Nmap Autodiscovery
This page covers how to use Nmap (network mapper) discovery to identify services running on ports across your network. Device42 combines Nmap data with NetFlow data to automatically create a map of services and application dependencies.
Nmap is a tool primarily used for security scanning, but it can also identify which services are running on which ports.
Create an Nmap Discovery Job
Navigate to the Discovery > Nmap list page and click Create to add a new Nmap discovery job.
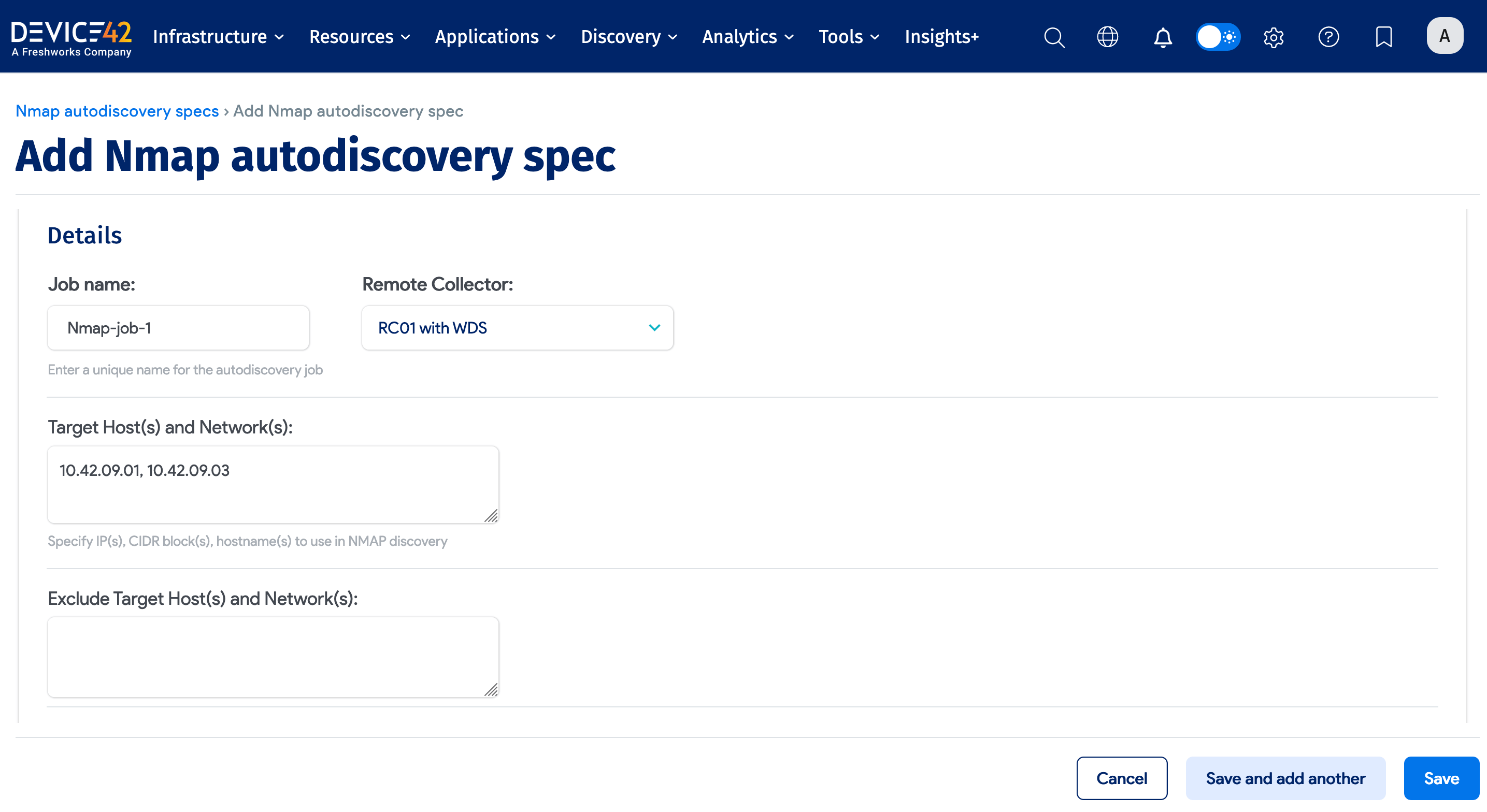
Enter the following required fields for the Nmap job:
- Name: A unique name for the job.
- Remote Collector: The name of the Remote Collector to use. A Local Collector cannot be used.
- Target Host(s) and Network(s): A comma-separated list of IP addresses, IP ranges, CIDR block(s), or hostname(s) to use for Nmap discovery.
Nmap Discovery Job Options
You can optionally configure these Nmap job options:
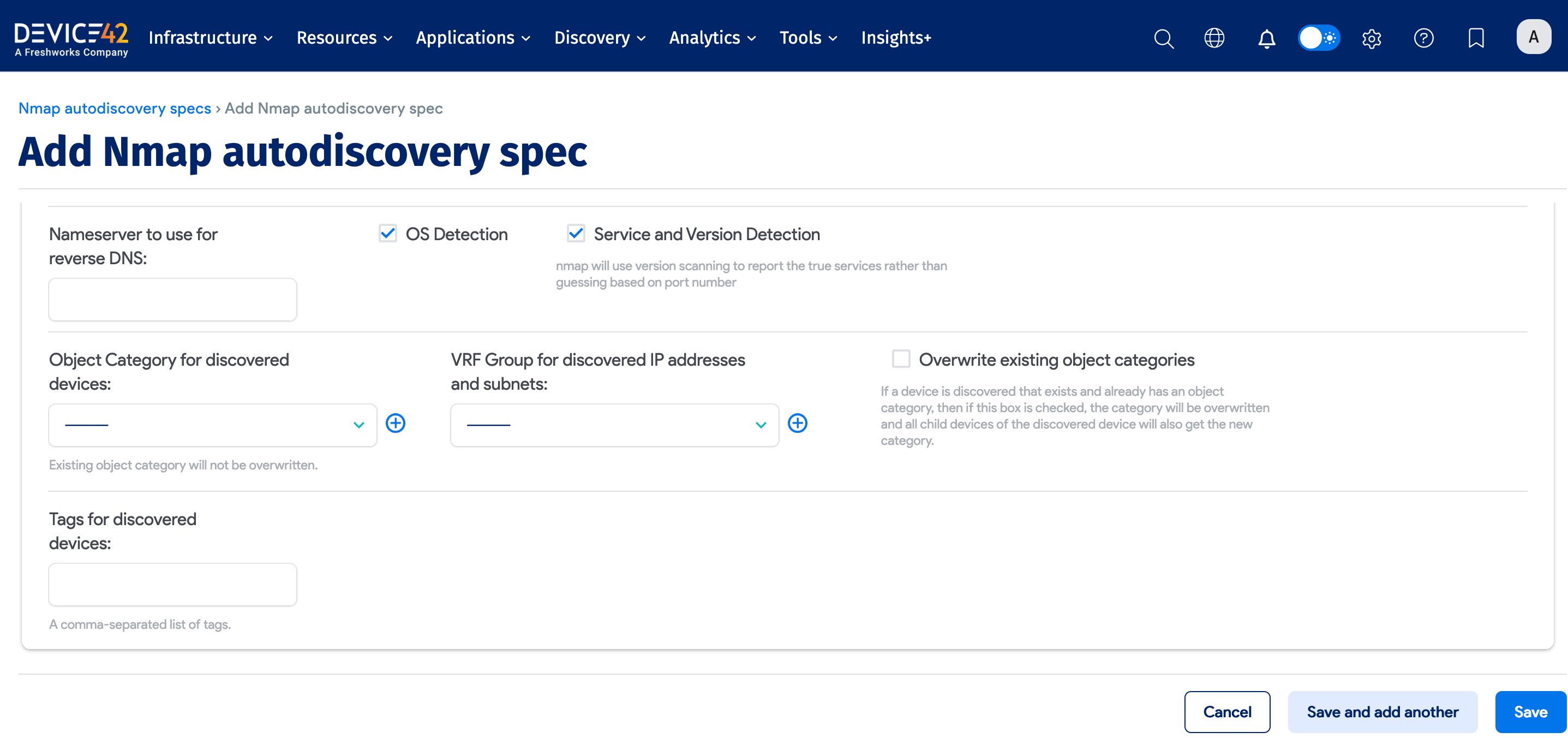
- Exclude Target Host(s) and Network(s): A comma-separated list of IP addresses, IP ranges, CIDR block(s), or hostname(s) to exclude from Nmap discovery.
- Nameserver to use for reverse DNS: The IP address or FQDN of the nameserver.
- OS Detection: On by default. Detects operating systems and versions.
- Service and Version Detection: On by default. Detects running services.
- Object Category for discovered devices: Select an existing object category or add a new category.
- VRF Group for discovered IP addresses and subnets: Select an existing VRF group or add a new group.
- Overwrite existing object categories: Overwrite the object categories for existing discovered devices and child devices.
- Tags for discovered devices: Add a comma-separated list of device tags.
Run Now or Schedule
Select Add another Auto Discovery Schedule when creating or editing the job to add a schedule.
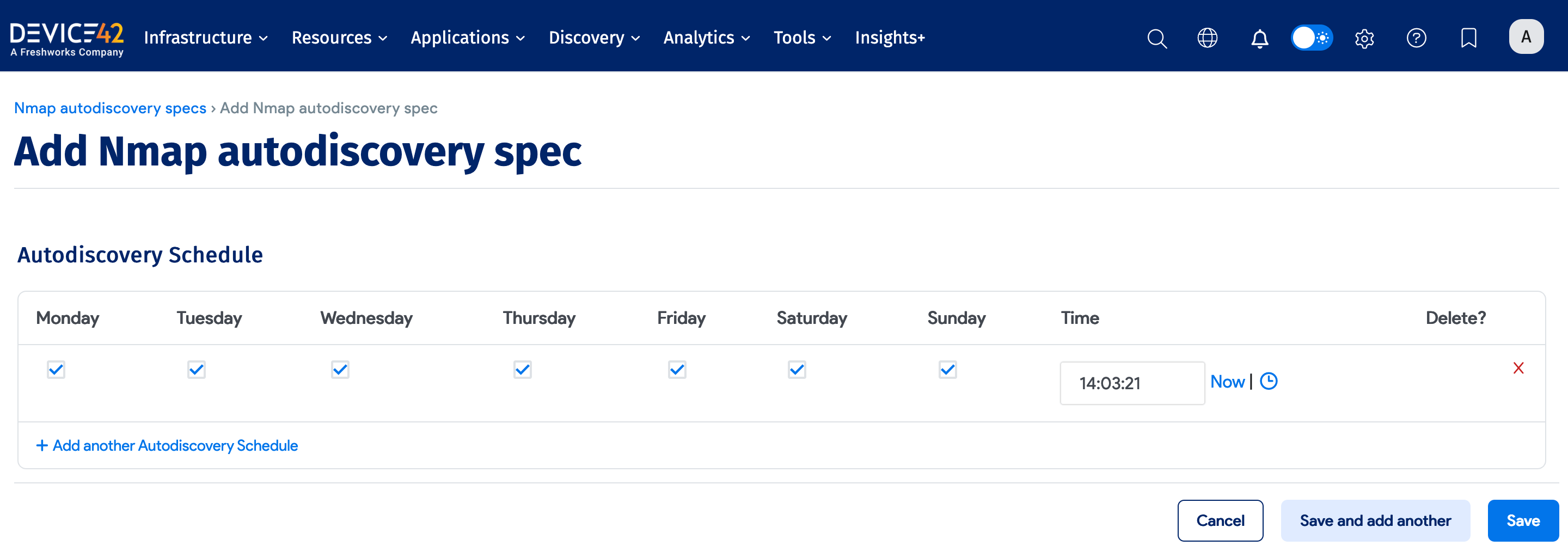
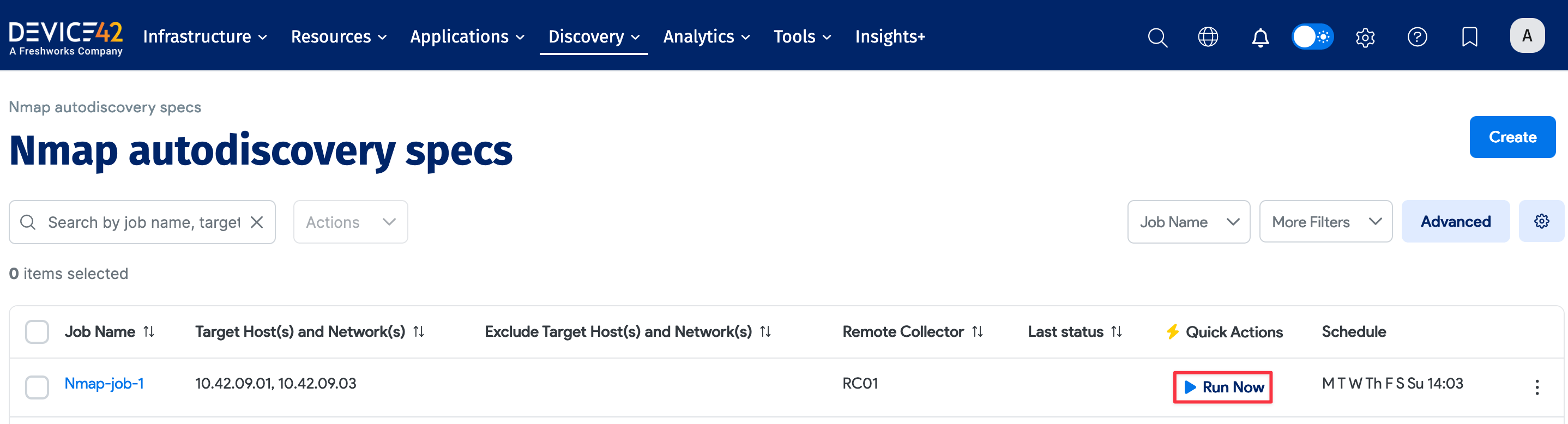
Newly created jobs do not run on the first day they are created to prevent an unintentionally large number of jobs from running initially. To run a job after its initial creation, click the Run Now button on the job summary page displayed after you save a new job.
The Run Now button is also available on the list page (Discovery > Nmap).
Nmap and NetFlow Discovery Notes
In Device42, NetFlow and Nmap can be used by themselves, together, or in combination with point-in-time discovery. Using NetFlow and Nmap data together but without point-in-time discovery results in good service dependency mapping. However, using only these two data sources has the following limitations:
- A map of service inter-dependencies and interrelationships can be created, but many services often combine applications and associated information to form the entire application. For example, there might be multiple Oracle services plus configuration files that together form the Oracle application. Installed apps on a web server, and instances and named pipes on a database, cannot be discovered by the NetFlow/Nmap combination.
- The services that Nmap finds are guesses, and the guessed version number is probably wrong as often as it is right.
- Some enterprises have such restrictive firewall rules that Nmap discovers few, if any, services.
- NetFlow cannot see application interactions inside a physical, virtual, or cloud server. NetFlow can only see interactions that go through the router, so many dependencies are missed.
- While NetFlow works well for physical routers and switches, it's not effective for the virtual routers and switches found in hypervisors because many hypervisors do not support NetFlow.
- On routers and switches, NetFlow must be set up for every segment. If some segments are not set up, the application interactions are not found.
To overcome these limitations, use NetFlow and Nmap in conjunction with point-in-time discovery.