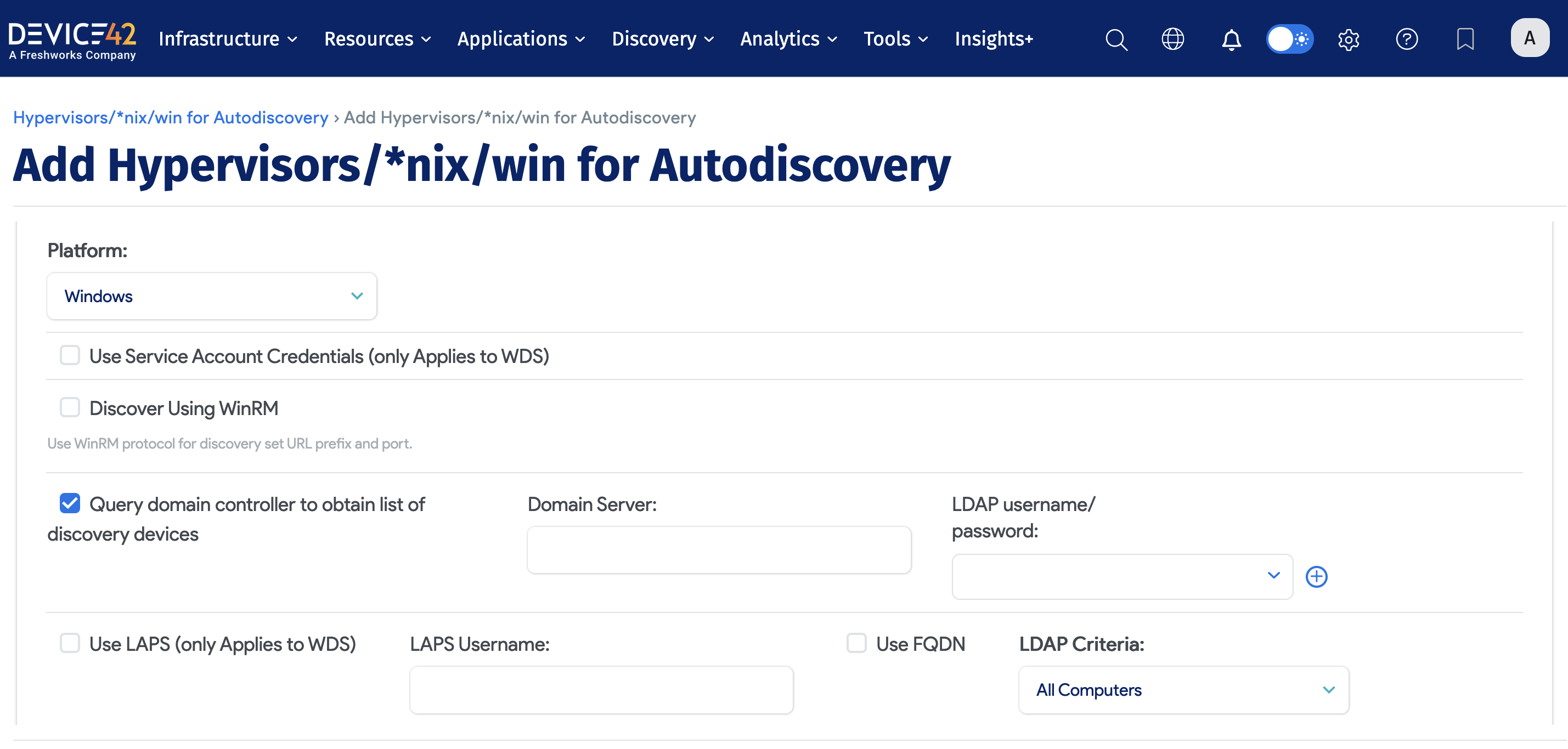
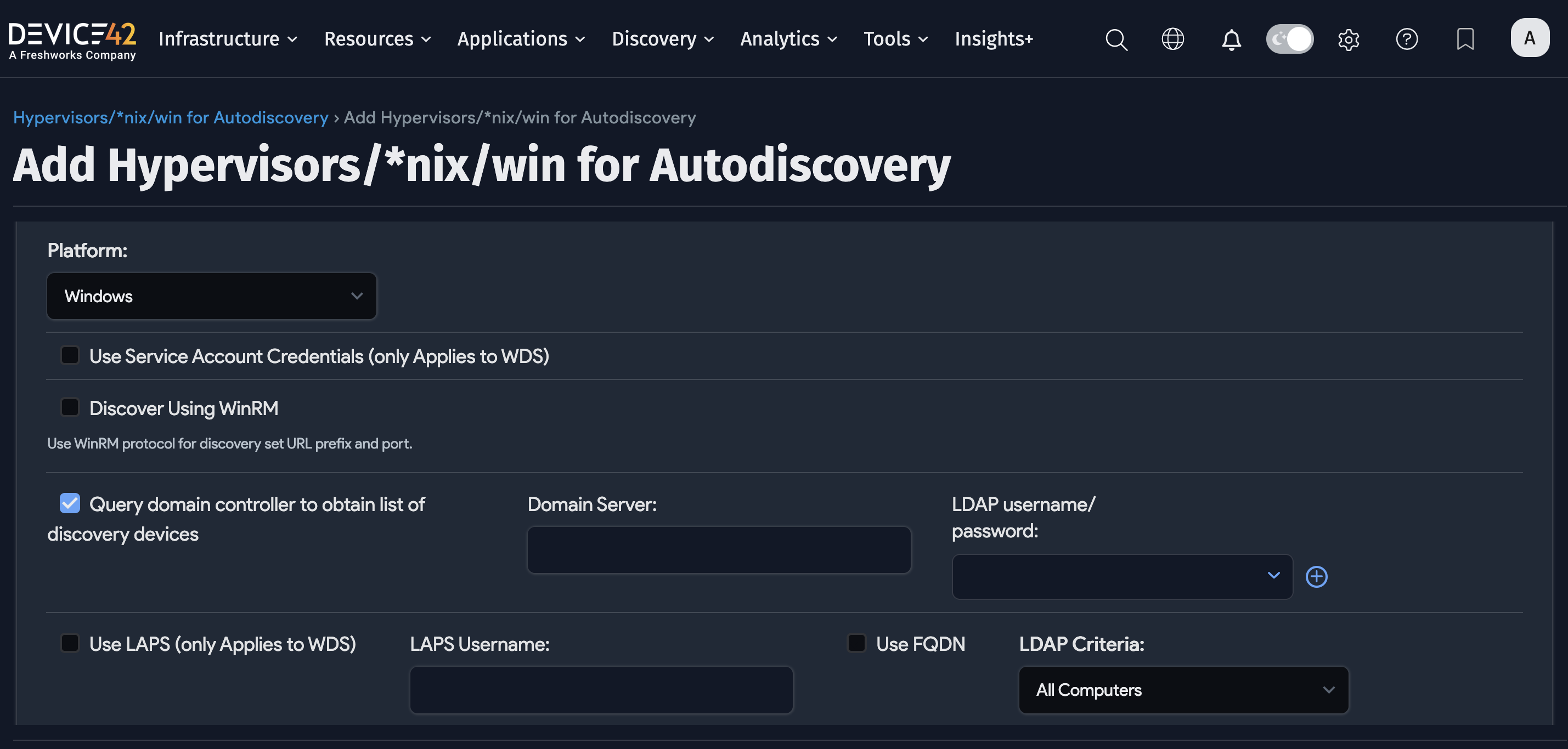
The relevant fields when using this discovery mode are as follows:
-
Use Service Account Credentials: Use whatever account credentials the WDS service executing the discovery is running as for authentication.
-
Domain Server: Hostname or IP address of the Active Directory server to run the LDAP query against.
-
LDAP username/password: Authentication credentials used to execute the LDAP query against the specified domain controller/server.
-
Use FQDN: Use the fully qualified domain name (FQDN).
-
LDAP Criteria: Choose an LDAP query to execute against Active Directory (AD). The resultant list will be targeted for Windows discovery. Select Custom to specify a custom LDAP filter or query.
LDAP Query Example: Query Domain Controller
The following query searches the domain server for all computers with DNS hostname d42sus.pvt and discovers the matches:
(&(objectCategory=computer)(dNSHostName=d42sus.pvt))
Discovery with Microsoft LAPS
Microsoft Local Admin Password Solution (LAPS) secures AD member servers by randomly generating a server's local admin password and storing it as an attribute of that server's AD object.
This password can be looked up on demand via an AD LDAP query and is often used to support scripted actions that iterate through lists of AD member servers.
Resources:
- To install LAPS, visit the Microsoft LAPS download page.
- For more information, see the Microsoft security advisory article about LAPS.
- To deploy LAPS, see the Deploying LAPS guide.
Device42 supports pulling credentials from LAPS when discovering AD domain member servers that use Microsoft LAPS to manage their local admin passwords. This option appears only when you select Query domain controller to obtain list of discovery devices. Once selected, the Use LAPS (only Applies to WDS) option is displayed.
Select the Use LAPS (only Applies to WDS) checkbox to enable it.
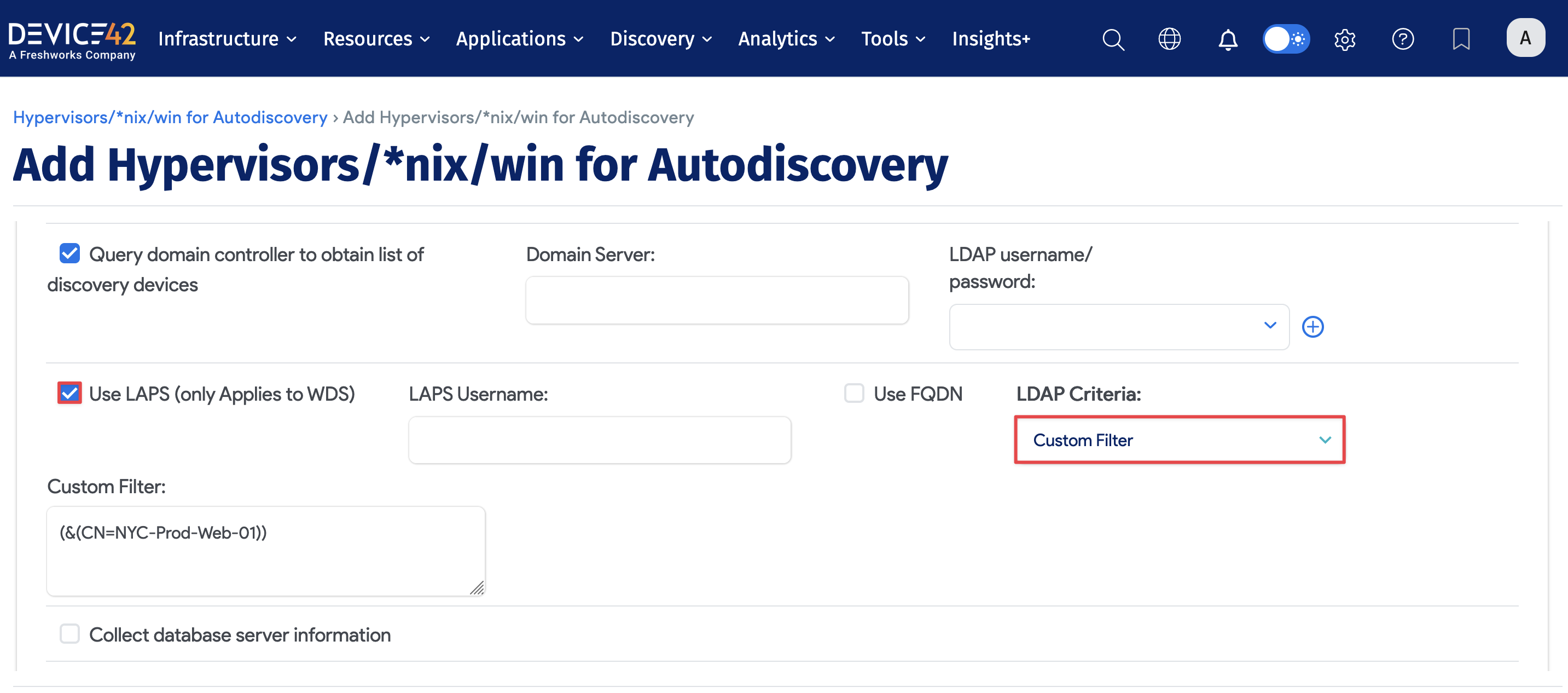
Fields and requirements for using LAPS discovery mode:
- Check the Query domain controller to obtain list of discovery devices option.
- Specify your domain server.
- Specify an LDAP username-and-password credential combination with permission to query the LAPS password for each server.
- You must have at least one instance of WDS installed (a requirement for all Windows-based discoveries).
- Choose All Computers or All Servers from the LDAP Criteria dropdown, or optionally supply your own custom LDAP query by selecting Custom Filter from the dropdown.
- Run your discovery job.
Hyper-V Discovery
To run a Hyper-V discovery job, set the Platform to Windows and enable the Discover VMs option.
The Hyper-V server's hardware details, name, UUID, and MAC addresses are pulled in from the VMs. In the Server(s) field, include the Hyper-V servers as hostnames, as IP addresses, or as part of a CIDR or IP range.
Additional Job Options
After completing the required options for your Windows or Hyper-V discovery job, scroll down to see additional options, including Exclusions, Naming, Host Discovery, Hypervisor Options, Software and Applications, and Miscellaneous. Click Show to expand each section.
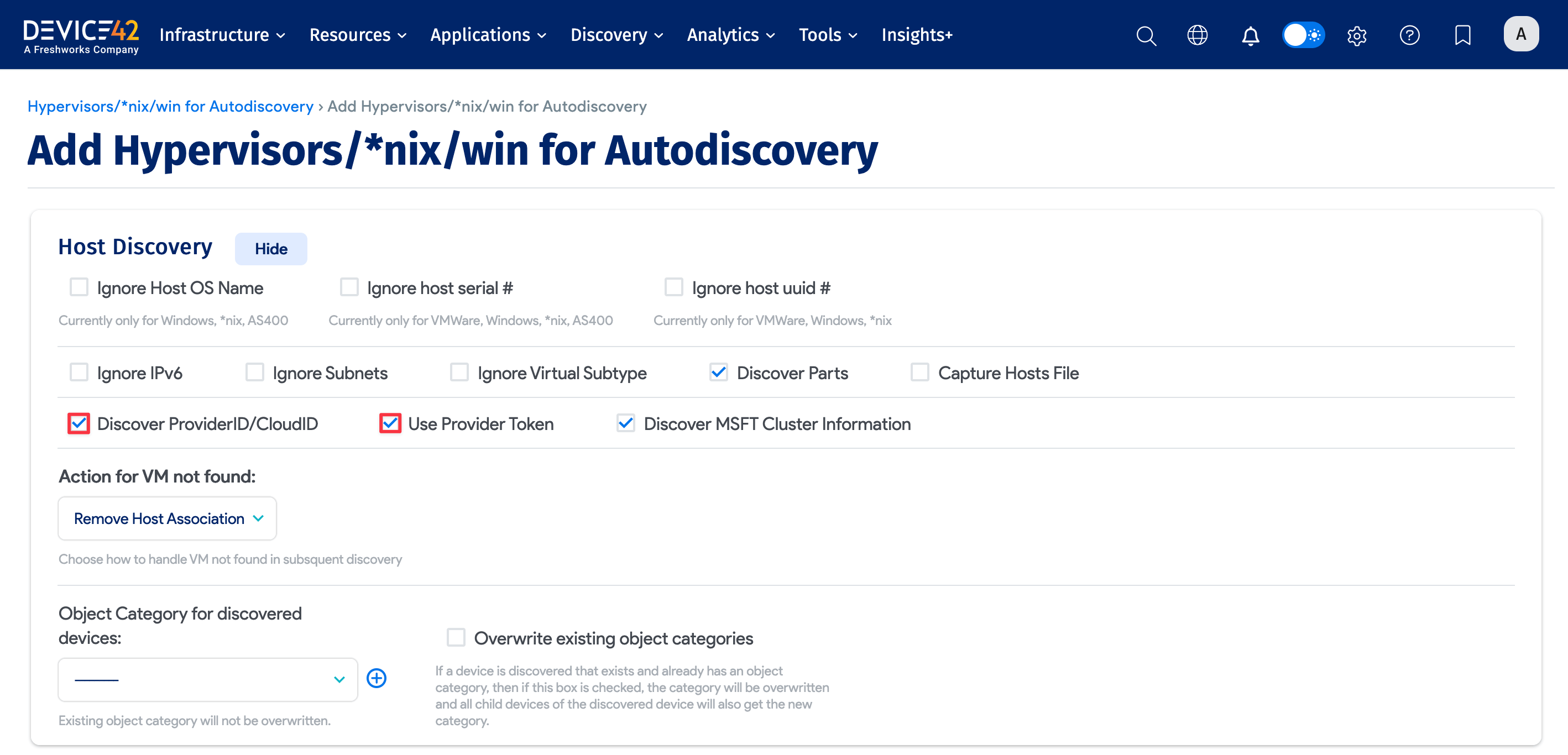
Host Discovery Options
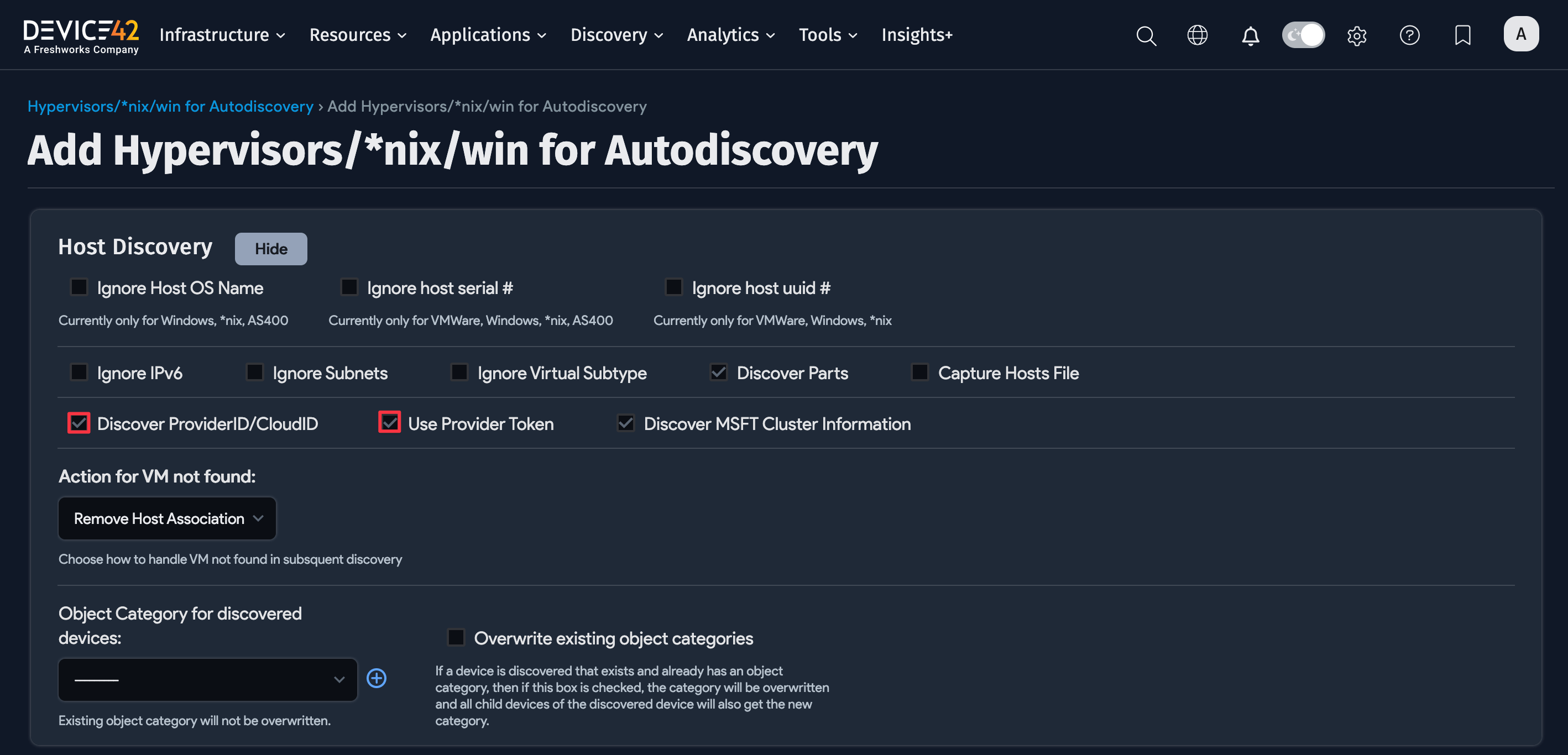
Expand the Host Discovery section to configure different types of hosts, what information to collect, and how to handle data during the discovery process.
Enabling the Discover ProviderID/CloudID option reveals the Provider Token option, which might be needed for authentication with the cloud service provider.
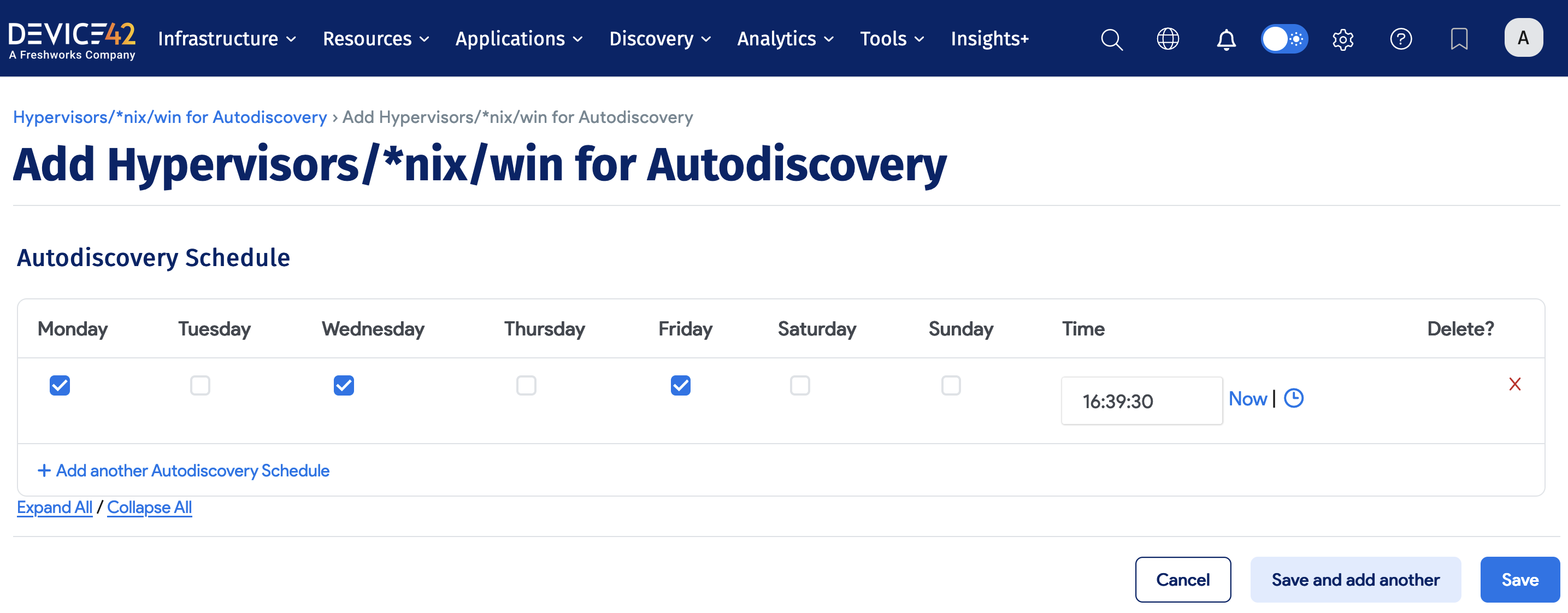
Schedule Discovery Jobs
In the Autodiscovery Schedule section, set as many different discovery schedules as you need to cover your environment. Choose specific times and days of the week to run the discovery job.
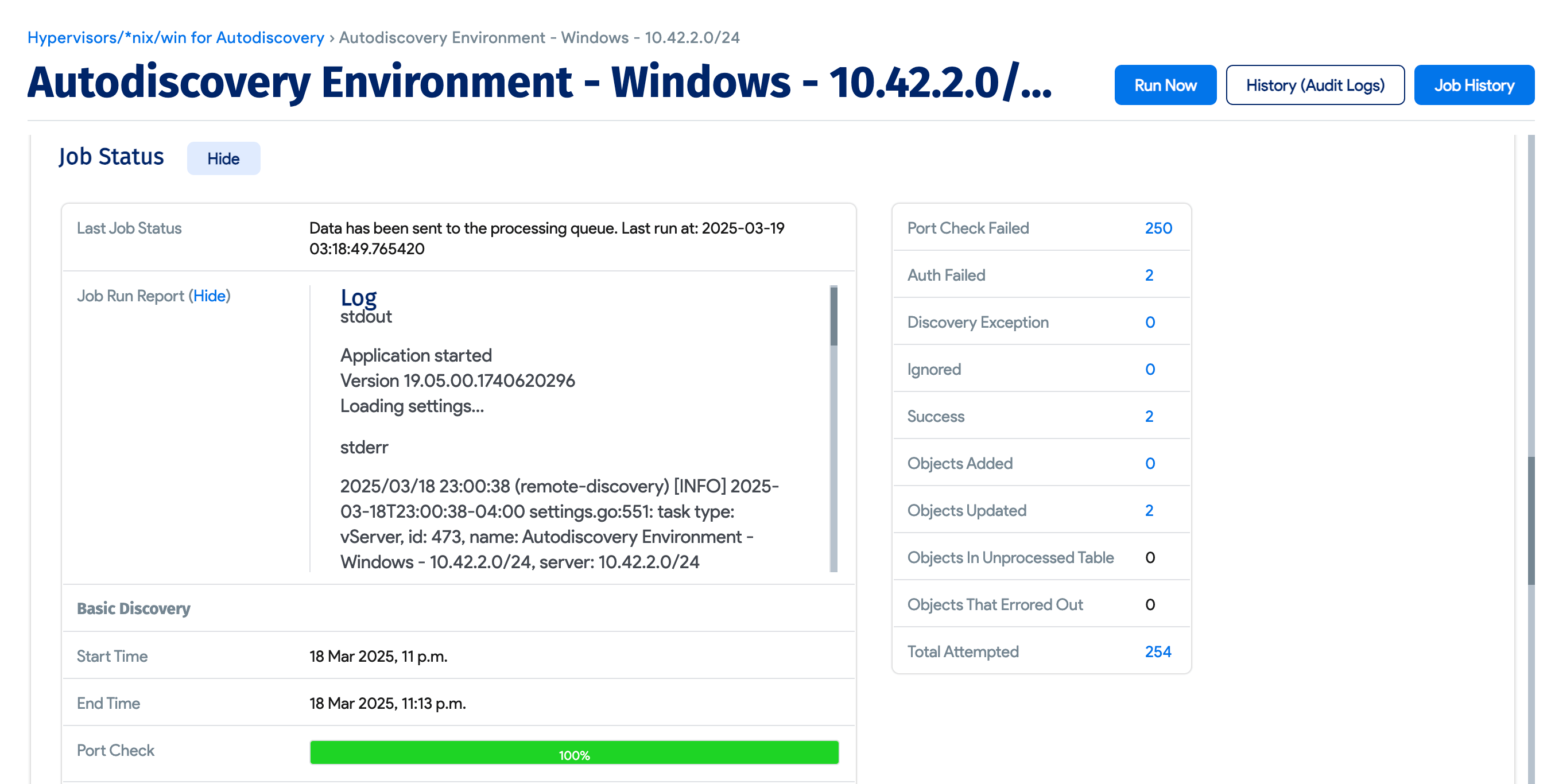
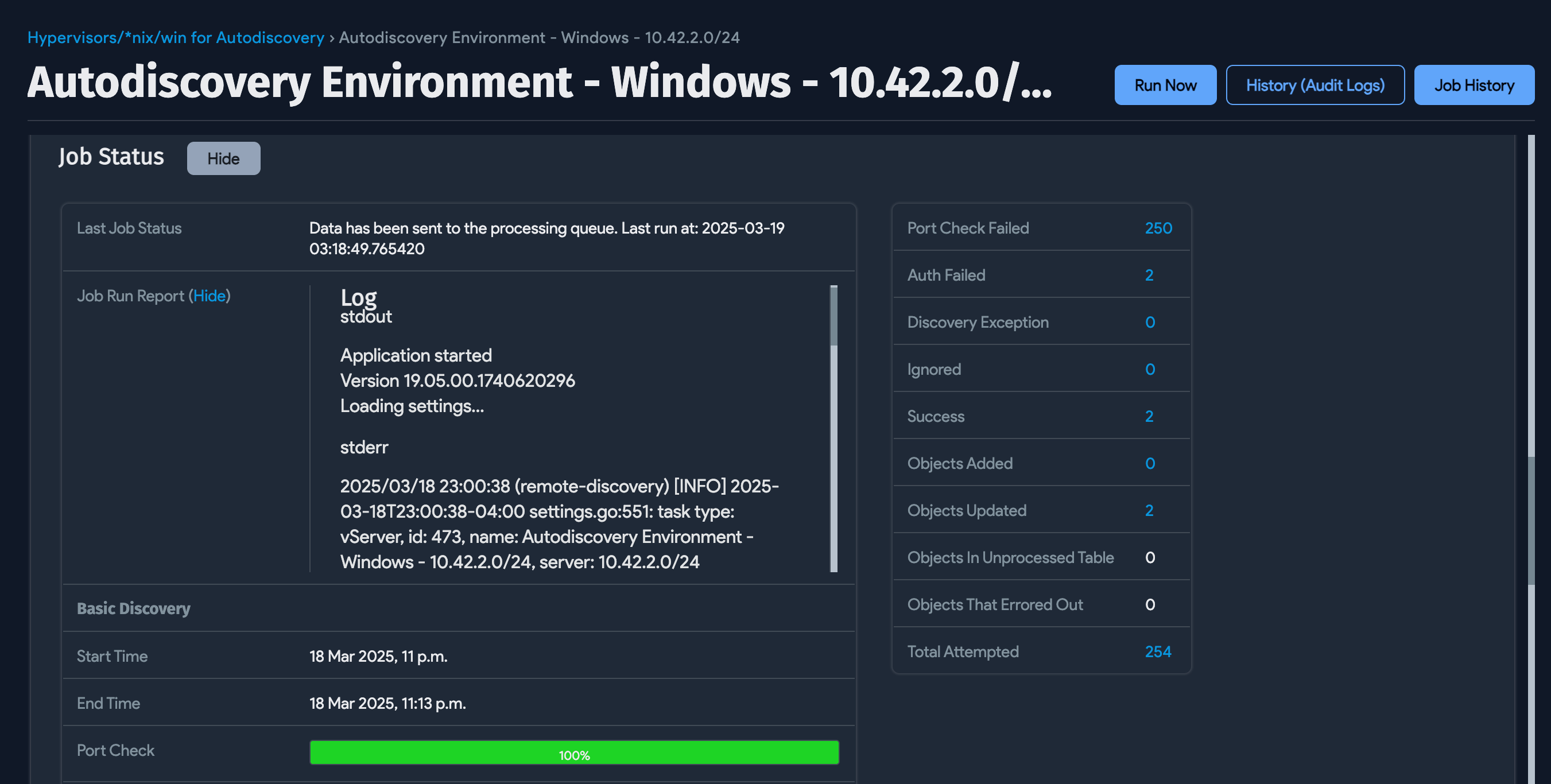
Job Status and Run Report
The Job Status section contains information about the last run status of the discovery job.
The Job Run Report has summary diagnostic details of stderr and stdout for the last job run.
Device Naming and Duplicate Device Prevention
To prevent or correct any duplicate devices, you can control the format for the names of devices added. For example, if you're running a VMWare discovery in tandem with a Windows discovery, there may be differences in discovered device names. vSphere will often show the short hostname, but a WMI query against the OS will return server FQDNs.
Device42 tries to match devices by serial number, UUID, and then name. However, if duplicates are added, you can use the options detailed in the following section to correct them.
Configure Windows Hostname Discovery Details
From the Naming Options section of the discovery job, select the Strip domain suffix option to drop everything after the first . in the device name.
The Strip domain suffix setting works in conjunction with the Device Name Format setting.
Under the Device Name Format dropdown, you can add or update the Device Name of any targets with the hostname format of your choosing. The naming options are as follows:
- Hostname as Discovered
- Hostname plus Domain Name
- Hostname and add Hostname plus Domain Name as Alias
- Hostname plus Domain Name and add Hostname as Alias
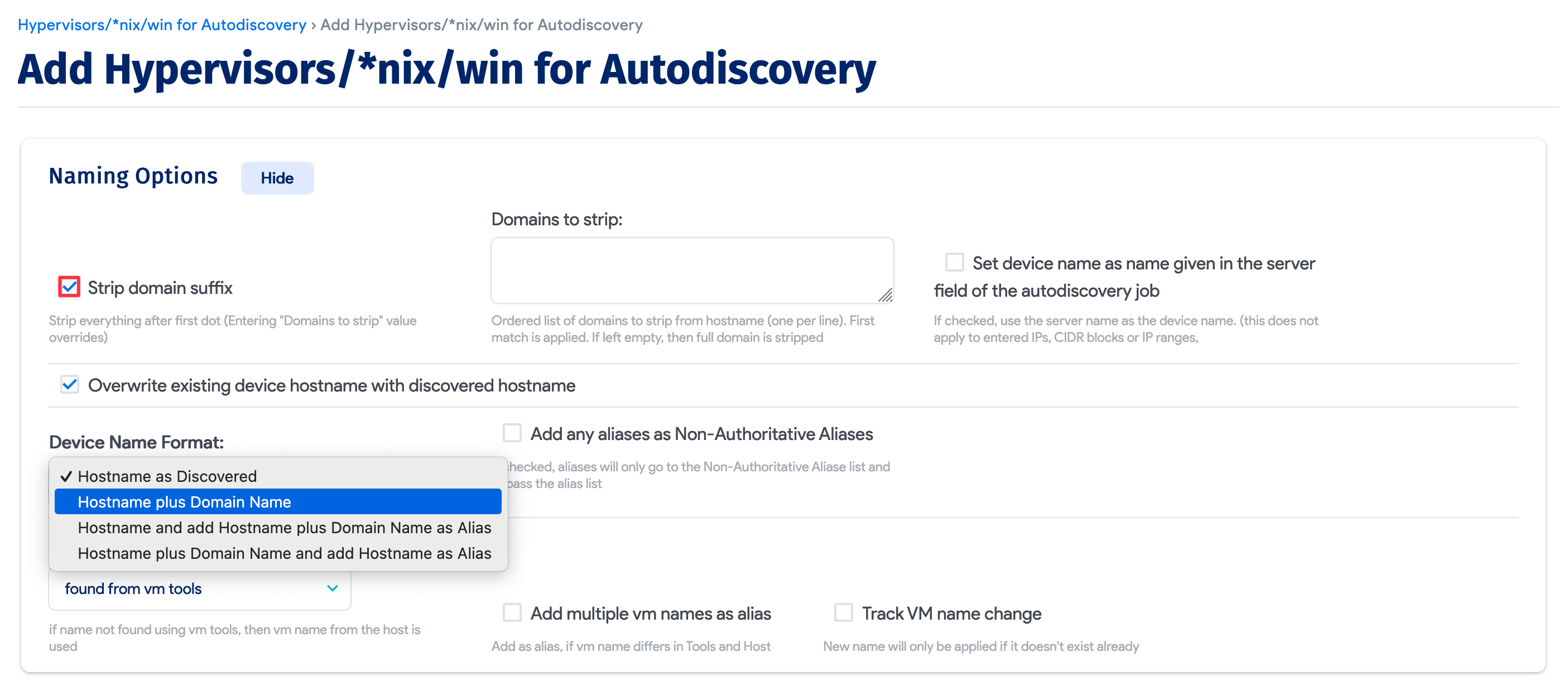
If your server hostnames are consistently named as you'd like them to appear, select the Hostname as Discovered option.
In environments with inconsistent naming conventions, select Strip domain suffix and Hostname plus domain Name. The options work together to strip the hostnames to short names and then append the found domains to those names.
If your server hostnames include domain names, such as server1.domain.com, and you do not strip the domain name suffix and choose the Hostname plus Domain Name option, the domain name will be appended again, resulting in names like server1.domain.com.domain.com.
Choose the Hostname and add Hostname plus Domain Name as Alias to add the discovered name as an alias, rather than replacing an existing device's name. This option adds devices using the discovered hostname as the device name, and the FQDN as the alias.
To set the Device Name to the FQDN of the device, make sure you select an option that includes Hostname plus Domain Name.
The Windows Hostname Discovery Process
Device42 uses the following WMI query to obtain host and domain details on Windows servers:
SELECT DNSHostName, Name, Manufacturer, Model, TotalPhysicalMemory, Domain, DomainRole
FROM Win32_ComputerSystem
Device42 uses the results of the query as follows:
For the Device Name, Device42 first checks the DNSHostName field, then falls back to the Name field if DNSHostName is empty.
If the DomainRole value is one of the following, Device42 uses the Domain value for the Domain Name:
WinDomainRoles.MemberWorkstationWinDomainRoles.MemberServerWinDomainRoles.PrimaryDomainControllerWinDomainRoles.BackupDomainController
Permission Requirements for WMI and Windows
Windows permission requirements are broken down into two parts:
- Minimum required permissions for discovering Windows host and guest information.
- Minimum required permissions for discovering services and application data for Application Dependency Mapping (ADM) on Windows.
WinRM-specific items are listed where applicable, but the permissions must be enabled on the target machine.
Windows WMI Discovery Minimum Permissions
The following requirements represent the minimum user account permissions for Device42 to connect to and discover a Windows host.
-
Ensure that at least Enable Account, Remote Enable, Read Security, and WMI permissions are applied to the discovery user account and to the following WMI namespaces and sub-namespaces:
CIMV2StandardCimv2defaultvirtualization(Hyper-V only)virtualizationv2(Hyper-V only)
MicrosoftIISv2(Only for IIS)WebAdministration(Only for IIS 7+)MicrosoftSqlServer(Only for SQL Server)SMS(Only for SCCM)MSCluster(Only used if 'Discover Cluster Information' is selected)
For Hyper-V discovery against Windows Server 2012 and newer: Because Microsoft verifies permissions differently on these newer operating systems, you may need to add your Device42 discovery account to the built-in Hyper-V administrators group if discovery fails due to a permissions error.
-
Enable the following firewall rules:
WinRM
- HTTP (5985)
- HTTPS (5986)
WMI
- Windows Management Instrumentation (DCOM-In)
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI-In)
-
Enable the following services and set them to automatic:
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
- Windows Management Instrumentation
-
Ensure the discovery user account is a member of the Performance Monitor Users Group and Distributed COM Users Group on the machines targeted for discovery.
If you discover servers that do not belong to a domain, your User Account Control (UAC) settings may be causing issues. Refer to this MSDN article to learn more about the effect of UAC on WMI.
Windows ADM Minimum Permissions
There are two options for configuring ADM permissions for admin users. The first option uses local administrative permissions and the IPC$ and ADMIN$ shares. The second option lets users configure their own shares.
For the local administrator method:
- ADM requires the local admin group on the target hosts and access to
IPC$andADMIN$shares. - Enable access to
IPC$andADMIN$shares: Device42 will utilize theIPC$andADMIN$shares to obtain service port communication details in Windows discovery. Ensure these shares are enabled and accessible over port 445, or inter-device communications will not be discovered. - Connection data is written to a path on the
admin$administrative share, which is only writable by the local admin group. This path is used because it is a standard, consistent path that can be found on all Windows deployments.
For the alternate method:
If the IPC$ and ADMIN$ shares are inaccessible when setting up the discovery job, you can use a network share instead.
- Specify a share. It can be local to the device or a shared location on your network.
- Give the scanning account read and write privileges to the new shared location.
- ADM also requires local admin permissions for this method.
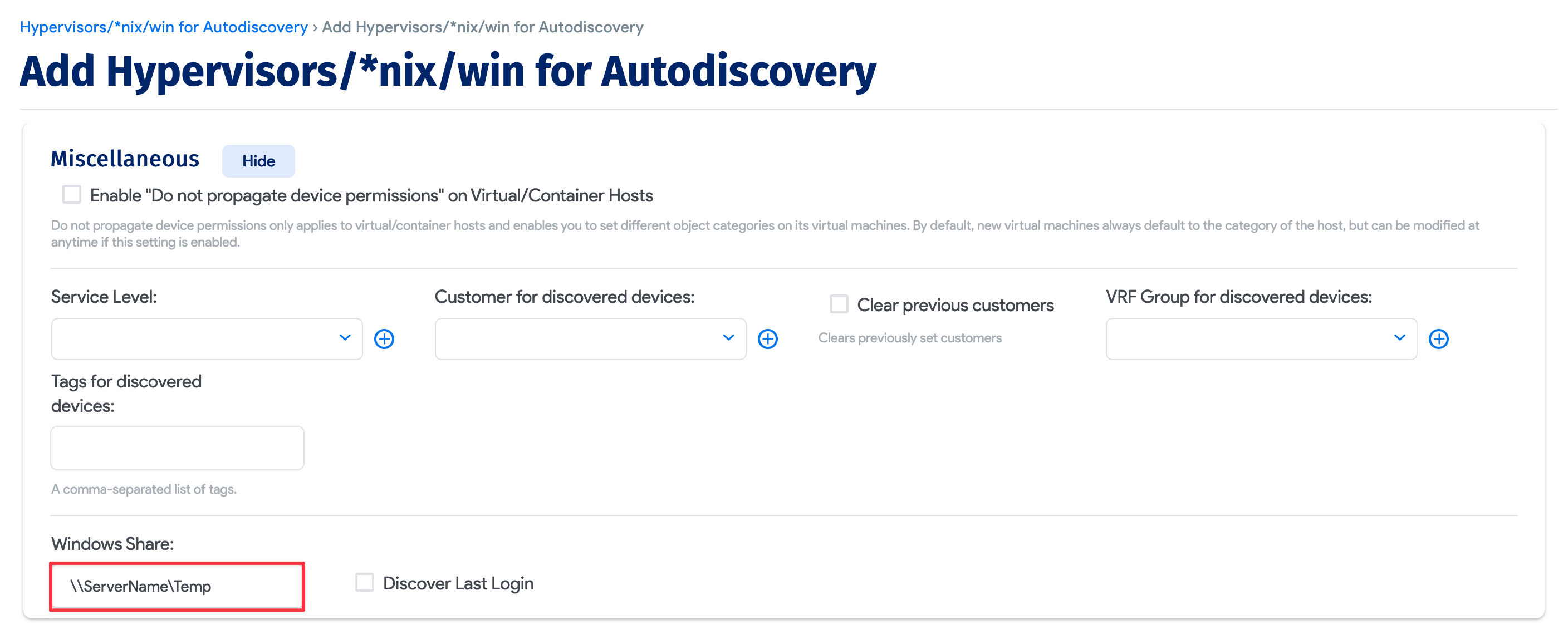
While it's best to use an admin account for complete discovery, you can try the following workaround to grant a non-admin user permission for service discovery.
Use the sc.exe sdset scmanager command to grant SC_MANAGER_CONNECT permission to the user:
-
First, find the SID of the non-admin user account that you want to grant permission.
-
Next, as an admin user, add the non-admin user's SID to the following command and execute it in PowerShell:
sc.exe sdset scmanager "D:(A;;CC;;;AU)(A;;CCLCRPRC;;;IU)(A;;CCLCRPRC;;;SU)(A;;CCLCRPWPRC;;;SY)(A;;KA;;;BA)(A;;CC;;;AC)(A;;CCLCRPRC;;;SID_OF_DISCOVERY_USER)" -
Then try running the discovery process again as the non-admin user.
Port Matrix
| Ports | Protocol | Application Protocol | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5985 | HTTP | WinRM | Always required for WinRM. |
| 5986 | HTTPS | WinRM | Always required for WinRM. |
| 135 | TCP | WMI | Always required for WMI. |
| 137 | UDP | NetBIOS Name Resolution | Optional/Legacy. Windows 2000 and newer versions of Windows can work over port 445. |
| 138 | UDP | NetBIOS Datagram Service | Optional/Legacy. Windows 2000 and newer versions of Windows can work over port 445. |
| 139 | TCP | SMB | Optional/Legacy. Windows 2000 and newer versions of Windows can work over port 445. |
| 445 | TCP | SMB | Optional. Used by WDS to retrieve UDP communication and configuration files from targets. |
| 1024-5000 | TCP | RPC randomly allocated low TCP ports | Optional/Legacy. Used in Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003. Newer versions of Windows use high TCP ports 49152 - 65535. |
| 49152-65535 | TCP | RPC randomly allocated high TCP ports | Always required (unless the entire environment predates Windows Server 2008). Used in Windows Server 2008 and later versions, and in Windows Vista and later versions. |
Best Practices and Limitations
- If you've populated Device42 with devices before your first discovery run (using CSV imports, spreadsheets, or manual entry), test discovery against a few devices to verify that the selected discovery naming options are correct for your naming convention. For example, if you added
nh-linux01as a device, discovery could find the hostnamenh-linux01.example.comand add it as a new device because the names don't match. See the Device Naming and Duplicate Device Prevention section. - Run device discovery after running network discovery or after defining the subnets where your network IPs reside.
- Floating IPs that logically belong to a cluster but are found on a device during discovery will be assigned to that device and not the cluster resource.
- You can run the WDS from any or multiple network segments. Communication from the discovery client back to the main Device42 instance requires access via port TCP/443 (HTTPS) on your network.
Legacy Windows 2000 Discovery Prerequisites
To discover a legacy Windows 2000-based operating system, adjust the following OS settings on the machine hosting your WDS:
- Change or create the
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\LmCompatibilityLevelelement so that it has the value1. - Change the WDS service user from
Systemto one of the host users (like an admin account). You can try to run a discovery job without this step, but users report failure without making this change.