Database Discovery
About Database Discovery
Database (DB) discovery currently supports Windows and *nix-based discovery jobs detecting Microsoft SQL (aka MSSQL), Oracle, PostgreSQL, and DB2 databases.
Database discovery requires an Application Dependency Mapping license. Go to Tools > Settings > Licensing to see if the license is enabled. Contact support@device42.com for licensing assistance.
By default, the target machine ports are defined by the database vendors as follows:
- Microsoft SQL (MSSQL): 1433
- IBM DB2: 50000
- Postgres: 5432
- Oracle: 1521
Dynamic discovery detects which ports to use. Device42 supports MSSQL and Oracle database discovery for customers with database instances configured to listen on non-standard ports, especially on shared database servers that host multiple instances. During database discovery, Device42 will identify and connect via the discovered active listening port.
If you want to specify database discovery details yourself, including the database server port, server IP address, and database access credentials, use Database Connections Discovery jobs (see below) to discover databases.
Discovery Exclusions
Set discovery exclusions in Tools > Settings > Global Settings in the Discovery Exclusions section.
If you enable the Ignore DB Login Names setting, database login names will not be collected during database discovery.
You can also specify interfaces, IP addresses, and MAC addresses to be ignored during discovery.
MSSQL Server Database Discovery (on Windows Targets)
Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL) server discovery is supported on discovery targets running Microsoft Windows, although it requires a separate set of credentials to authenticate to the database instance itself. Ensure the discovery credentials have appropriate permissions to view the databases you are interested in discovering.
Device42 supports autodiscovery on Windows and *nix platforms for the following MSSQL versions:
- MSSQL 2005
- MSSQL 2008
- MSSQL 11 on SQL Server 2012
- MSSQL 12 on SQL Server 2014
- MSSQL 13 on SQL Server 2016
- MSSQL 14 on SQL Server 2017
- Cluster MSSQL 12
Minimum Permissions Requirements for MSSQL Discovery
To query the tables below, please ensure you have View Server State permissions. For the discovery to return detailed information about your database instance, you need read permissions to the following system views:
|
|
The following snippet is necessary for retrieving data from some of the preceding views, such as sys.master_files, even when the user has read permissions enabled:
USE [master];
GO
GRANT VIEW ANY DEFINITION TO [discovery_user];
GO
Note: The discovery user must belong to the administrator’s user group to discover databases successfully.
Set Up Your MSSQL Discovery Job
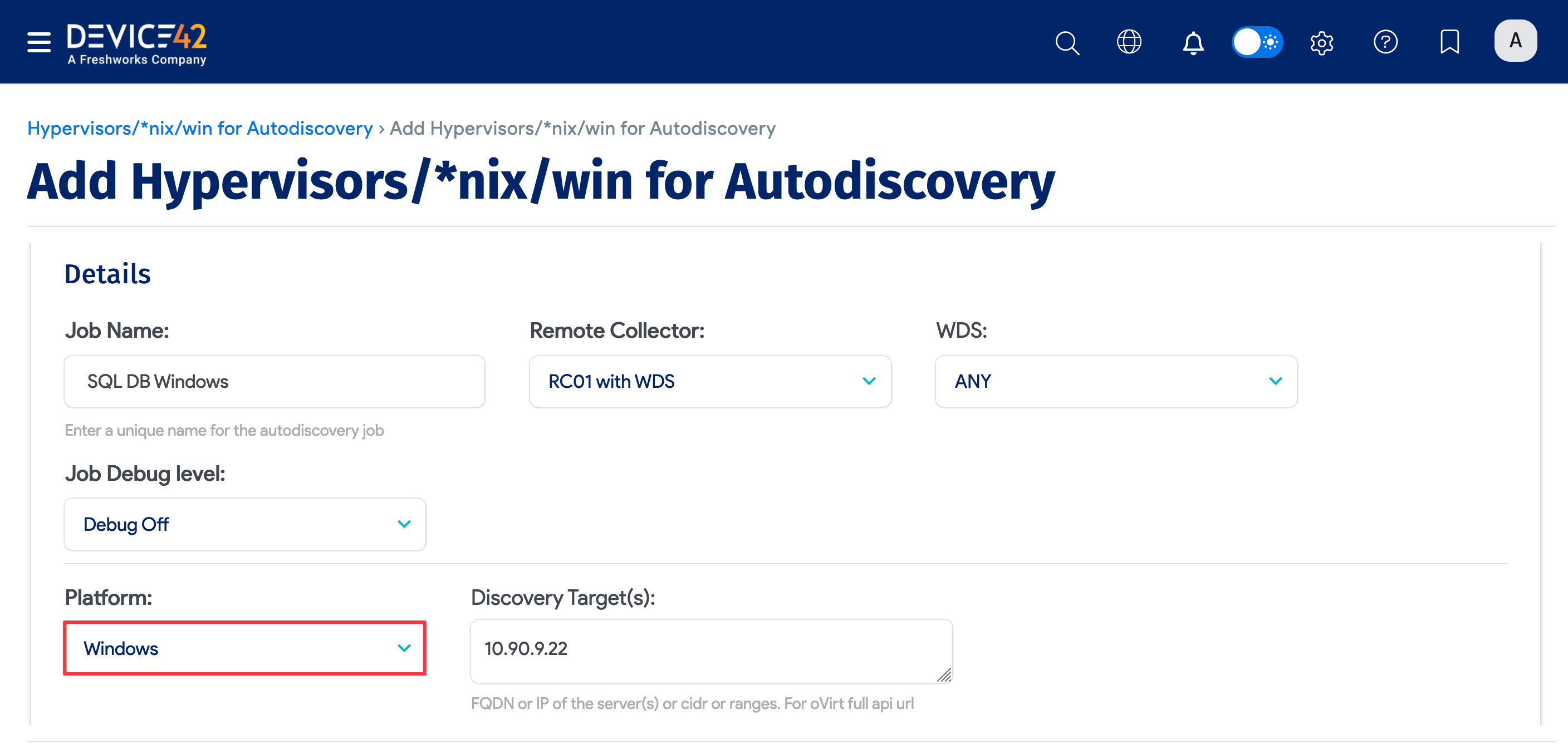
Create a new Windows discovery job under Discovery > HyperVisors /*nix /Windows to discover MSSQL databases running on Windows.
Enable database discovery by checking the Collect database server information checkbox.
Be sure to fill out both sets of credentials. Two sets of credentials must also be filled out for regular Windows-based discovery targets.
-
Database Username / Password(s): Credentials for authenticating to the Microsoft SQL database itself.


-
Discovery Target(s) Credential(s): Credentials for authenticating to the Windows server. You can enter an ordered list of preferred Discovery Target(s) Credential(s). When the job runs, it will use the credentials in the order that you entered them, stopping at the first successful authentication. Subsequent job runs use the last successful credential and then the remaining credentials in the ordered list.
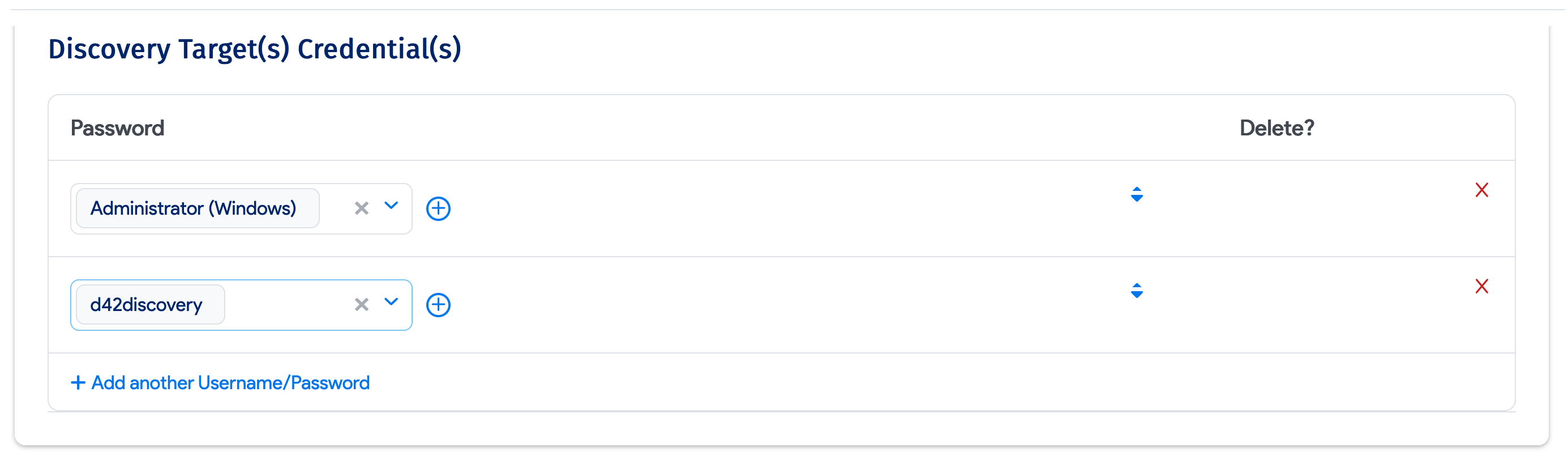
Run the autodiscovery job to test it by clicking Run Now from the autodiscovery jobs list.
As MSSQL databases are detected, discovery will import a list of all the instances, databases, and connection details it finds.
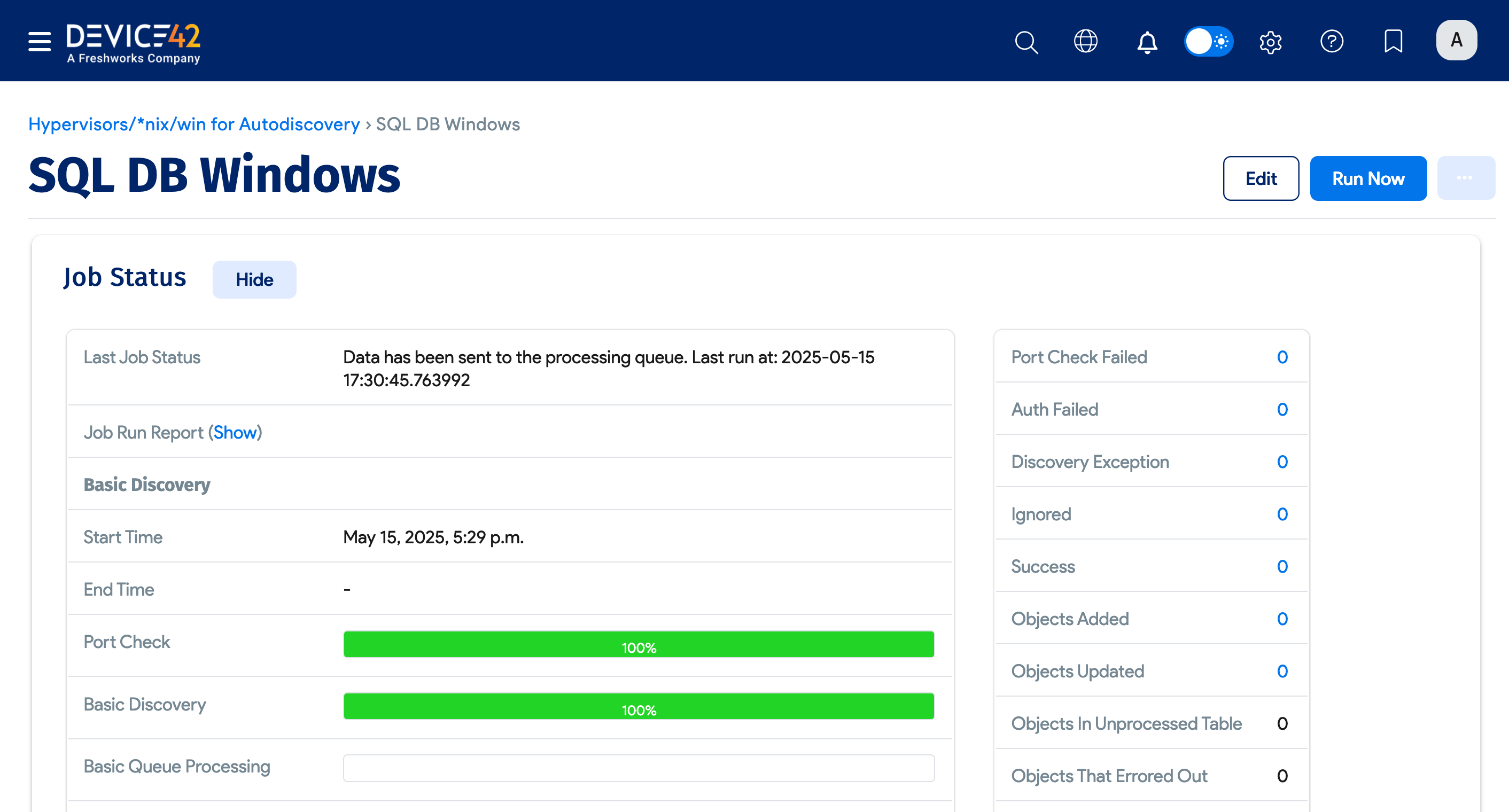
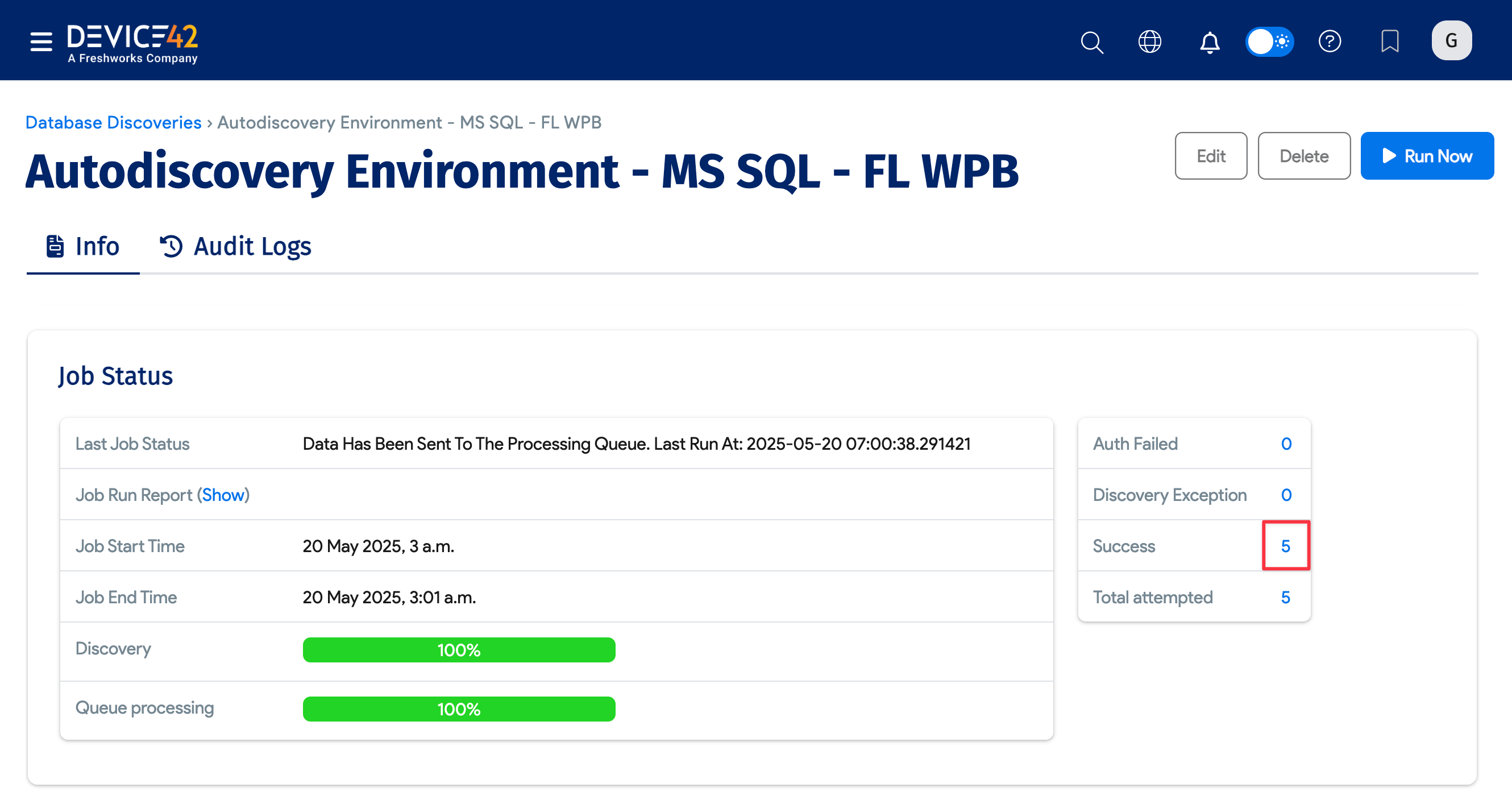
You can see the status of the discovery job on the job setup page. Scroll down to the Job Status section and look for the bar graphs.
View Your MSSQL Discovery Job Results
Once the job finishes, there are multiple ways to view the results of your database discovery.
Access Your Results Through the Discovered MSSQL Application Components
The most direct method for viewing the discovered database details is via the discovered MSSQL application components themselves.
Navigate to the Device42 main menu and go to Applications > Application Components. If you don't see your SQL Server instances at the top of the list, you can search for "SQL" to narrow down the list.
You can see the newly discovered SQL Server instances in the example below. Click on the Name of one of the application components to view more details.
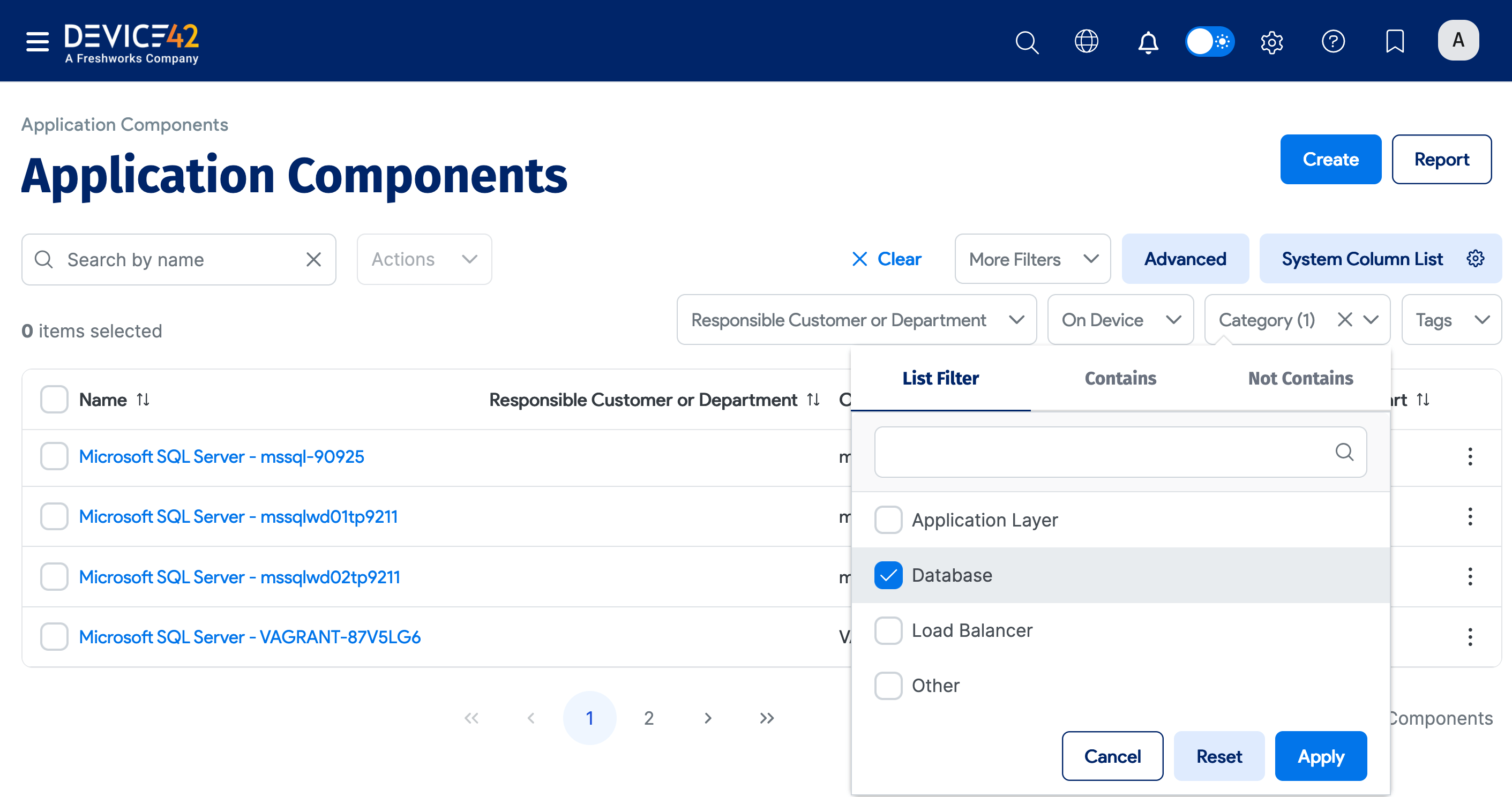
Scroll to the Application Components section at the bottom of the page and click the database instance name to view database details.
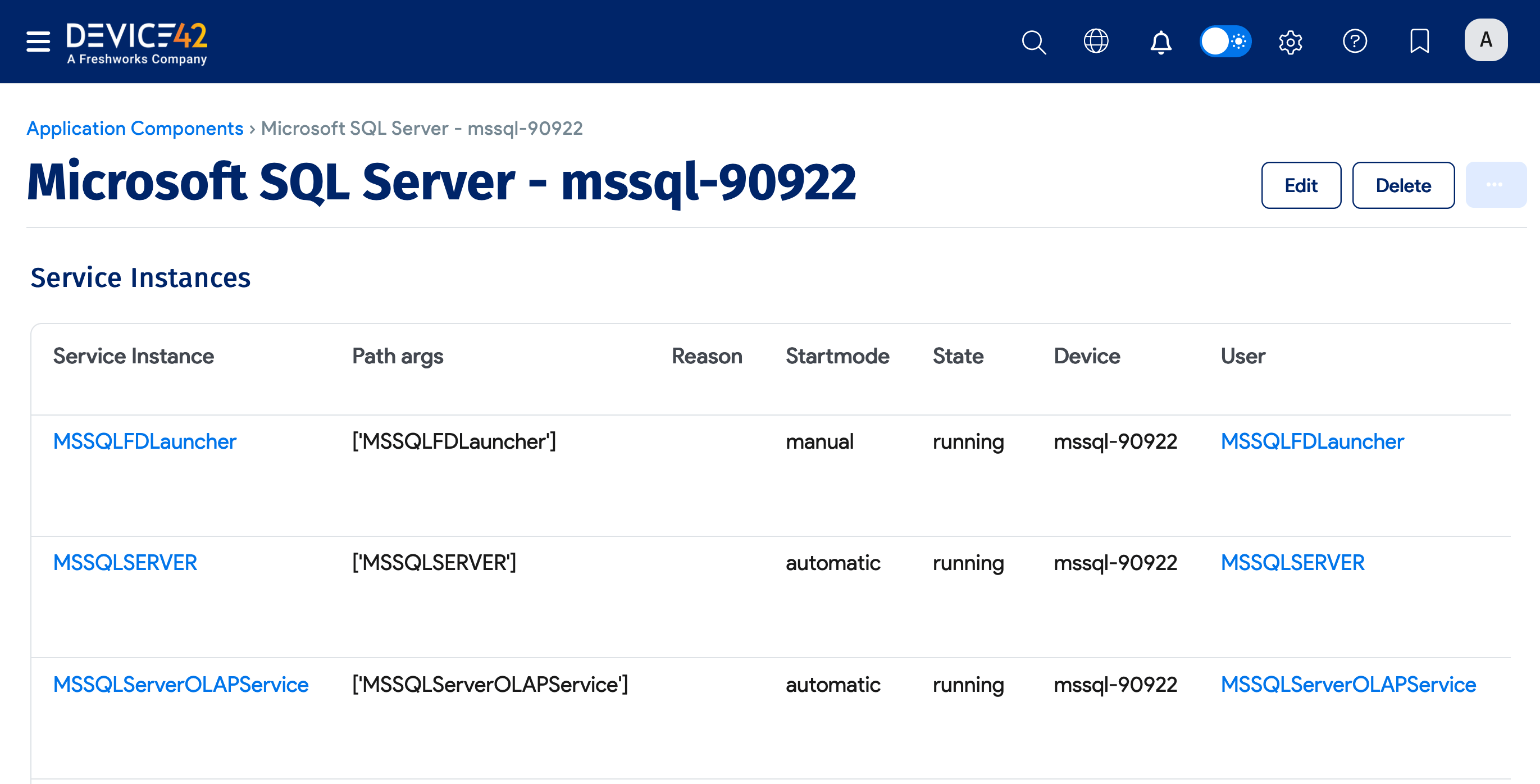
For a rundown of the database details that discovery provides, jump to the Available SQL Database Instance Information section.
Another Way To View SQL Database Details
Results are also available by browsing to the discovered Windows server instance's CI; either search for the device from the dashboard, via Devices > All Devices, go to Analytics > Discovery Scores and search for your discovery job, or navigate to your discovery job results page and access the servers from there.
-
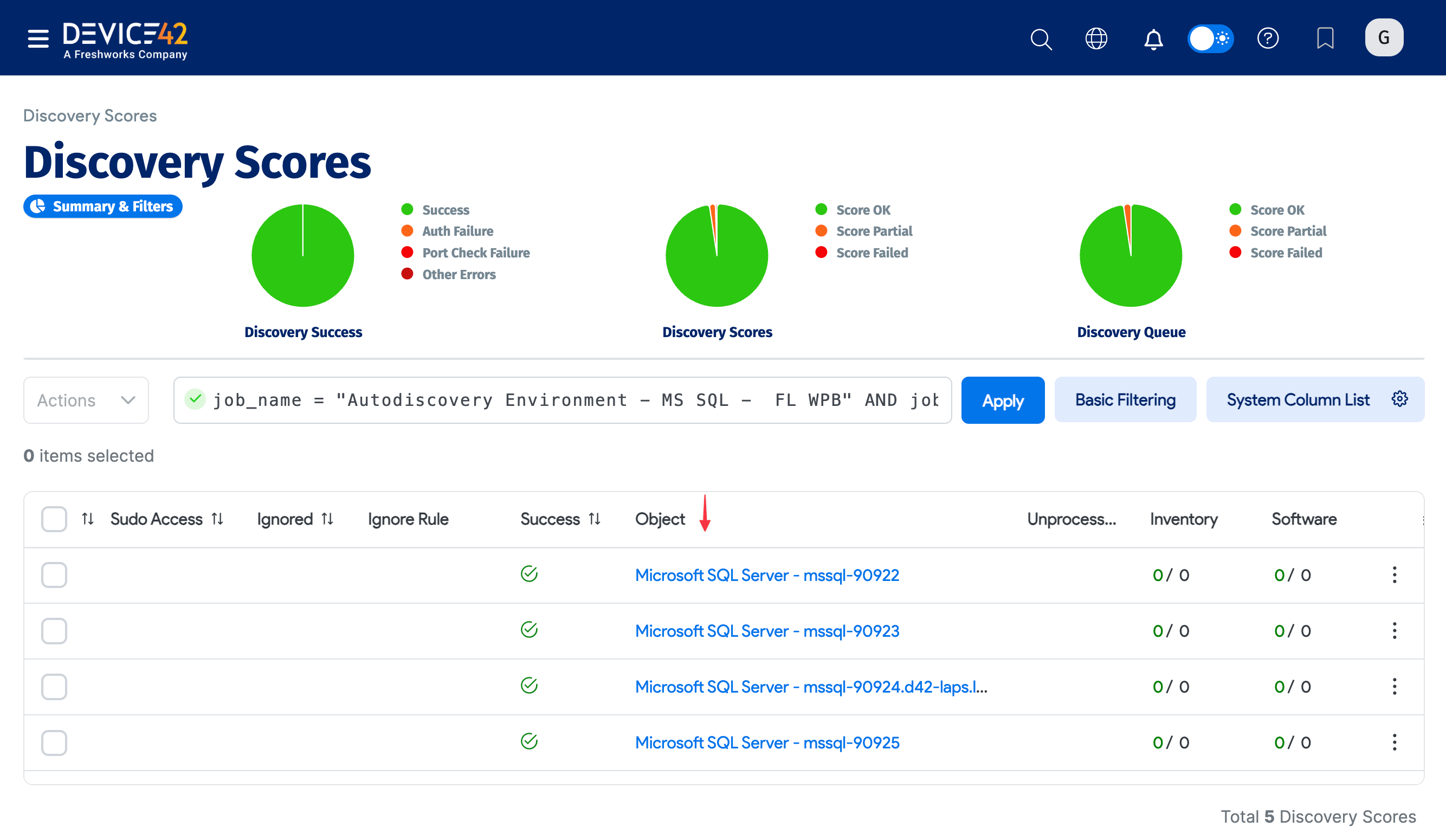
Click the success number to go to the Discovery Scores page and quickly see the newly discovered items.
-
Click the links under the Object column to view the server details.
-
From the details view, you can see Service Instances, Software, Database Instances, and other information.
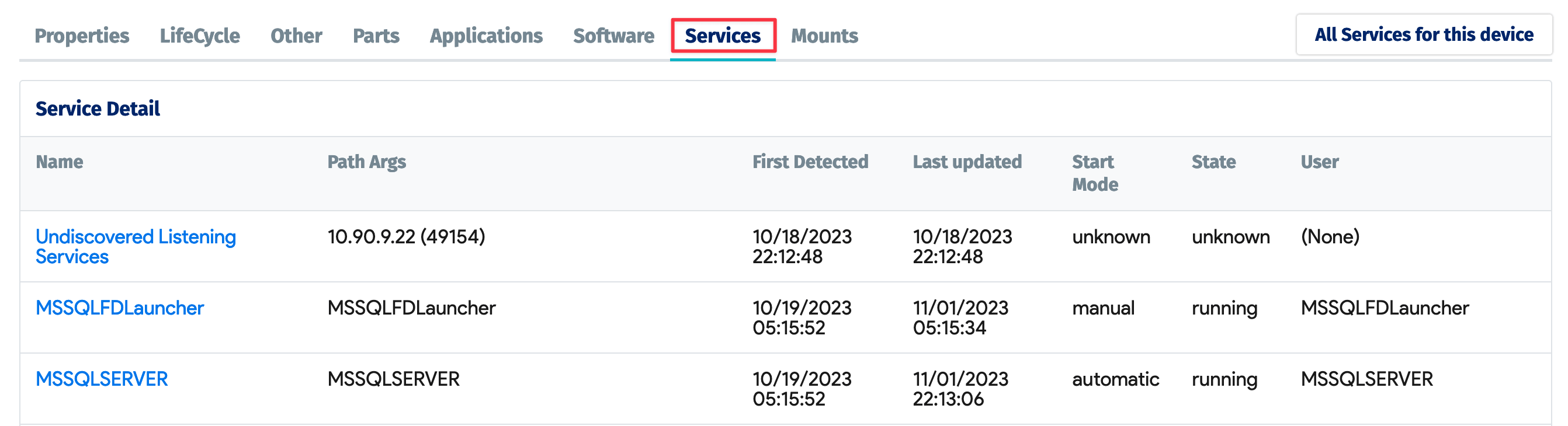
Available SQL Database Instance Information
You can click the name of a Database Instance from the Application Component view, or from the Resources list page, to view the following:
-
The Resource Details of the MSSQL database, including the SQL Server Start Time and memory stats.
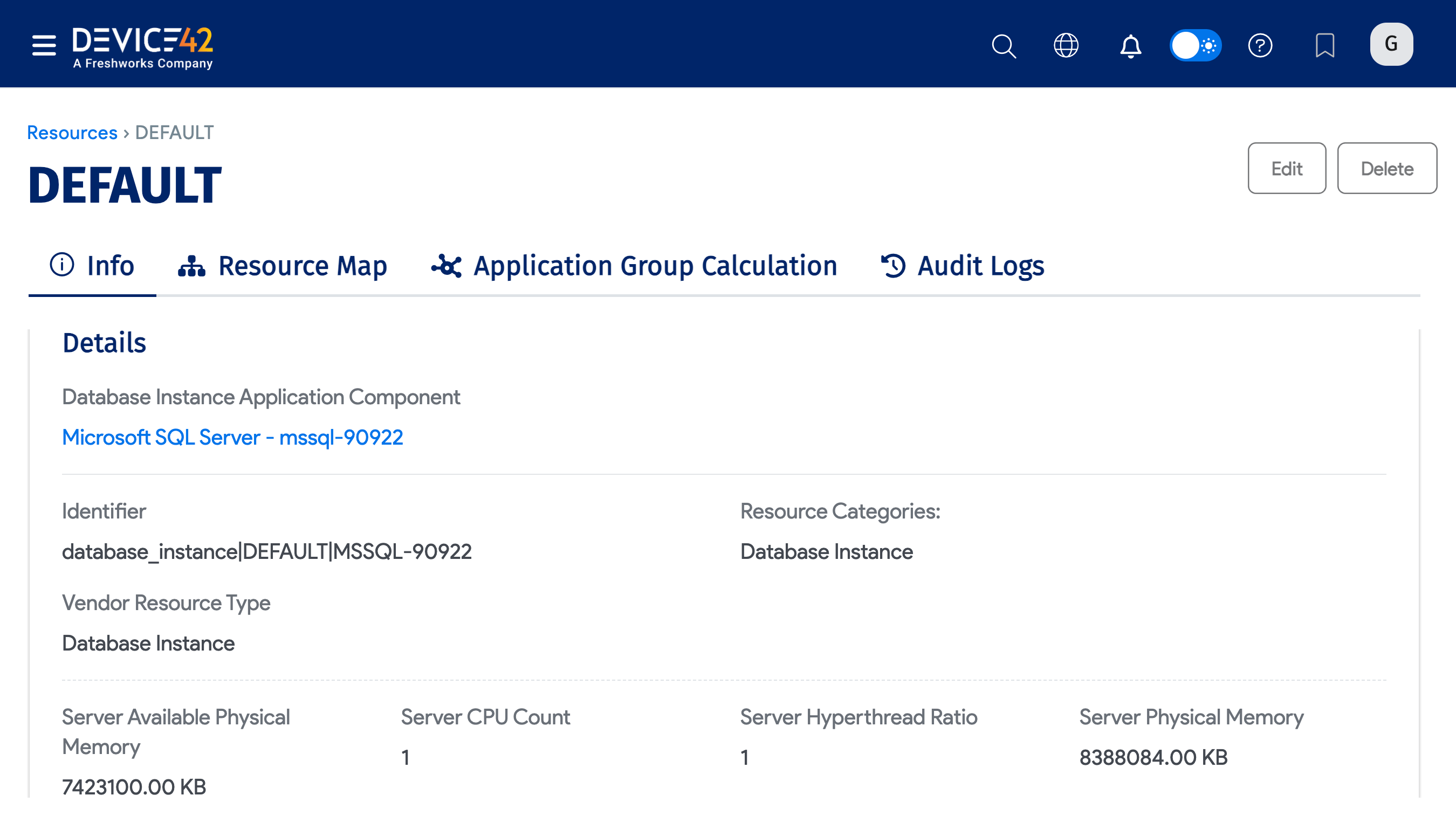
-
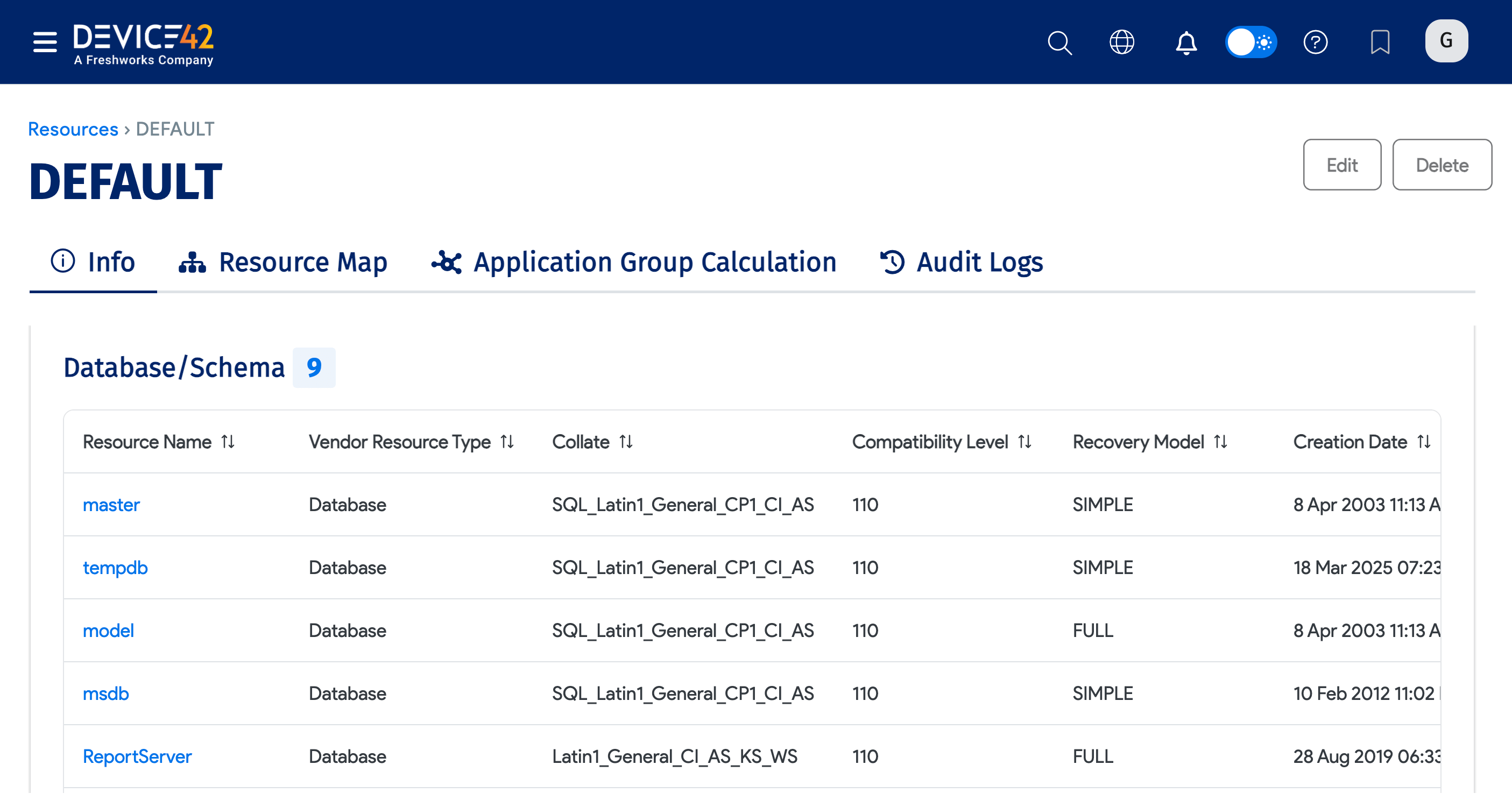
The Database/Schema of the instance. You can click on each database for more details.
-
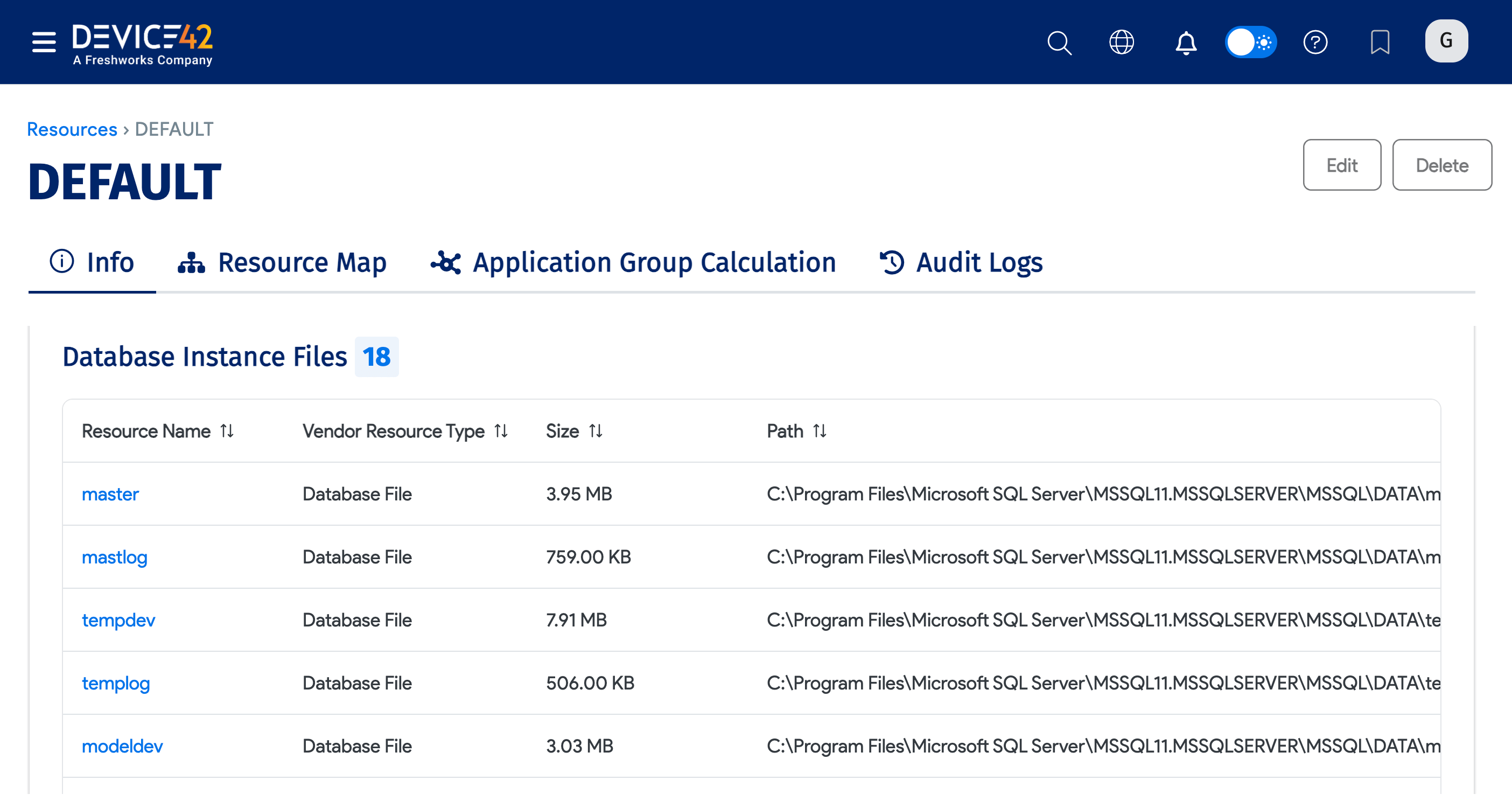
The Database Instance Files, including the Size and Path for each resource.
-
The Endpoints and Network Details.
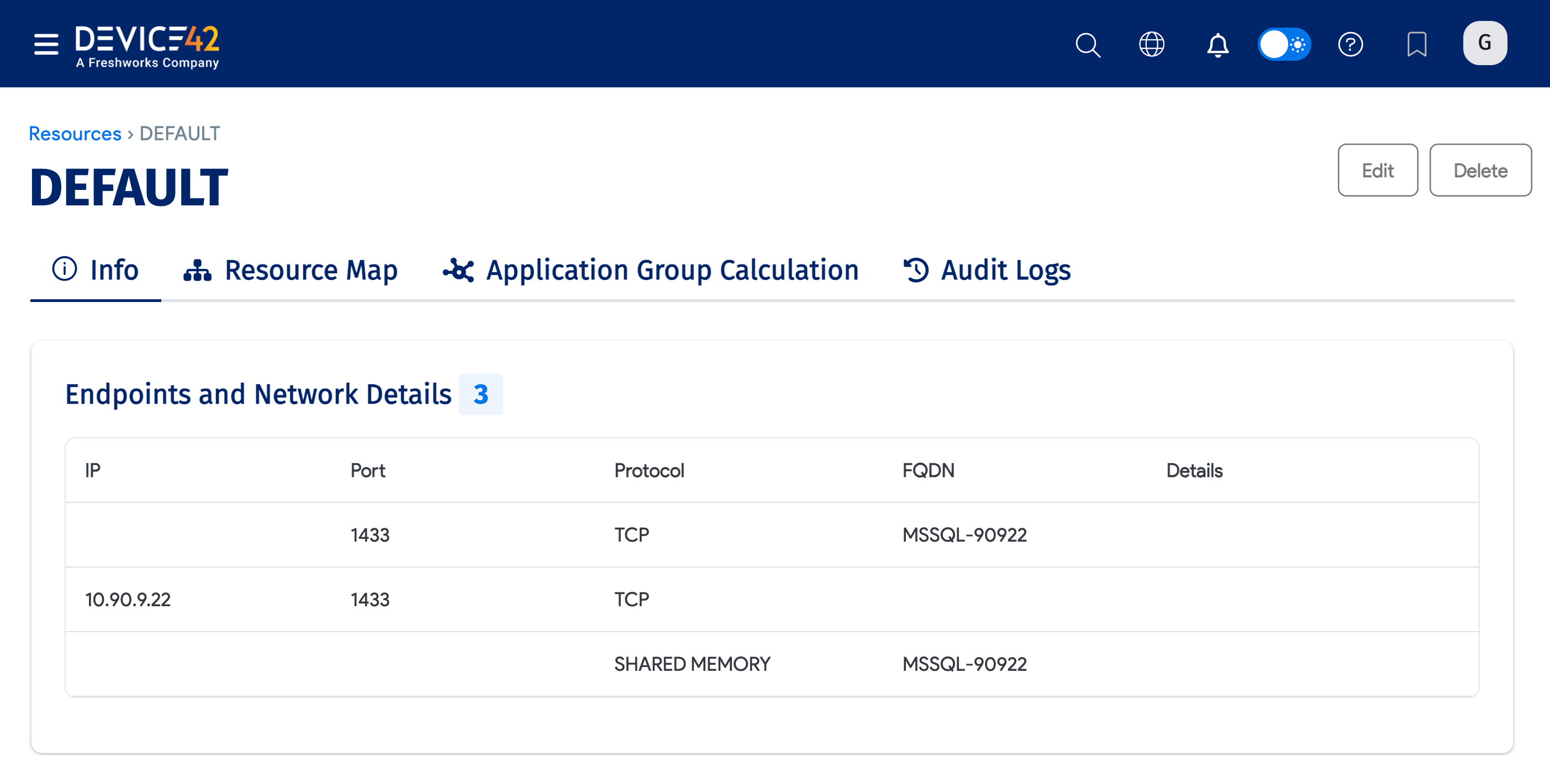
If your environment includes SQL cluster databases, discovery returns the following information about the clusters:
- SQL Cluster name
- SQL Cluster Node Role
- Is Node Active or Read-Replica
- Does Passive Node use Log Ship
- Does Passive Node use DB Mirroring
Oracle Database Discovery (on Windows and *nix targets)
Oracle database discovery is supported for Windows and *nix discovery targets. Oracle discovery jobs require a separate set of credentials to authenticate to the database instance itself. Ensure these additional credentials have the appropriate permissions for viewing the databases you want to discover.
Device42 supports autodiscovery on Windows and *nix platforms for the following Oracle database versions:
Oracle 10g
- Windows 32 bit
- CentOS 32 bit
Oracle 11g
- Windows 32 bit
- Windows 64 bit
- CentOS 32 bit
- CentOS 64 bit
Oracle 12c
- Windows 64 bit
- CentOS 64 bit
Oracle 18c
- CentOS 64 bit
- Windows 64 bit
Oracle 19c
- Windows 64 bit
- CentOS 7 64 bit
Device42 database autodiscovery for Windows and *nix targets supports discovery for Oracle RAC clustered database environments, which helps users better assess their cluster databases and understand all the IT assets tied to critical business applications. Discovery returns data about the RAC configuration, the RAC database, and the nodes (physical servers) running the RAC software. You can run the autodiscovery against one or more nodes in the Oracle RAC and return information about all connected nodes. Device42 requires the use of sudo for Oracle discoveries to mitigate the risk of lockout.
Minimum Database-Level Permissions
For discovery to return detailed info about your database instance, you will require read or view permissions for the following system views and tables:
|
|
To get information about pluggable databases (PDBs) within an Oracle container database (CDB), two key permission configurations are required for non-DBA users:
-
SELECT permission on the V$CONTAINERS view.
-
Set
container_data=all container=currentfor context configuration. For example:ALTER USER c##<username>
SET
CONTAINER_DATA = ALL
CONTAINER = CURRENT;
System-Level Permissions
In addition to the minimum DB-level permissions above, discovery also needs shell access to the target system to run OS-level commands to get information about the Oracle environment.
For example, shell access is needed to read the tnsames.ora file, which contains network connection details:
/usr/bin/cat: /dbprog/oracle/product/19.3.0.0.26/network/admin/tnsnames.ora
Another example is the lsnrctl status command, which checks the status of the Oracle listener:
oracle -c 'lsnrctl status'
To allow Device42 to run these commands securely, you can grant limited sudo access by adding the following to the /etc/sudoers file or by creating a separate sudoers file for Device42 Oracle discovery:
Click to expand the code block
# Basic Oracle Discovery Commands
Cmnd_Alias DEVICE42_ORACLE = \
/usr/bin/ps -ef, \
/usr/bin/pwdx *, \
/usr/bin/su - oracle -c lsnrctl status, \
/usr/bin/su - oracle -c echo "select * from product_component_version;" | sqlplus -L -S -M "HTML ON" / as sysdba, \
/usr/bin/cat /etc/oratab, \
/usr/bin/su - oracle -c /u01/app/19.1.0.0/grid/bin/lsnrctl status, \
/usr/bin/su - oracle -c echo "select * from product_component_version;" | /u01/app/19.1.0.0/grid/bin/sqlplus -L -S -M "HTML ON" / as sysdba
# Oracle RAC Additional Commands
Cmnd_Alias DEVICE42_ORACLE_RAC = \
/usr/bin/su - oracle -c /u01/app/19.1.0.0/grid/bin/olsnodes -c, \
/usr/bin/su - oracle -c /u01/app/19.1.0.0/grid/bin/olsnodes -n -i -s, \
/usr/bin/su - oracle -c /u01/app/19.1.0.0/grid/bin/olsnodes -l -n -i -s, \
/usr/bin/su - oracle -c /u01/app/19.1.0.0/grid/bin/srvctl config scan_listener, \
/usr/bin/su - oracle -c /u01/app/19.1.0.0/grid/bin/srvctl config scan, \
/usr/bin/su - oracle -c /u01/app/19.1.0.0/grid/bin/crsctl stat res -t | grep *, \
/usr/bin/su - oracle -c srvctl config database -d *
# Grant these permissions to your Device42 discovery user:
# username ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: DEVICE42_ORACLE, DEVICE42_ORACLE_RAC
Set Up Your Oracle Discovery Job
To begin discovering your Oracle databases, navigate to Discovery > HyperVisors /*nix /Windows. Create a new discovery job for Windows or *nix (or both) targets, and be sure to check the Collect database server information checkbox.
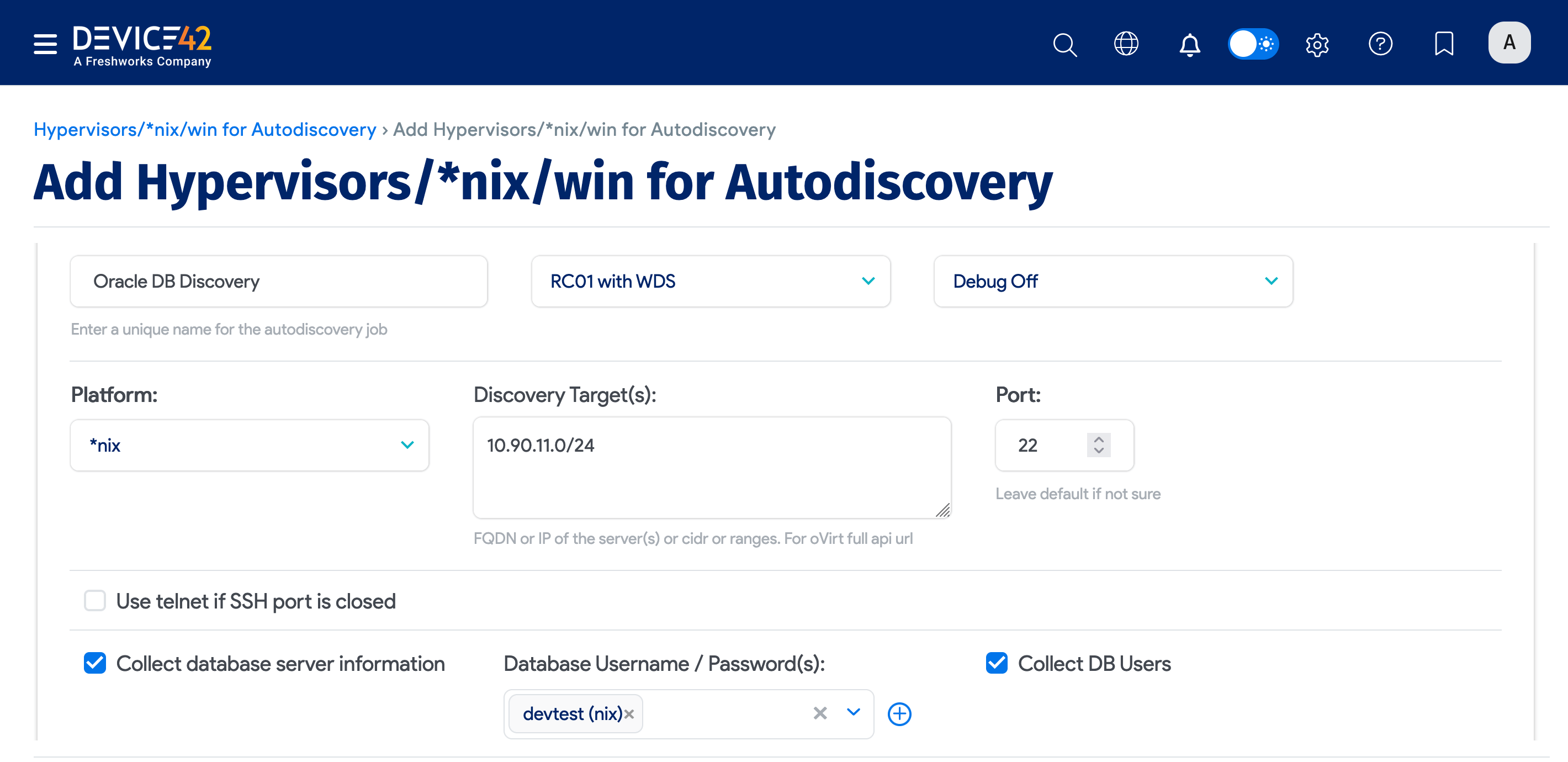
Be sure to fill out both sets of credentials:
- Database Username / Password(s) to authenticate to the Oracle database.
- Discovery Target(s) Credential(s) to authenticate to the Windows or *nix server.
You can enter an ordered list of preferred Discovery Target(s) Credential(s) when you create a database discovery job. When the job runs, it will use the credentials in the order that you entered them, stopping at the first successful authentication. Subsequent job runs use the last successful credential and then the remaining credentials in the ordered list.

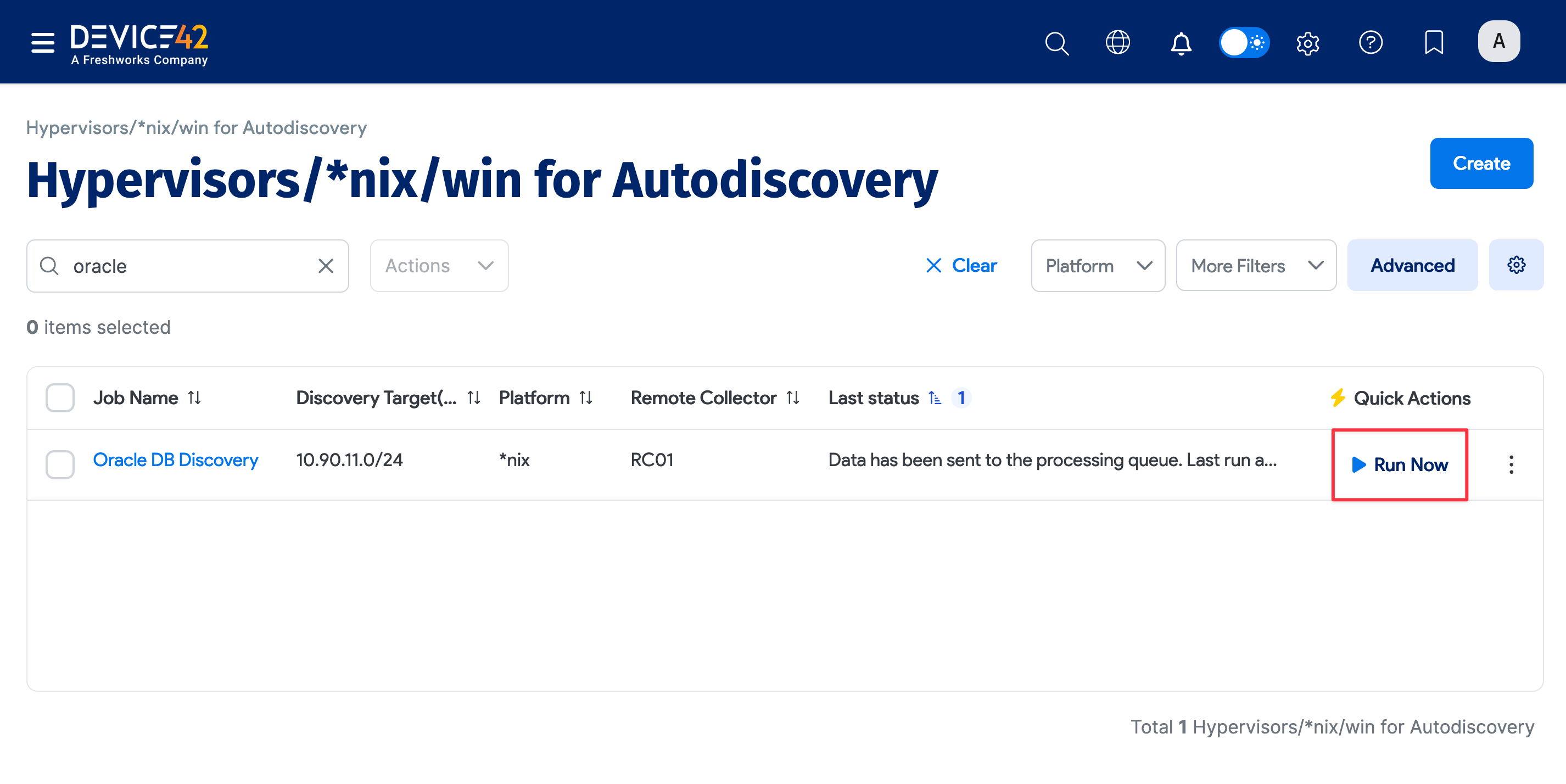
Run your new discovery job to test it. Click Run Now on the job details page or on the list page under Discovery > HyperVisors /*nix /Windows. As Oracle databases are detected, discovery will import a list of all the instances, databases, and connection details it finds.
View Oracle Database Discovery Job Results
When the job finishes, the most direct way to view the results of your database discovery is via the discovered Oracle Application Components.
On the Device42 main menu, select Applications > Application Components. If you don't see your Oracle database instances at the top of the list, you can search for "Oracle" to narrow down the list.
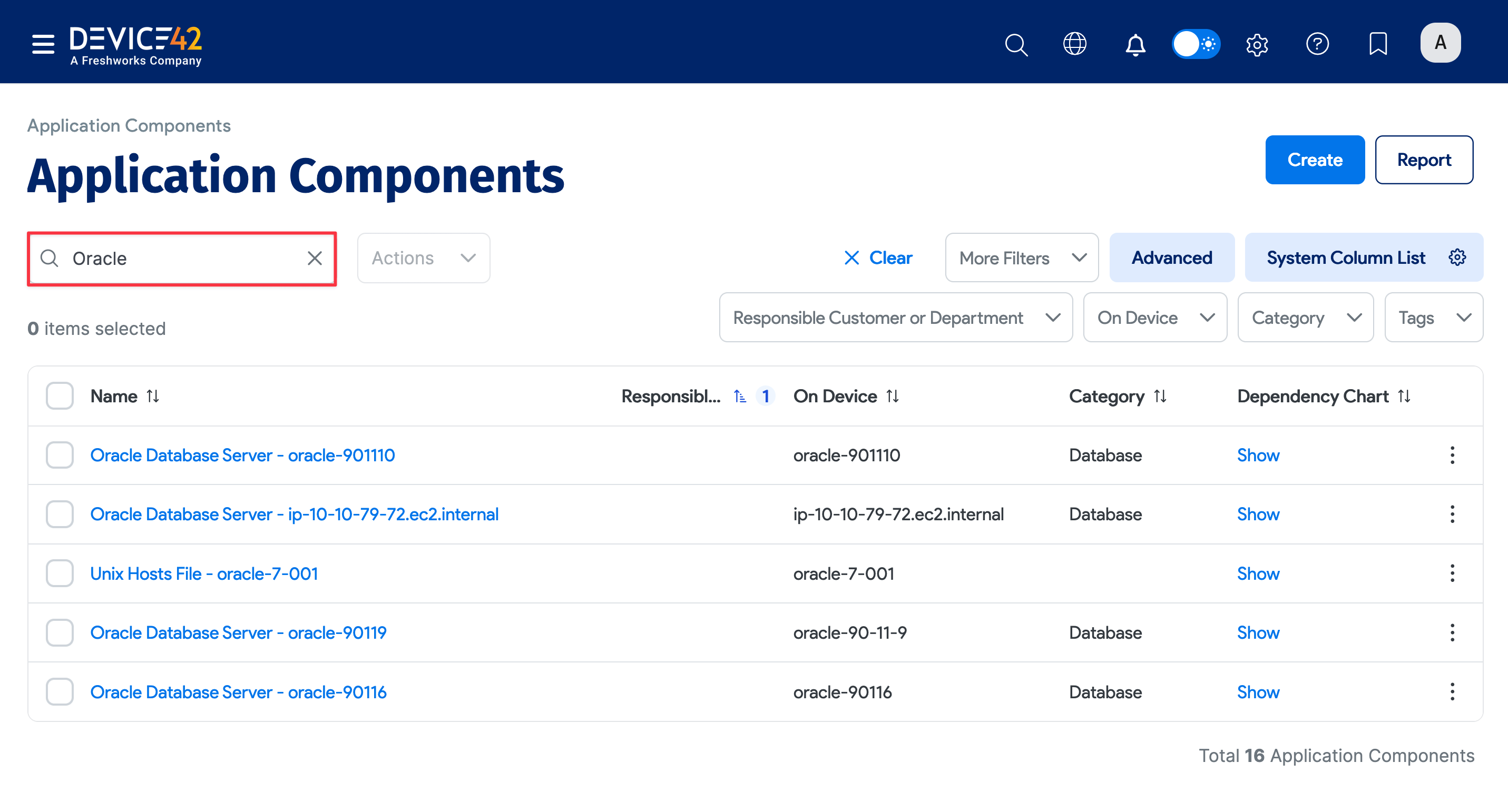
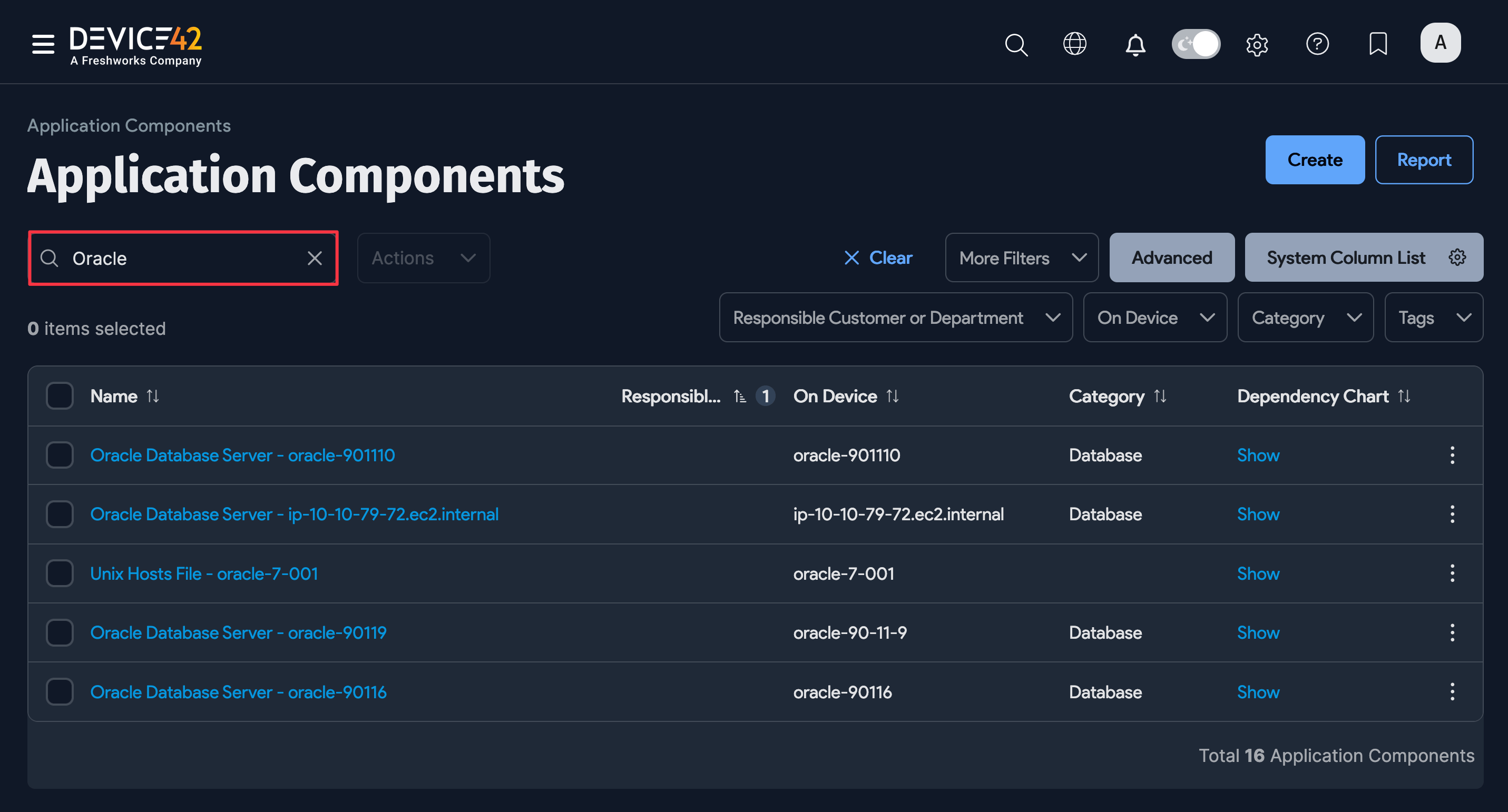
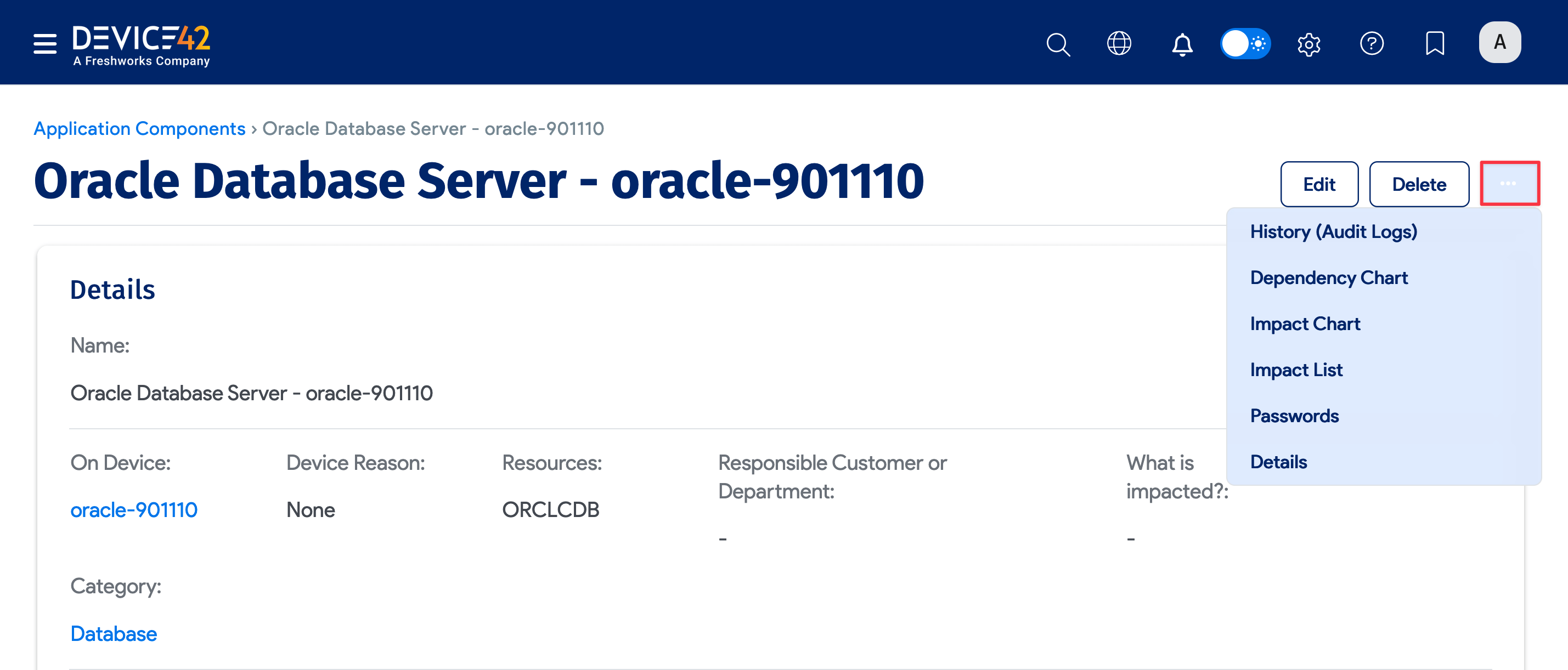
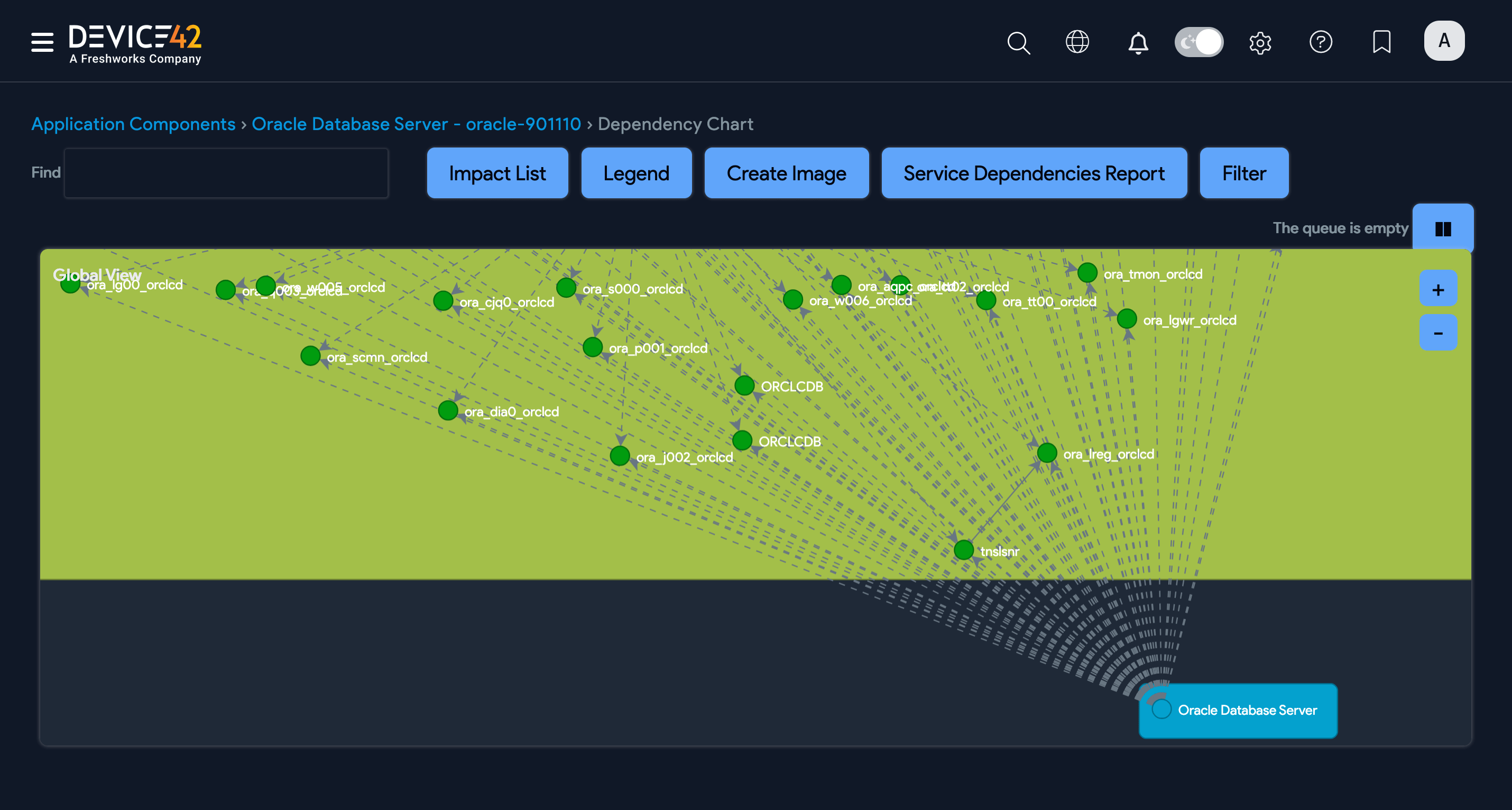
Click on a database name on the Application Components list page to view the details of that specific application component. On the View Application Component page, click the ellipsis icon to view the database Dependency Chart, Impact Chart, Impact List, Passwords, and Details.
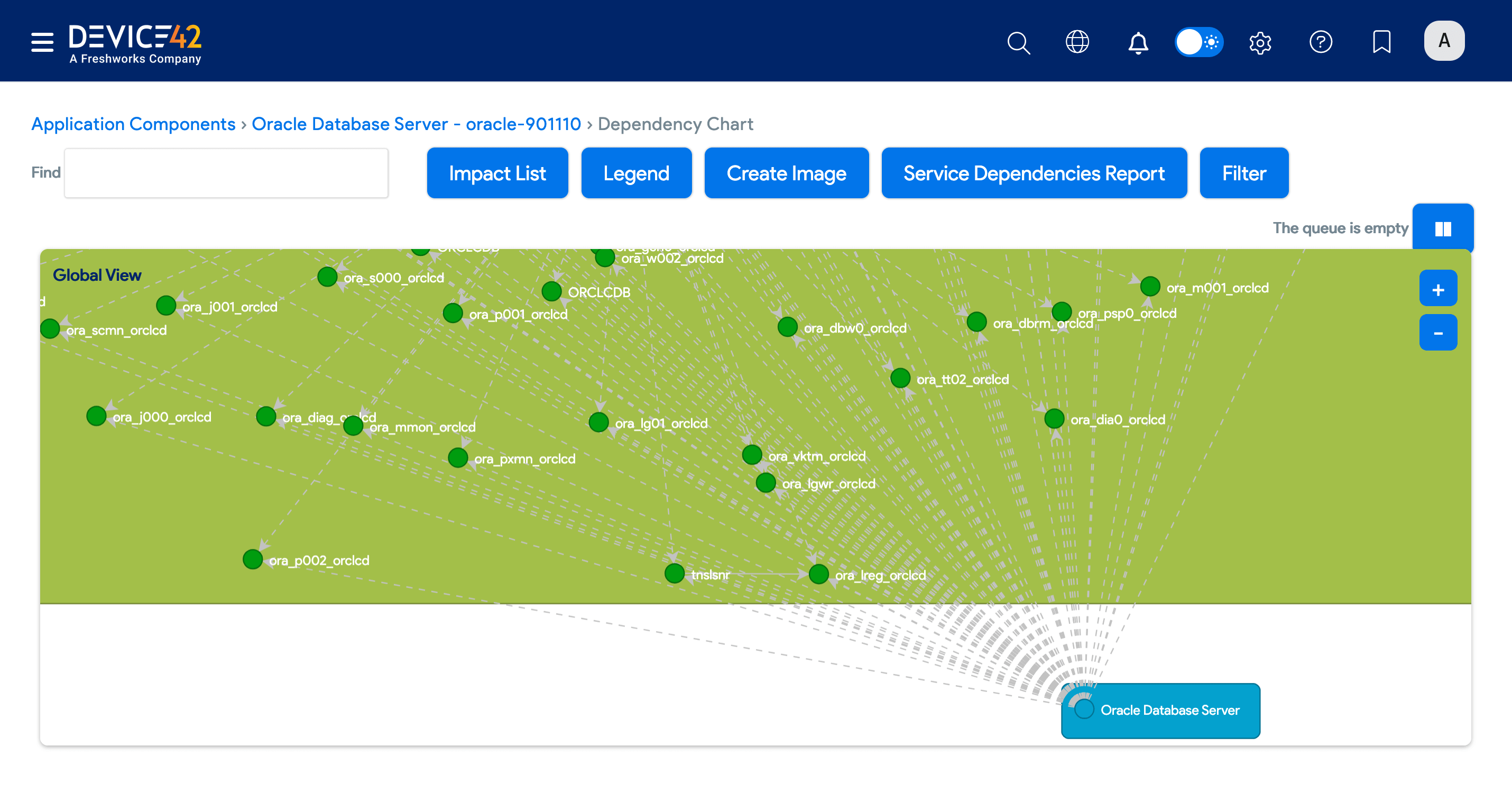
Example Oracle database dependency chart:
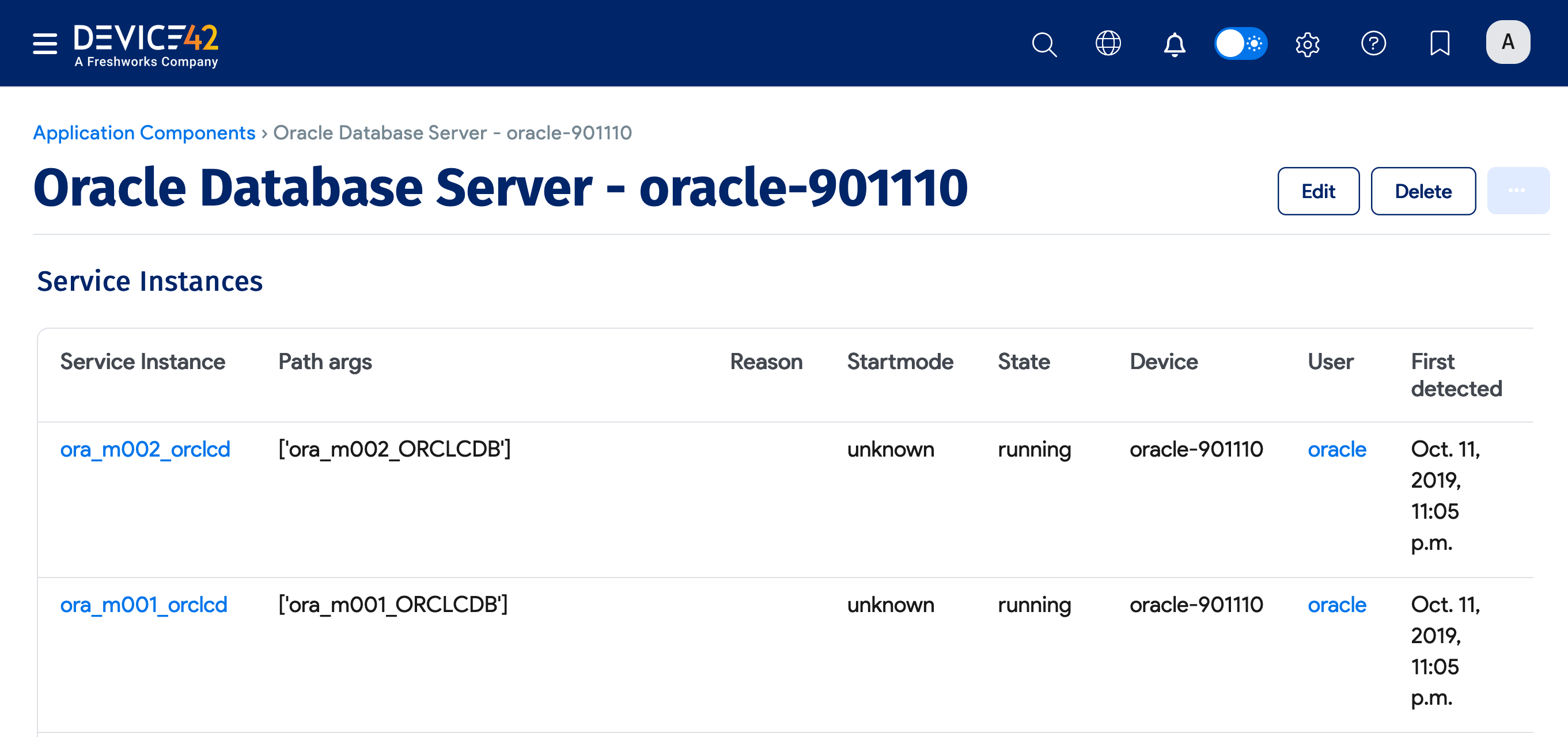
You can scroll down the View Application Component page to see a list of the Oracle database Service Instances.
Scroll further down to see Software and Database Instances associated with the Oracle database.
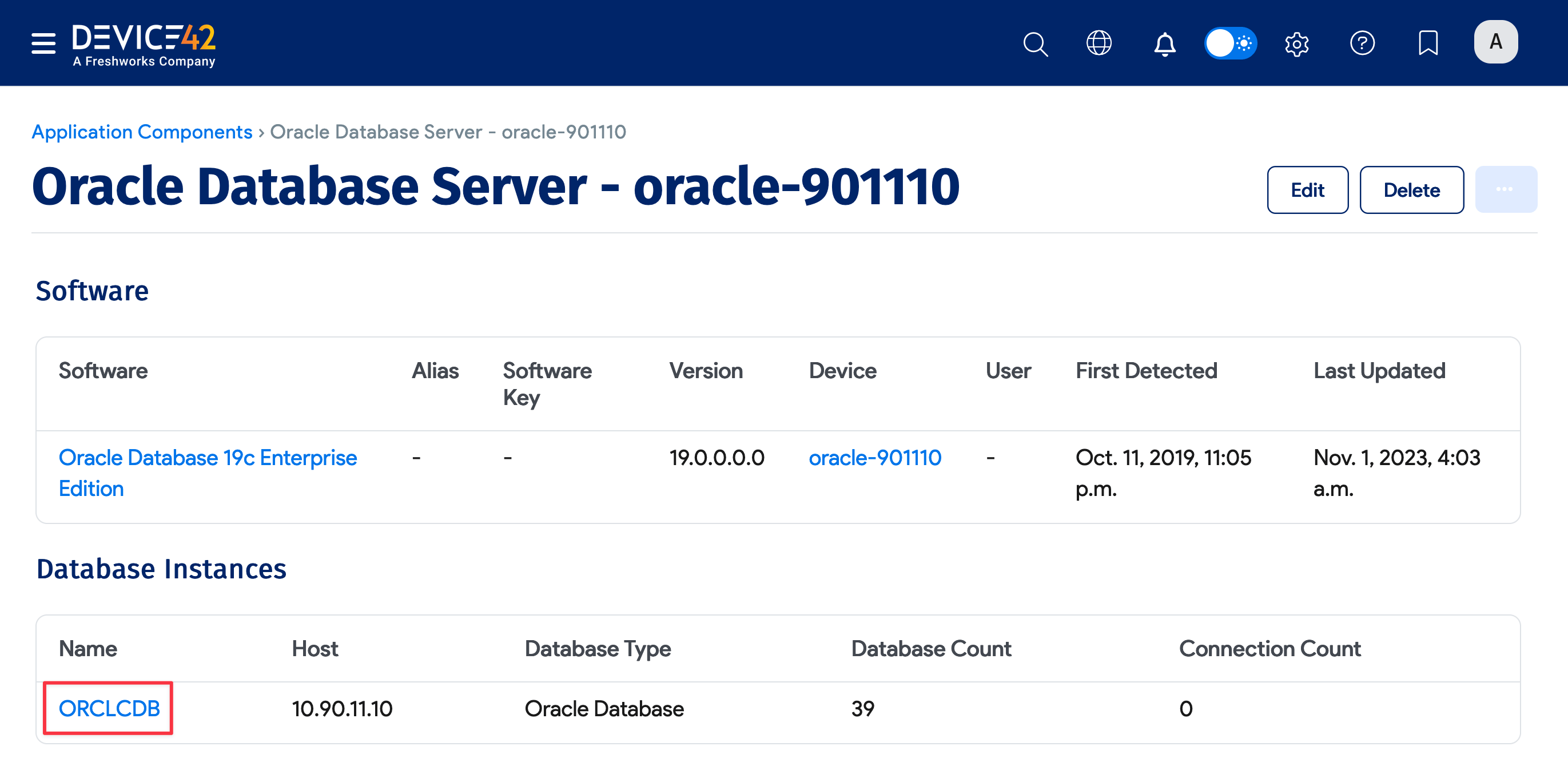
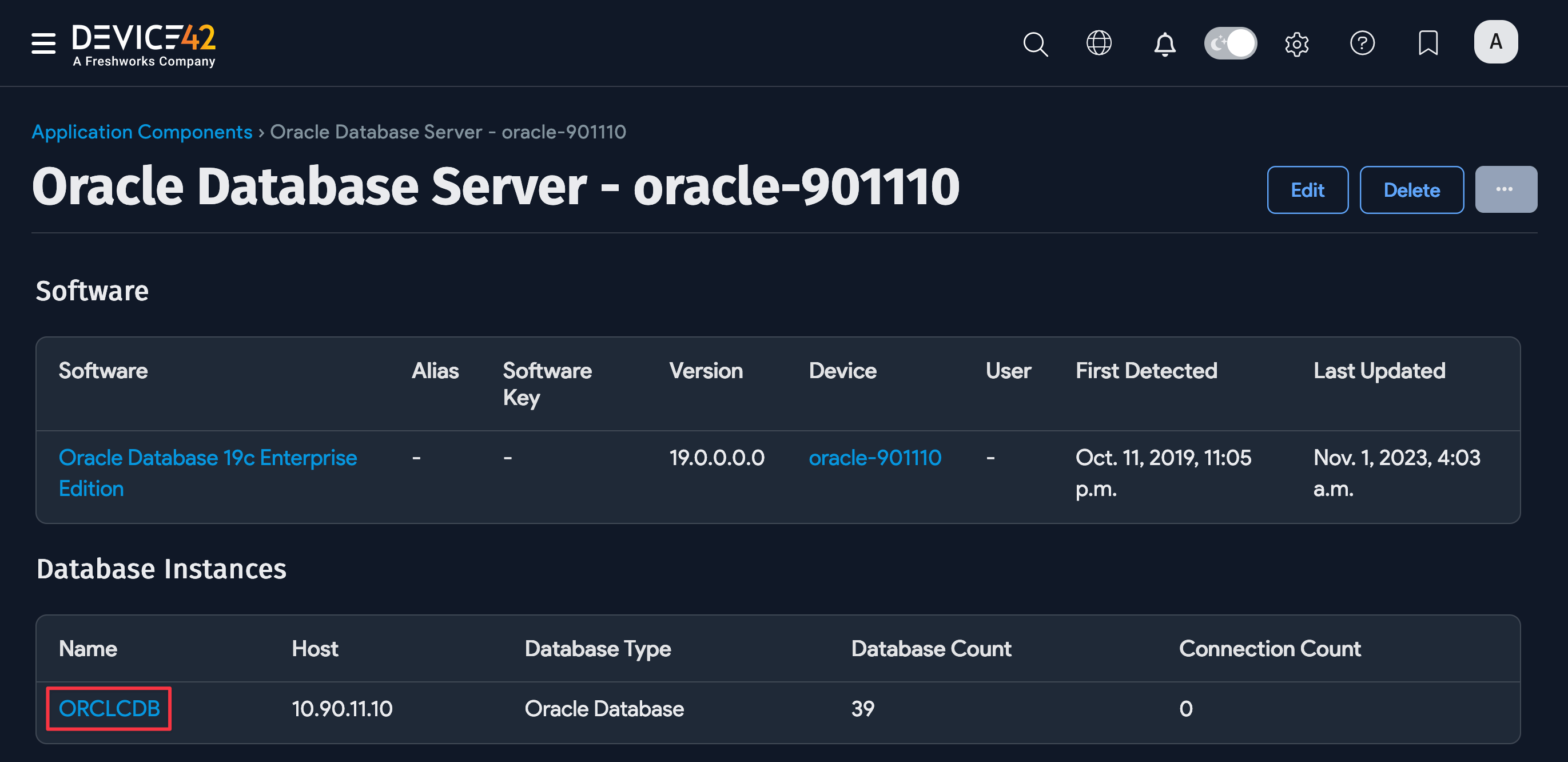
You can click on a database instance to view more details, including Containers and Database/Schema information.
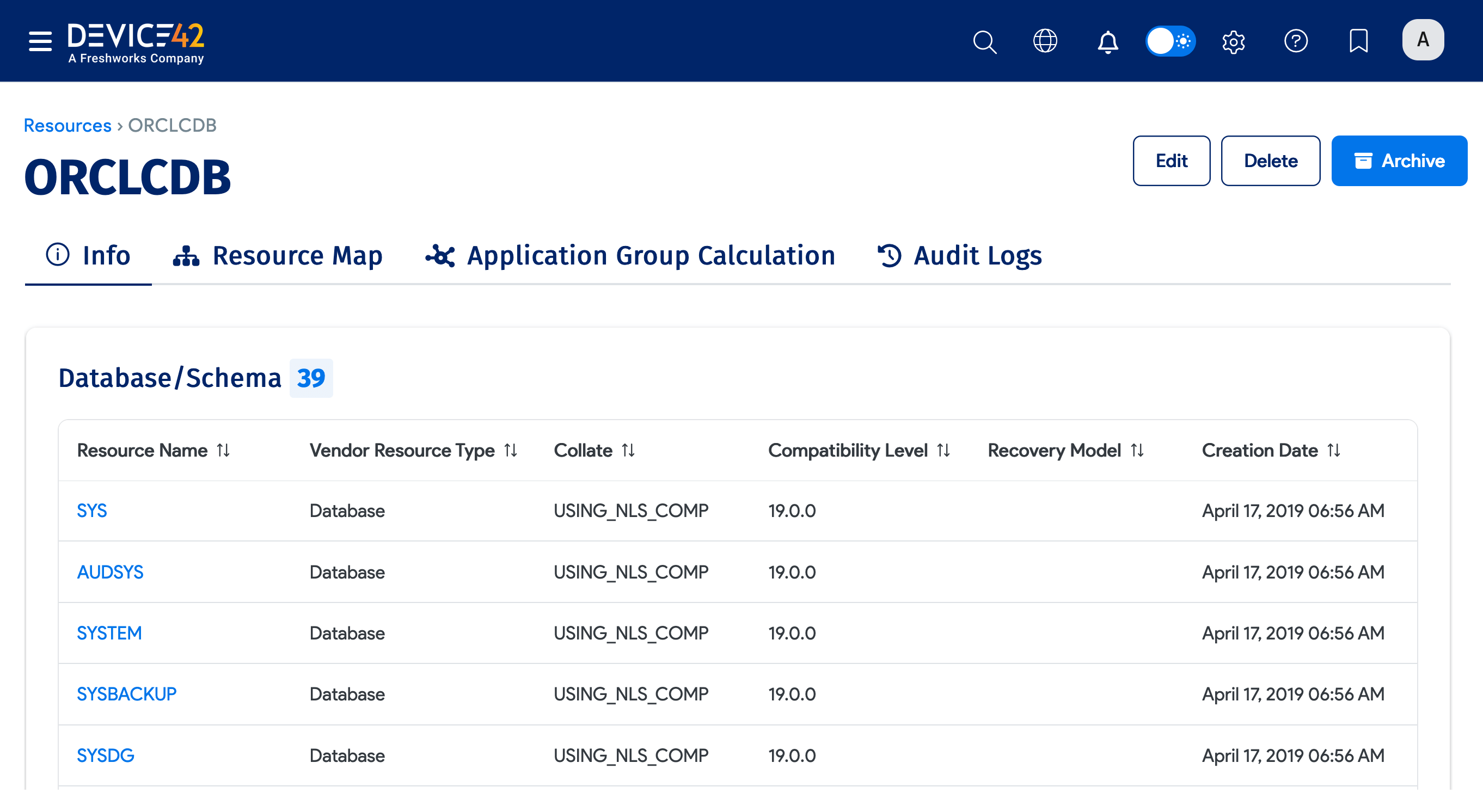
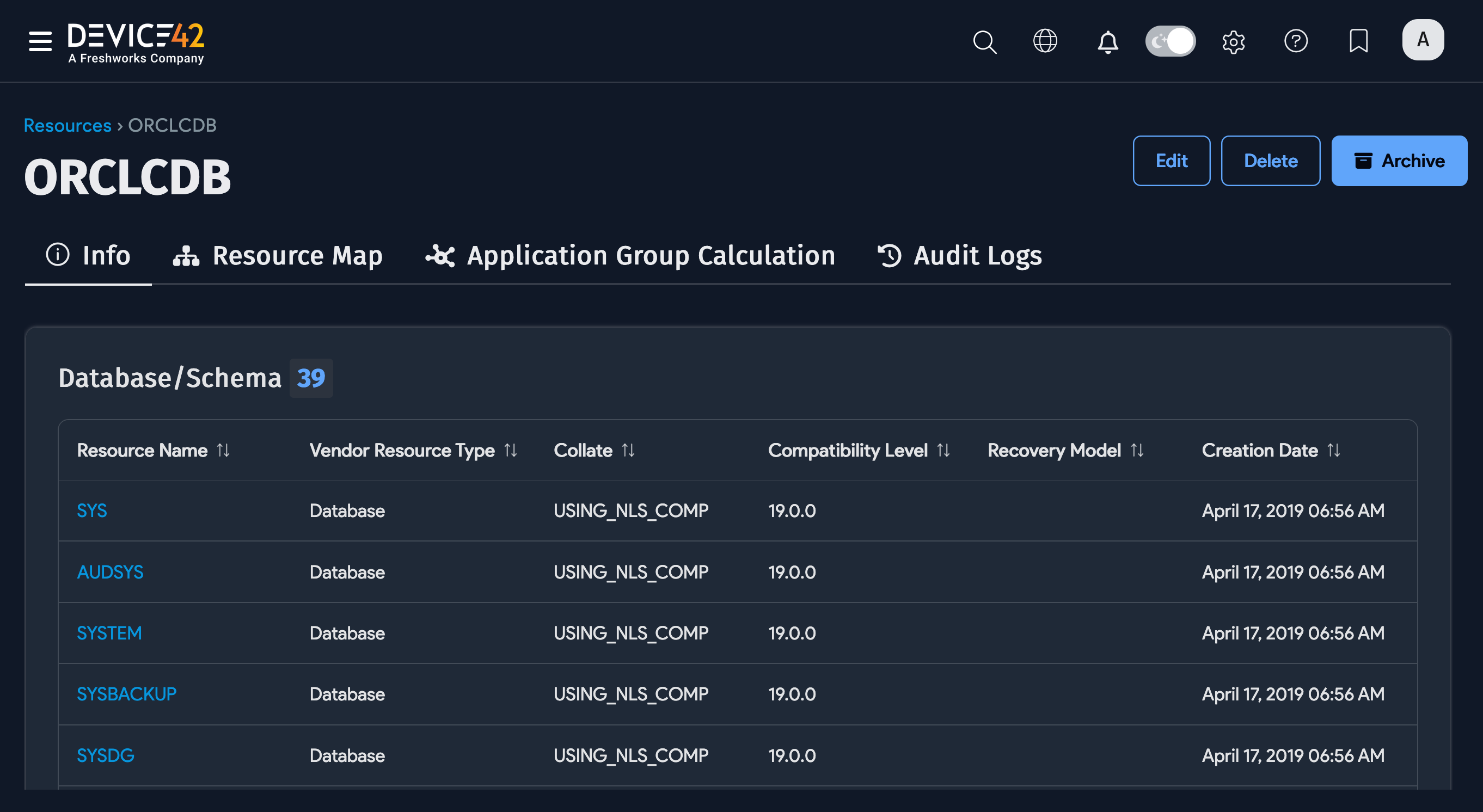
Oracle CDB/PDB Matching Process and Regular Processing Procedures
An Oracle database instance is created for each Container Database (CDB) and Pluggable Database (PDB), even in cases where they share the same endpoint listener.
We attempt to match any root database instance (CDB) with the same endpoint as our incoming resource (CDB or PDB). If we find a root database instance (CDB), we try to locate all related child databases (PDBs) for it and iterate through all of the child records. If any child database name matches the name of the incoming resource, we identify this database instance as the same as the incoming one and update the existing record with the new incoming resource data.
If we can't find any child database instance resources, we match the resource to the root resource. If there's no match to the root resource, we proceed with regular processing.
We don't aim to match orphaned PDBs to the CDB if a fresh CDB is incoming.
If a candidate database instance is detected to be a child of a CDB, we skip the matching process.
Oracle User Discovery Updates
We've made the following changes to the UI:
- Added Database Instance Name under the identifier (generally the service name).
- Renamed Database to Database/Schema and only show ones with attached objects for Oracle.
We previously gathered all Oracle users and collected them as "Device42 Databases." Then, we only retrieved Oracle users that had at least one associated database object, and from there, we implemented changes to ignore user schemas. As a result, some Oracle database connections may no longer show under specific user schemas. These 'orphaned' database connections now map to the main database instance, instead of mapping to a specific Database/Schema resource. While they’re not linked to individual schemas anymore, key details like the user login and schema names are still preserved in the database instance details.
PostgreSQL Database Discovery (on *nix targets)
Device42 offers PostgreSQL database discovery for *nix discovery targets, although it requires a separate set of credentials to authenticate to the database instance itself. Ensure these additional credentials have the appropriate permissions for viewing the databases you are interested in discovering.
Minimum Permissions Requirements for PostgreSQL Discovery
For discovery to return detailed information about your database instance, you will need access to the following tables:
pg_database(table)pg_tablespace(table)pg_stat_activity(table)inet_server_addr()(function)
Set Up Your PostgreSQL Discovery Job
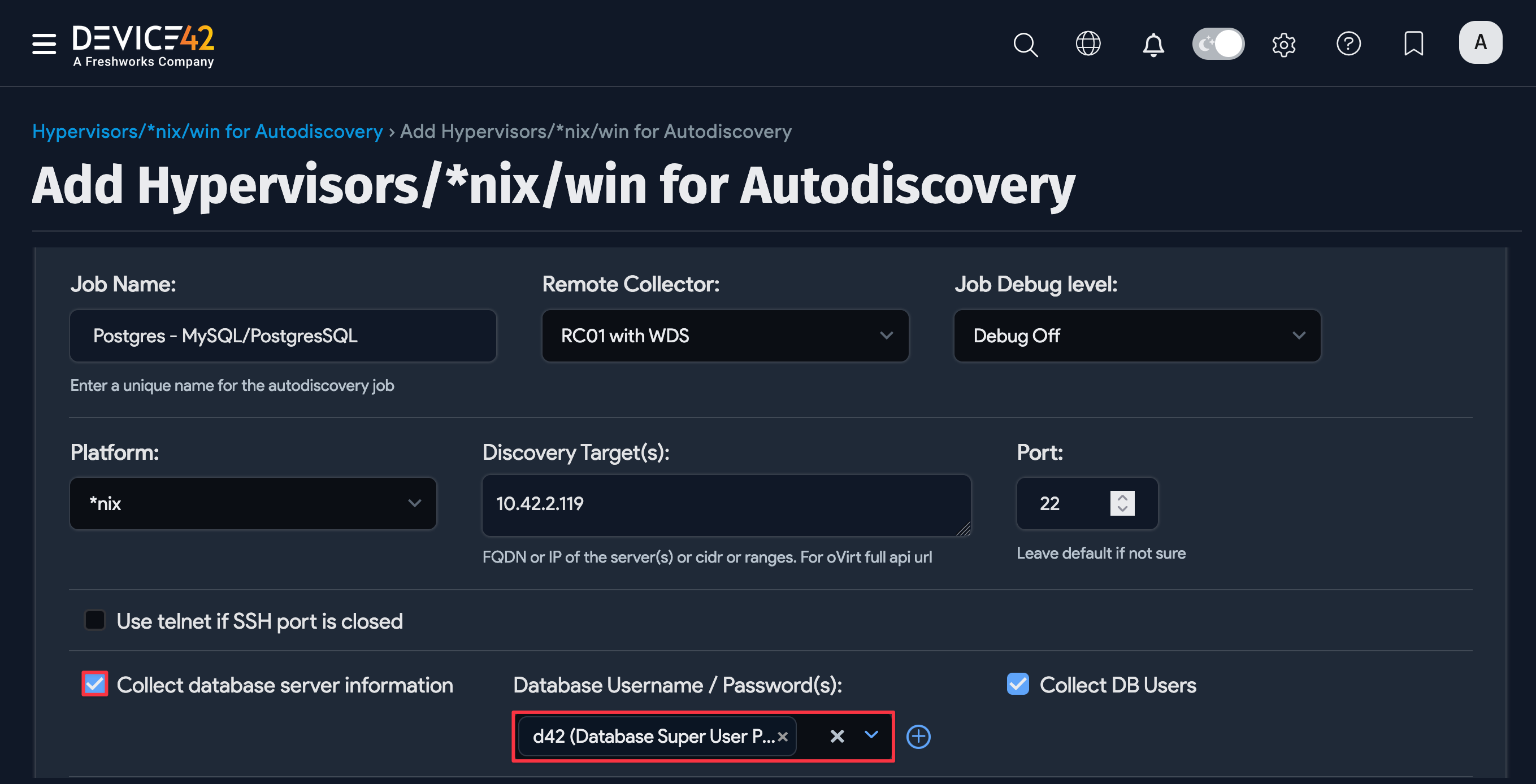
To begin discovering your PostgreSQL databases, create a new discovery job for *nix targets, and be sure to enable database discovery by checking the Collect database server information checkbox.
Fill out both sets of credentials:
- Database Username / Password(s): These credentials are used to authenticate to the Postgres database.
- Discovery Target(s) Credential(s): These credentials are used to authenticate to the *nix server.
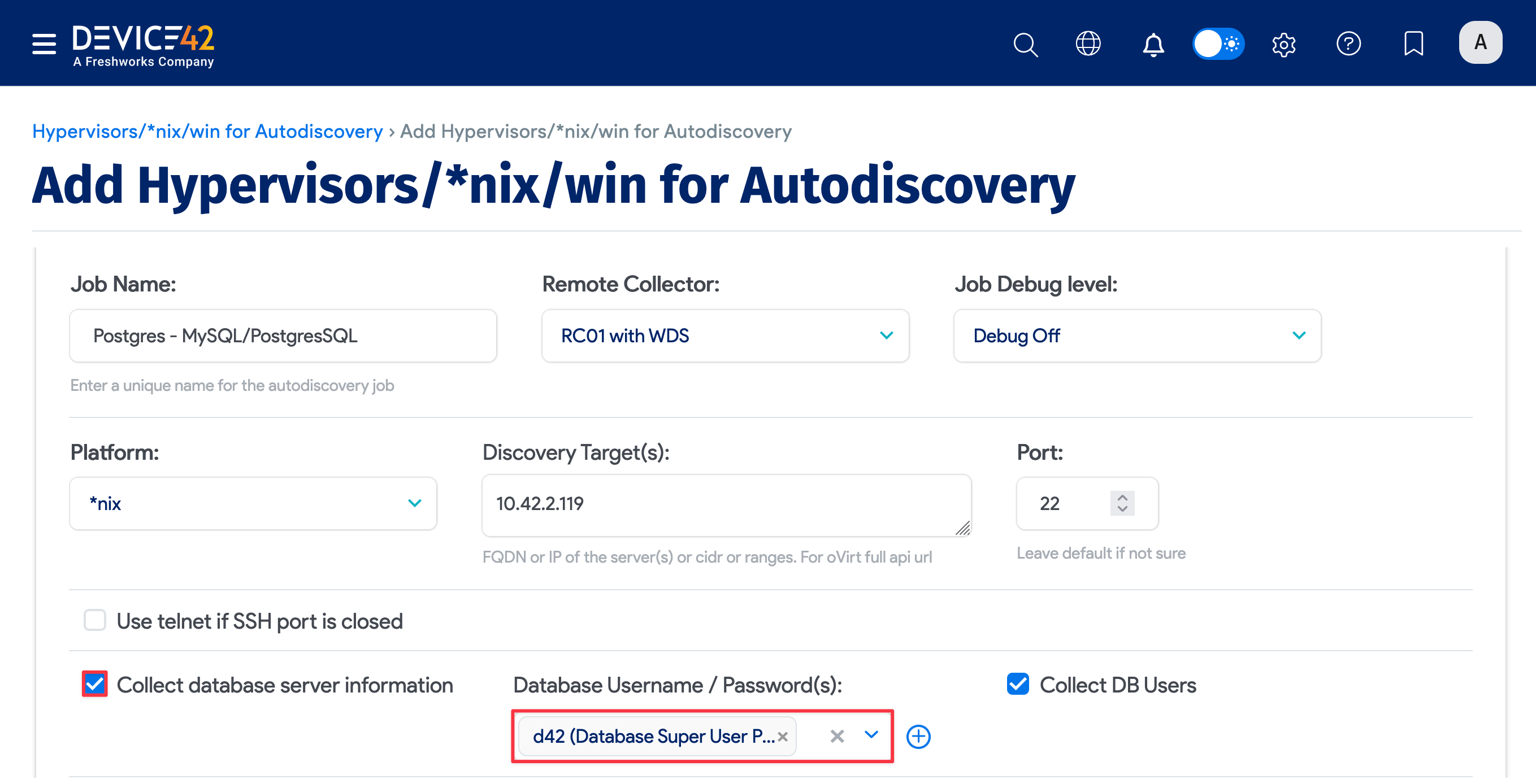
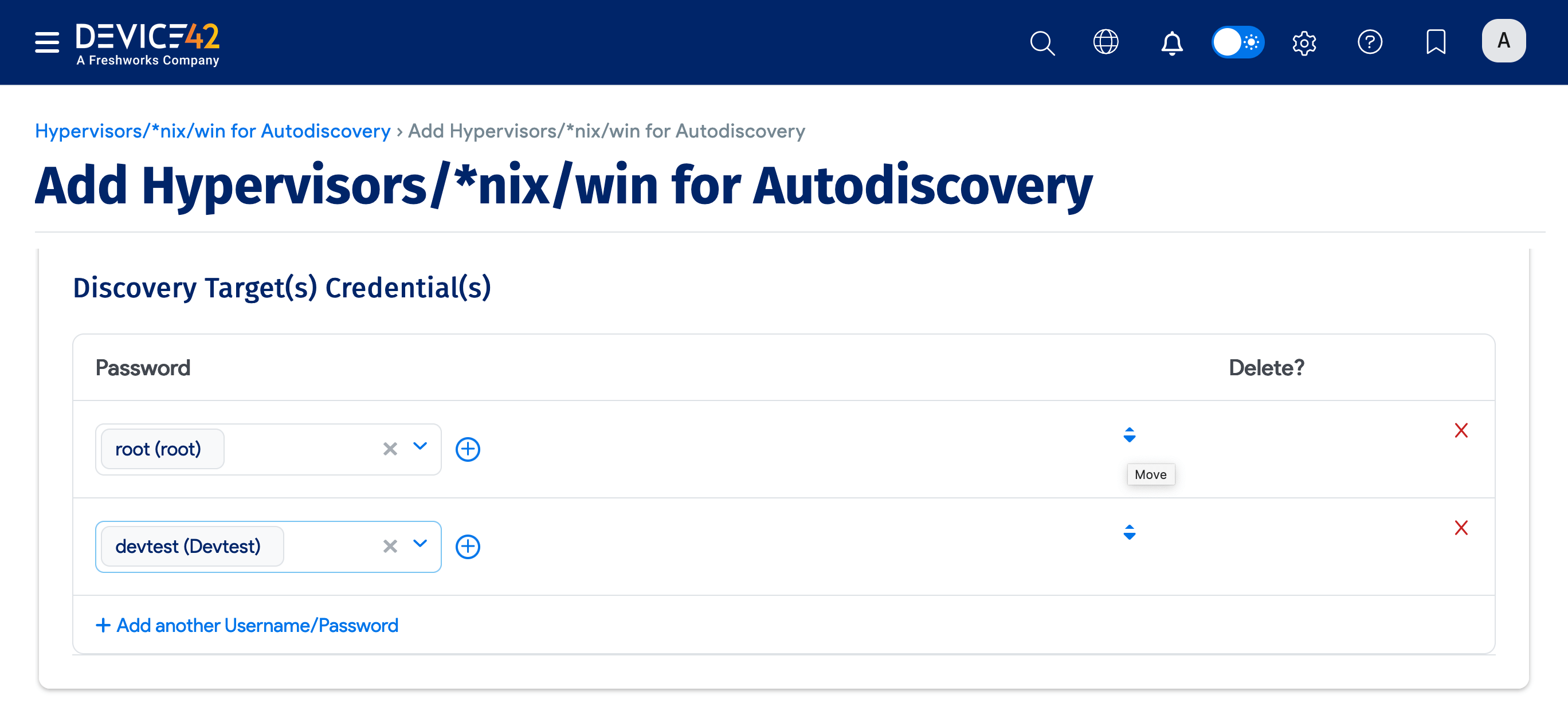
You can enter an ordered list of preferred Discovery Target(s) Credential(s) when you create a database discovery job. When the job runs, it will use the credentials in the order that you entered them, stopping at the first successful authentication. Subsequent job runs use the last successful credential and then the remaining credentials in the ordered list.
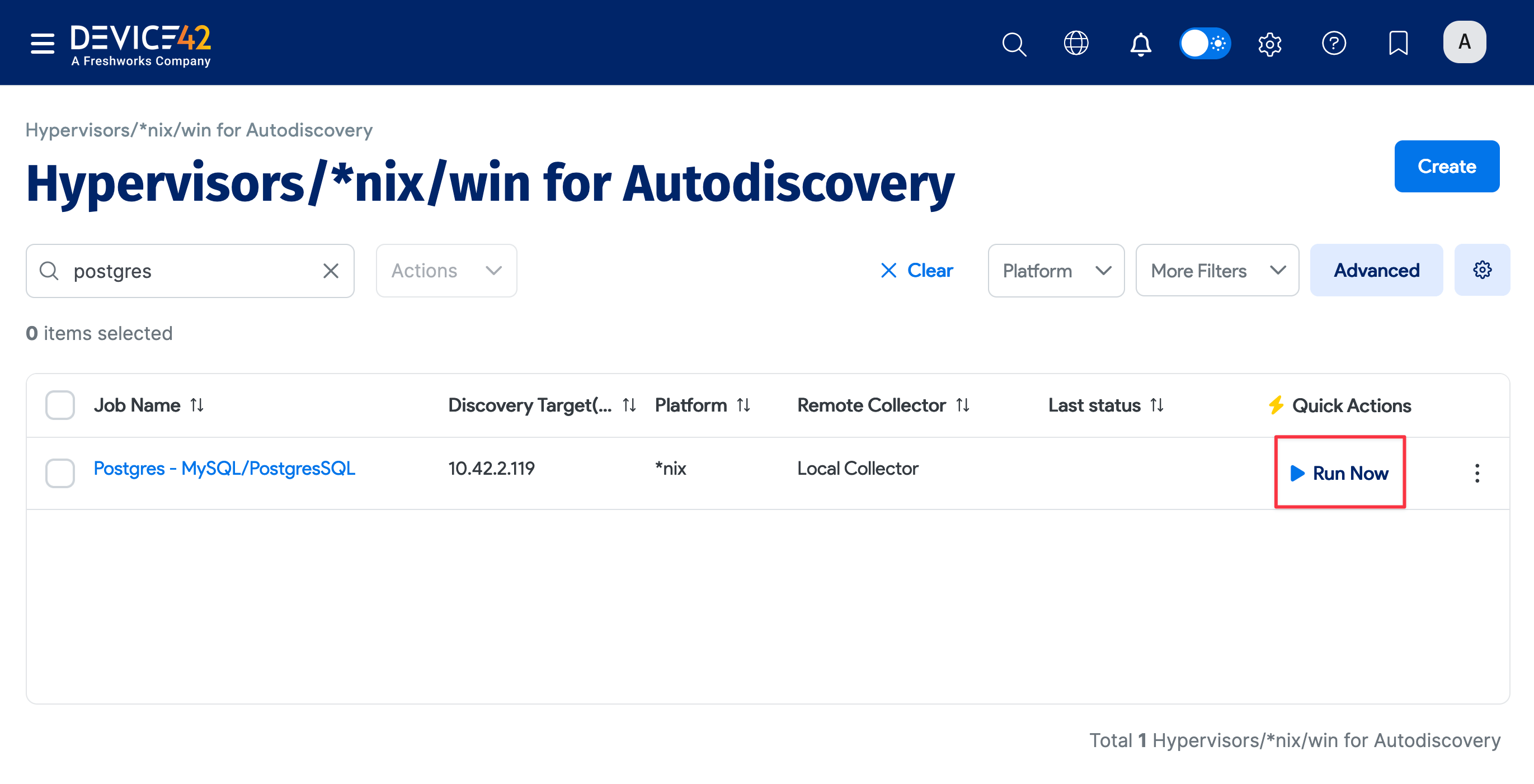
Run your new discovery job to test it. Click Run Now on the job's details page or on the list page under Discovery > HyperVisors /*nix /Windows. As Postgres databases are detected, discovery will import a list of all the instances, databases, and connection details it finds.
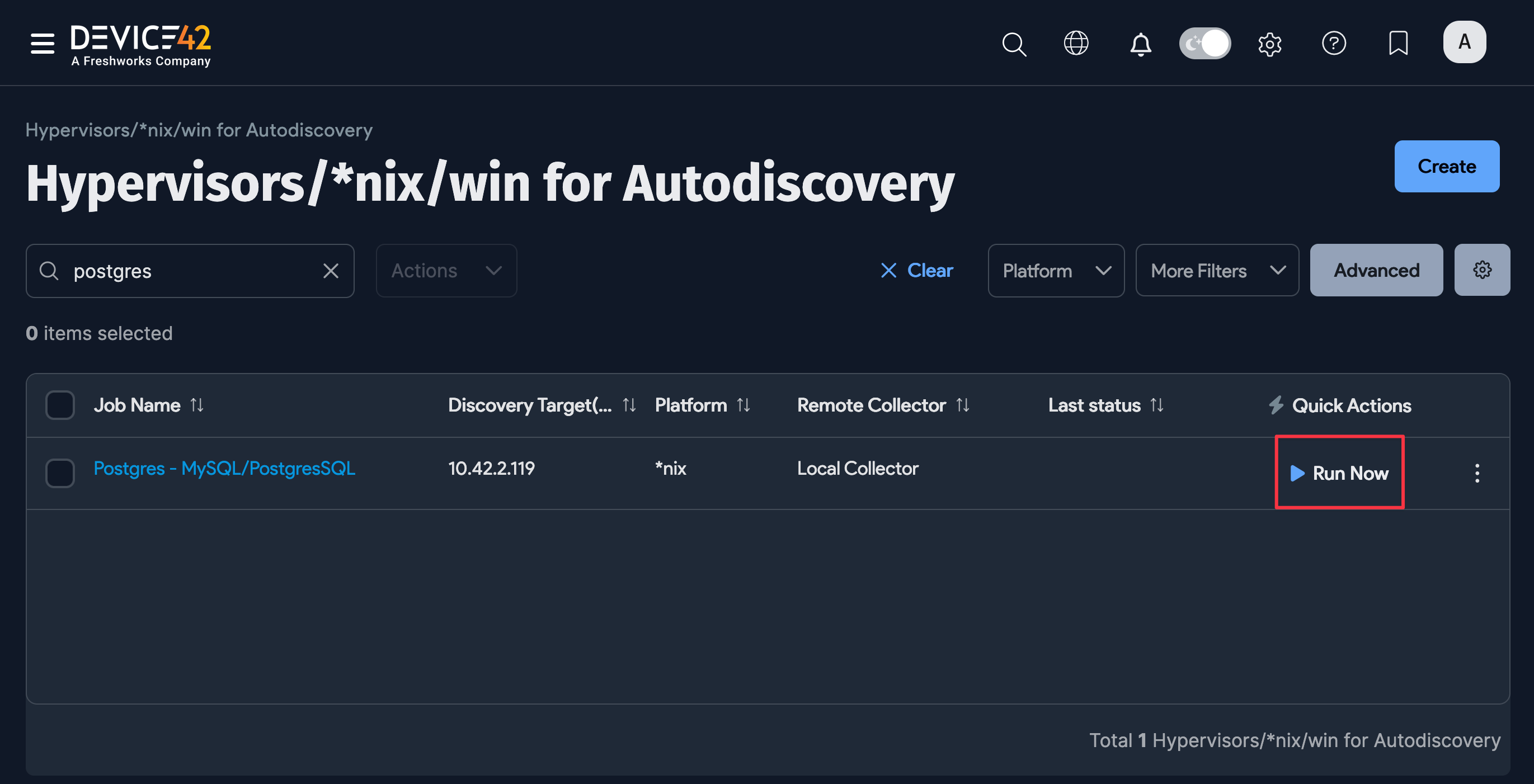
View PostgreSQL Database Discovery Job Results
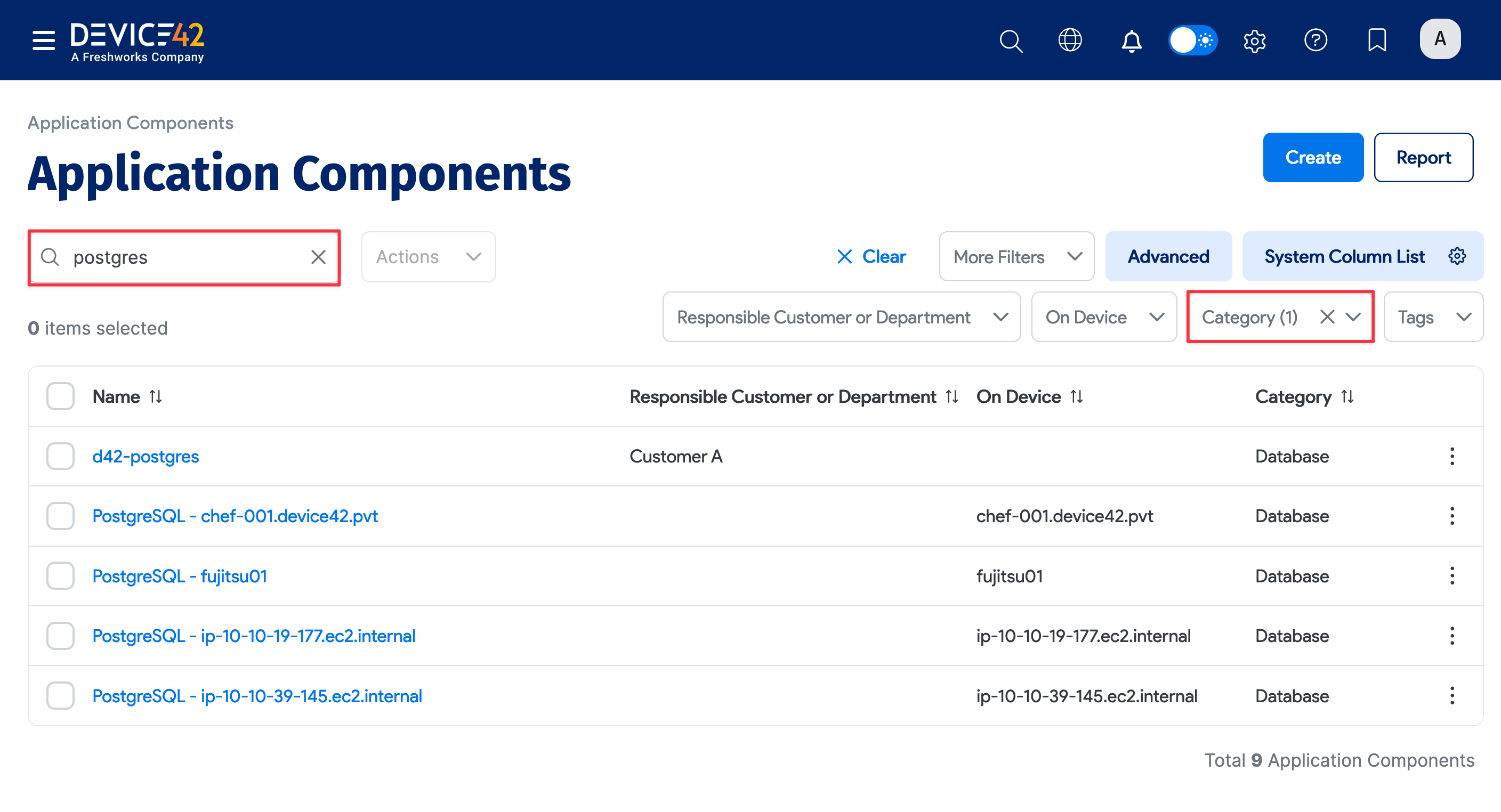
When the job finishes, the most direct way to view the results of your database discovery is via the discovered Postgres application components themselves. On the Device42 main menu, select Applications > Application Components. If you don’t see your Postgres DB instances at the top of the list, you can search for "Postgres" to narrow down the list, or filter the list By Category > Database.
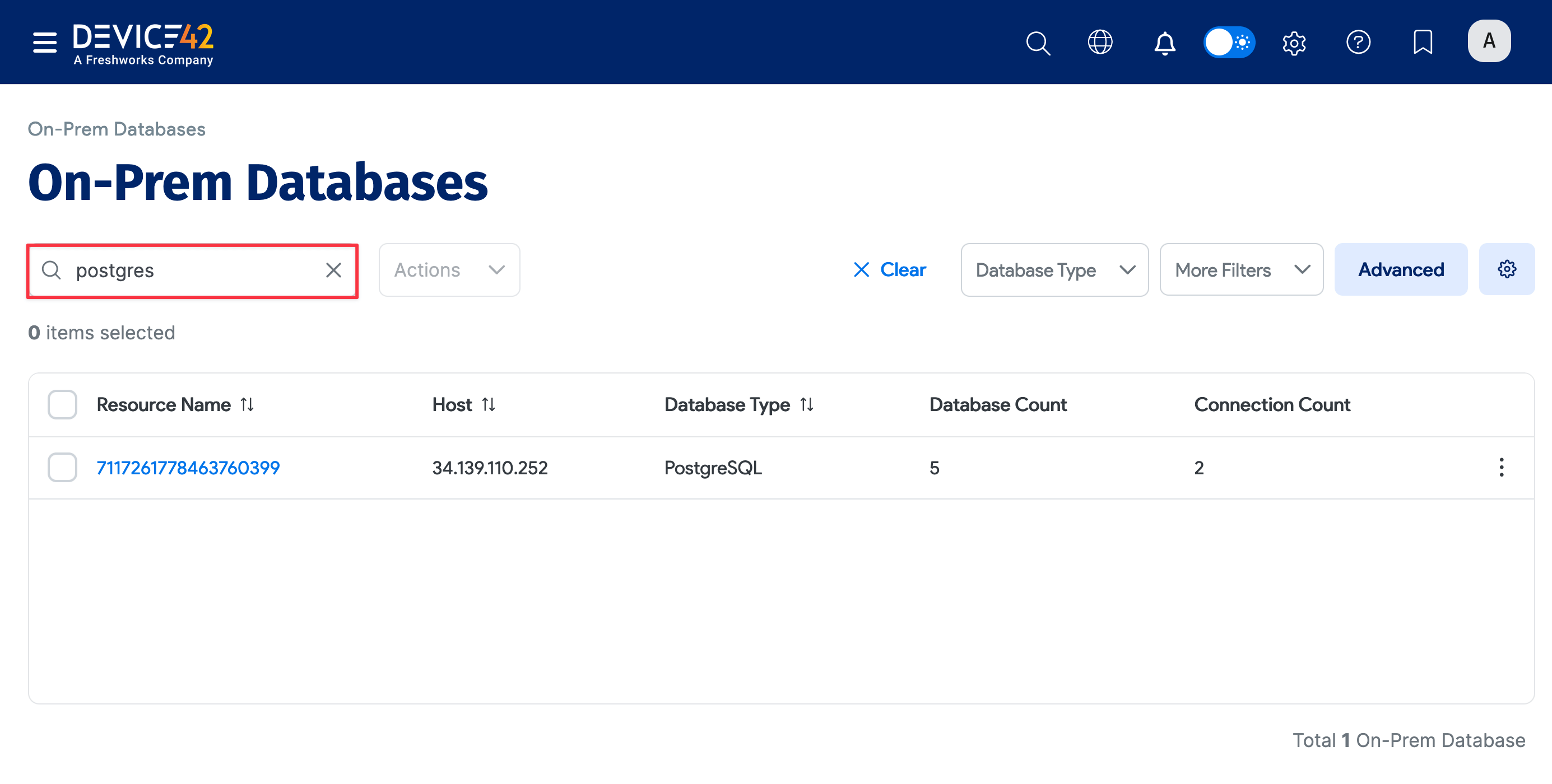
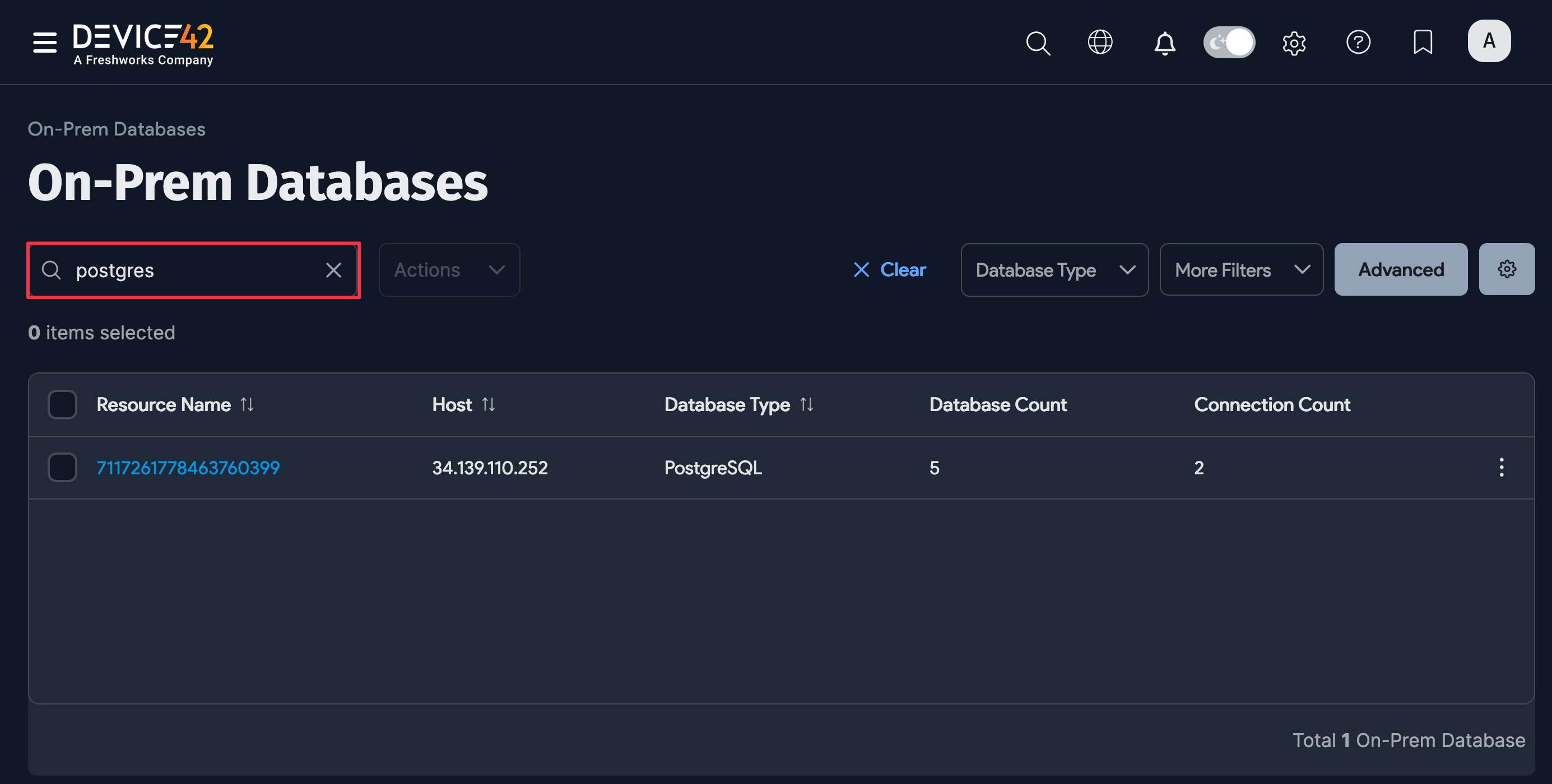
You can also select Resources > Databases > On-Prem Databases and search for Postgres databases.
DB2 Discovery (on *nix targets)
DB2 database discovery is for *nix discovery targets and requires a separate set of credentials to authenticate to the database instance itself. Ensure these credentials have the appropriate permissions for viewing the databases you are interested in discovering.
Permissions for DB2 Discovery
For discovery to return detailed info about your database instance, you will require the following permissions:
1. Privileges for ENV_SYS_INFO:
- SELECT or CONTROL privilege on the
ENV_SYS_INFOadministrative view. - EXECUTE privilege on the
ENV_GET_SYS_INFOtable function.
2. Privileges for SNAPAPPL_INFO:
- SELECT or CONTROL privilege on the
SNAPAPPL_INFOadministrative view - EXECUTE privilege on the
SNAP_GET_APPL_INFO_V95table function or DATAACCESS authority.
3. Privileges for ENV_INST_INFO:
- SELECT or CONTROL privilege on the
ENV_INST_INFOadministrative view - One of the following authorities: DATAACCESS, DBADM, SQLADM, ACCESSCTRL, or SECADM.
4. Privileges for DBCFG:
- SELECT or CONTROL privilege on the
DBCFGadministrative view - One of the following authorities: DATAACCESS, DBADM, or SQLADM.
5. Privileges for CONTAINER_UTILIZATION:
- SELECT or CONTROL privilege on the
CONTAINER_UTILIZATIONadministrative view. - One of the following authorities: DATAACCESS, DBADM, SQLADM, ACCESSCTRL, or SECADM.
6. Privileges for Monitoring:
- EXECUTE privilege on the
MON_GET_CONNECTION. - One of the following authorities:
DATAACCESS,DBADM, orSQLADM.
7. Privileges for Routines:
- EXECUTE privilege on the
GET_DBSIZE_INFO,WLM_SET_CONN_ENV,MON_GET_CONTAINER, andMON_GET_TABLESPACEroutines. - One of the following authorities: DATAACCESS, DBADM, or SQLADM.
Additional SELECT Privileges:
- SELECT privilege on the
SYSIBM.SYSTABLESPACES - SELECT privilege on the
SYSIBM.SYSDUMMY1 - SELECT privilege on the
SYSIBM.SYSVERSIONS
Required Authorities:
- One of the following authorities is required for overall access:
- SYSMON
- SYSMAINT
- SYSCTRL
- SYSADM
Set Up Your DB2 Discovery Job
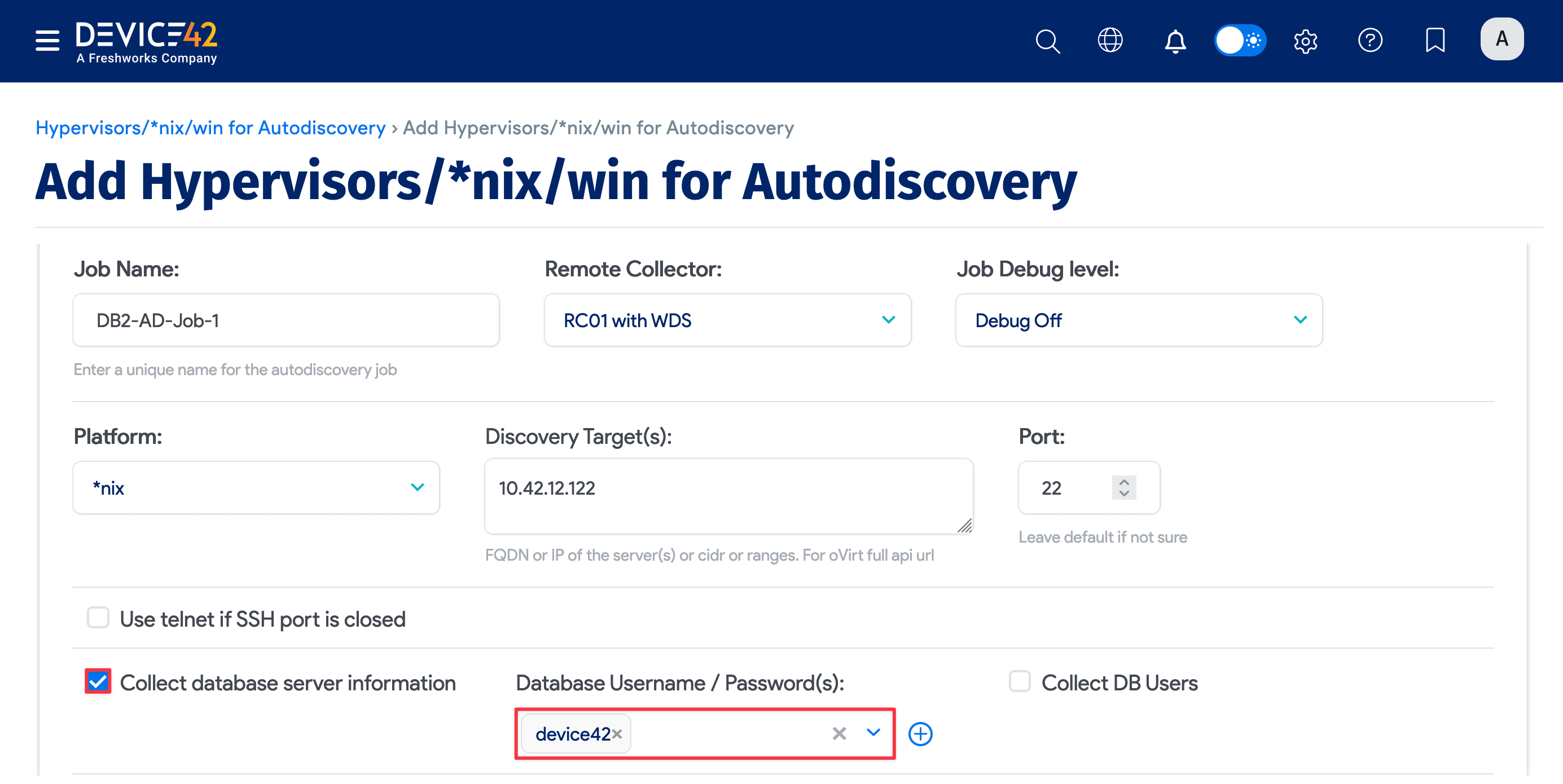
To begin discovering your DB2 databases, create a new discovery job for *nix targets, and be sure to enable database discovery by checking the Collect database server information checkbox.
Be sure to fill out both sets of credentials.
- Database Username / Password(s): These credentials are used to authenticate to the DB2 database.
- Discovery Target(s) Credential(s): These credentials are used to authenticate to the *nix server itself.
You can enter an ordered list of preferred Discovery Target(s) Credential(s) when you create a database discovery job. When the job runs, it will use the credentials in the order that you entered them, stopping at the first successful authentication. Subsequent job runs use the last successful credential and then the remaining credentials in the ordered list.
View DB2 Discovery Job Results
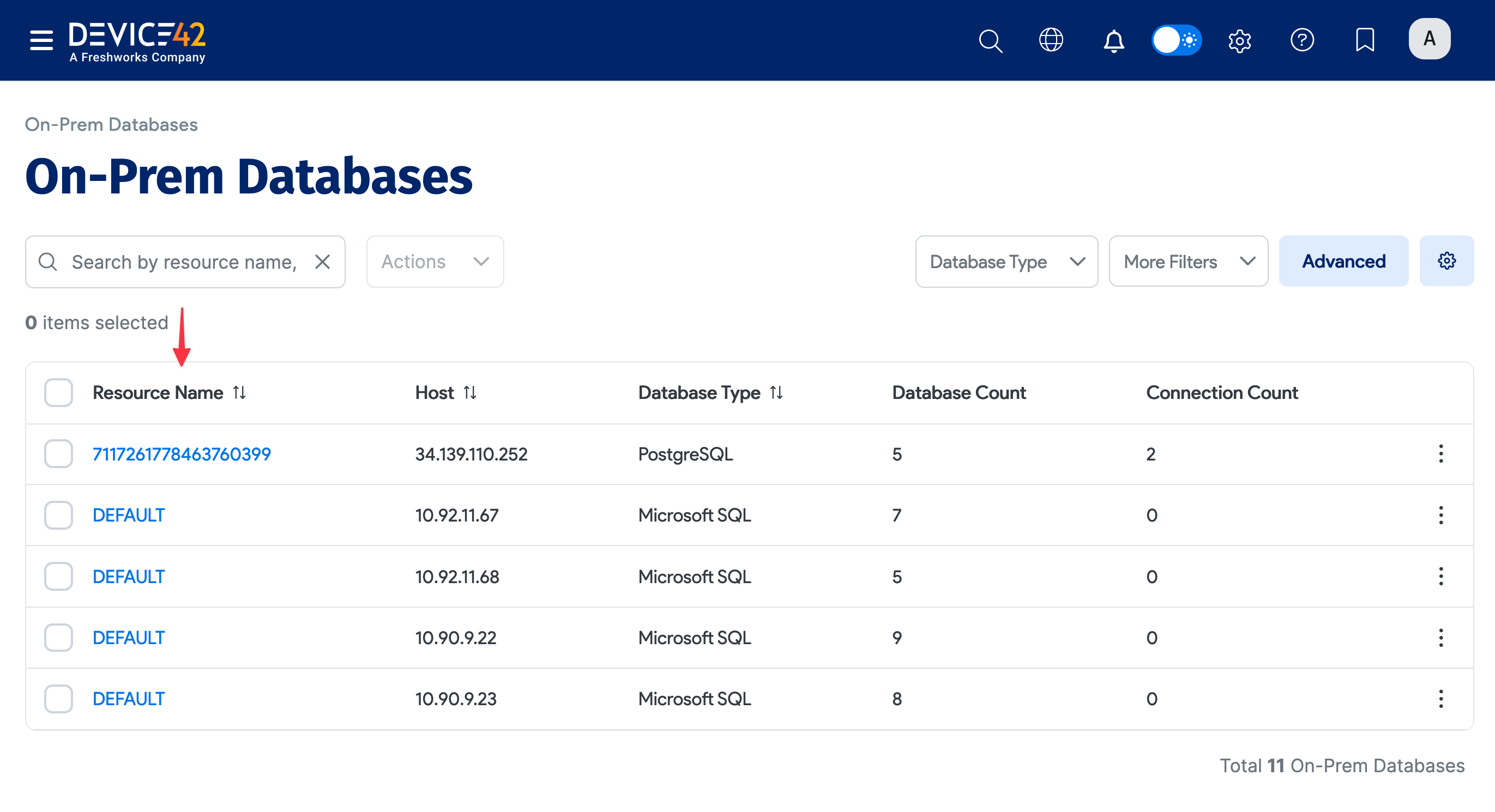
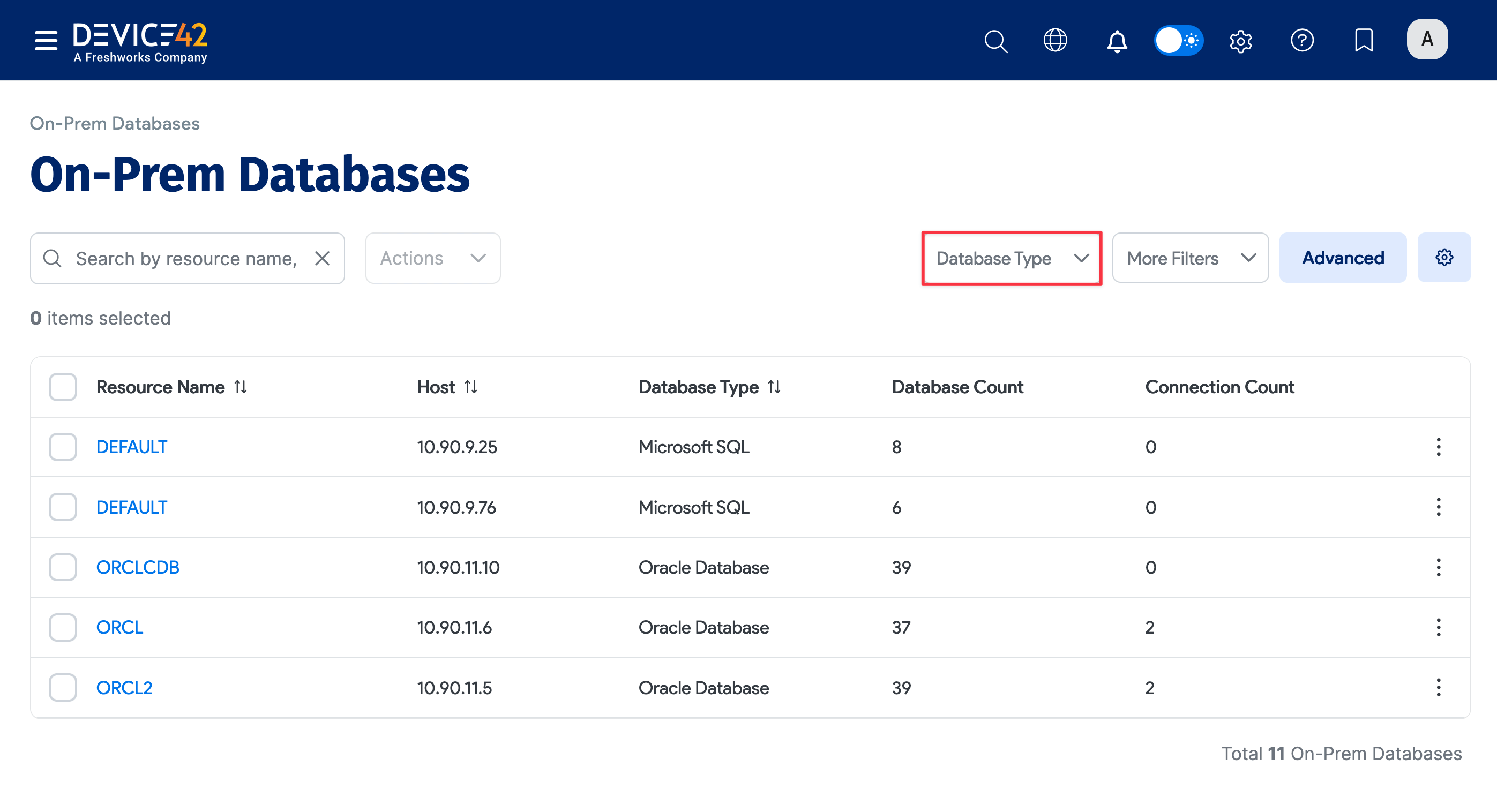
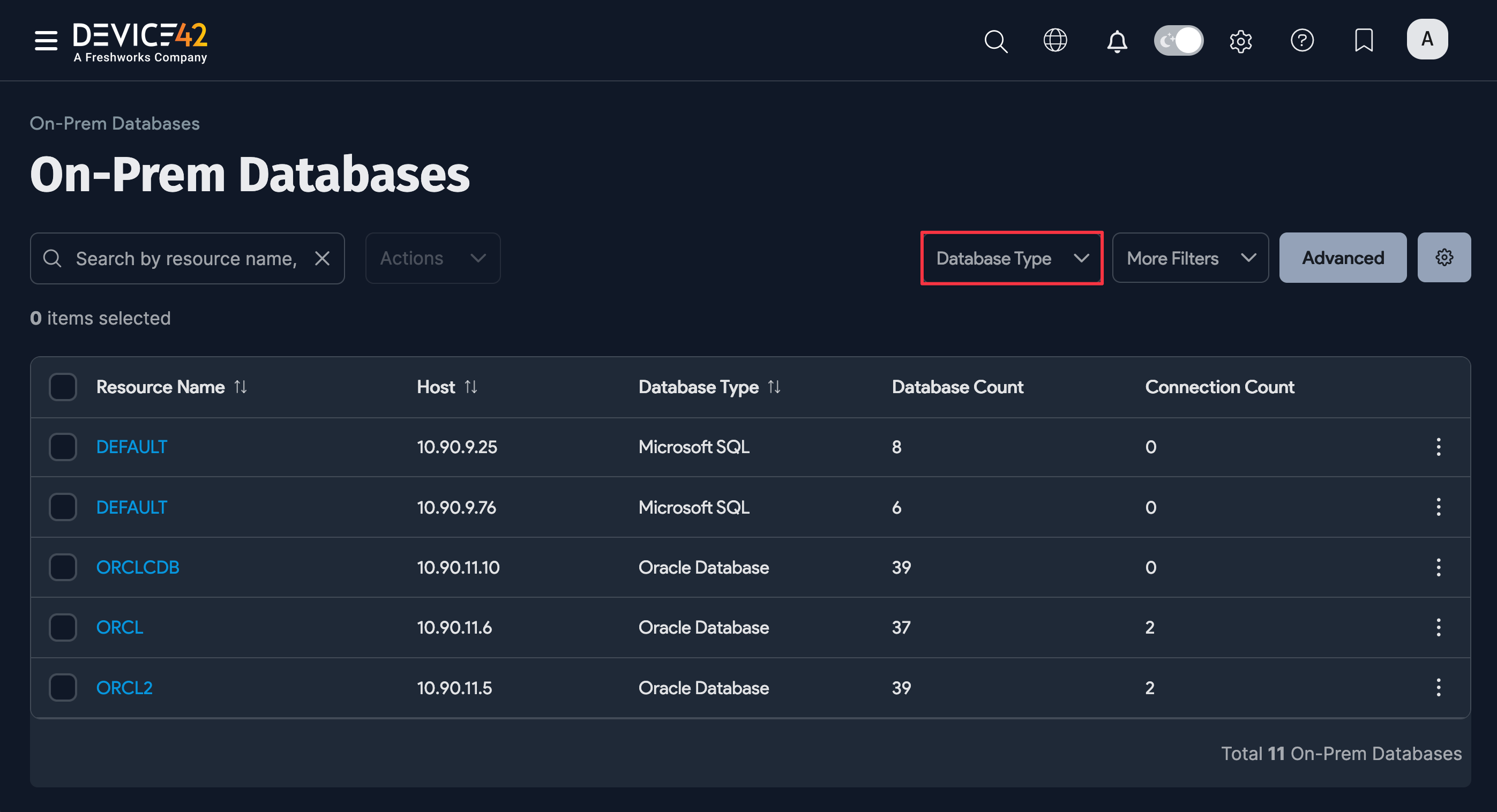
When the job finishes, you can view the results of your database discovery. Discovered DB2 databases are added to the On-Prem Databases list page.
On the Device42 main menu, select Resources > Databases > On-Prem Databases to display the page. You can use the search bar and filters to narrow down the list.
Click on your DB2 instance name under the Resource Name column to view more information about the database.
Database Connections Discovery Jobs
Discover information about the databases in your environment using the database discovery job type. Database discovery is based on the database connection information, such as the application components and DB server details, that you supply for the job. Returned database information is added to the On-Prem Databases list page.
This database discovery job type is useful when the main detailed database discovery (in OS jobs) cannot determine the proper connection settings for a specific database, because the database connection discovery job instead uses a string containing connection settings provided by the user.
If you have already discovered cloud databases using cloud autodiscovery jobs when you perform a database connection discovery using FQDN, Device42 will not duplicate the databases (which was the previous behavior).
-
Select Discovery > Autodiscovery >Database from the main menu to display the Database Discoveries list page.
-
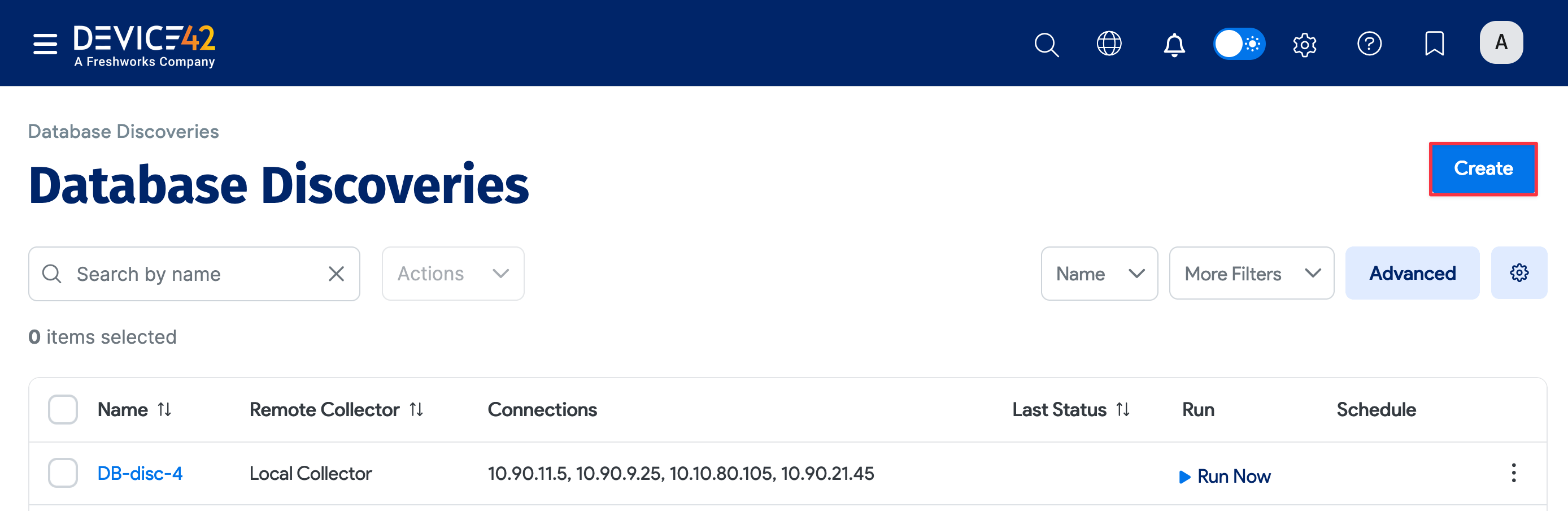
Click on a database discovery name to view that job and Edit to make changes to it. Click Create on the top right of the page to add a new database discovery job.
-
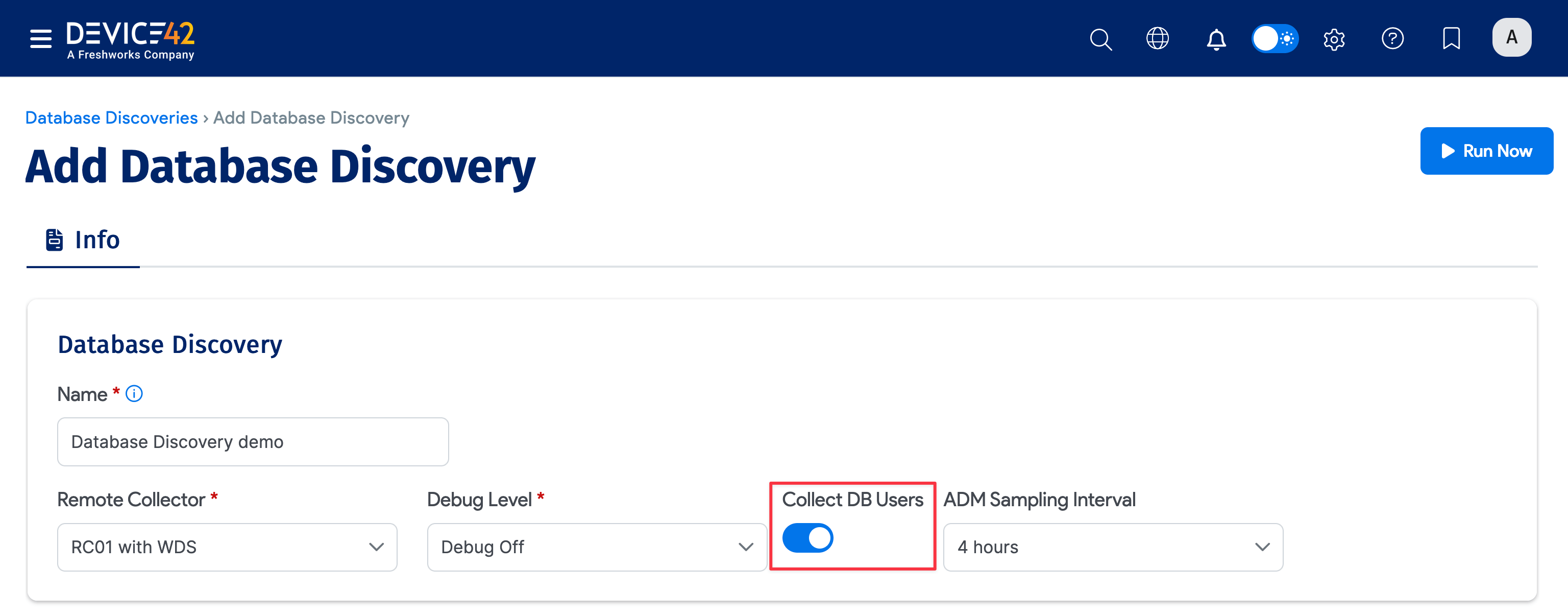
The Collect DB Users option applies to Oracle discovery. In Oracle, both databases and users are treated as schemas, and user schemas can exist without any database objects. By default, Device42 only discovers Oracle users that own objects, treating them as databases. Enable the Collect DB Users option to also include user schemas that don’t contain any objects.
-
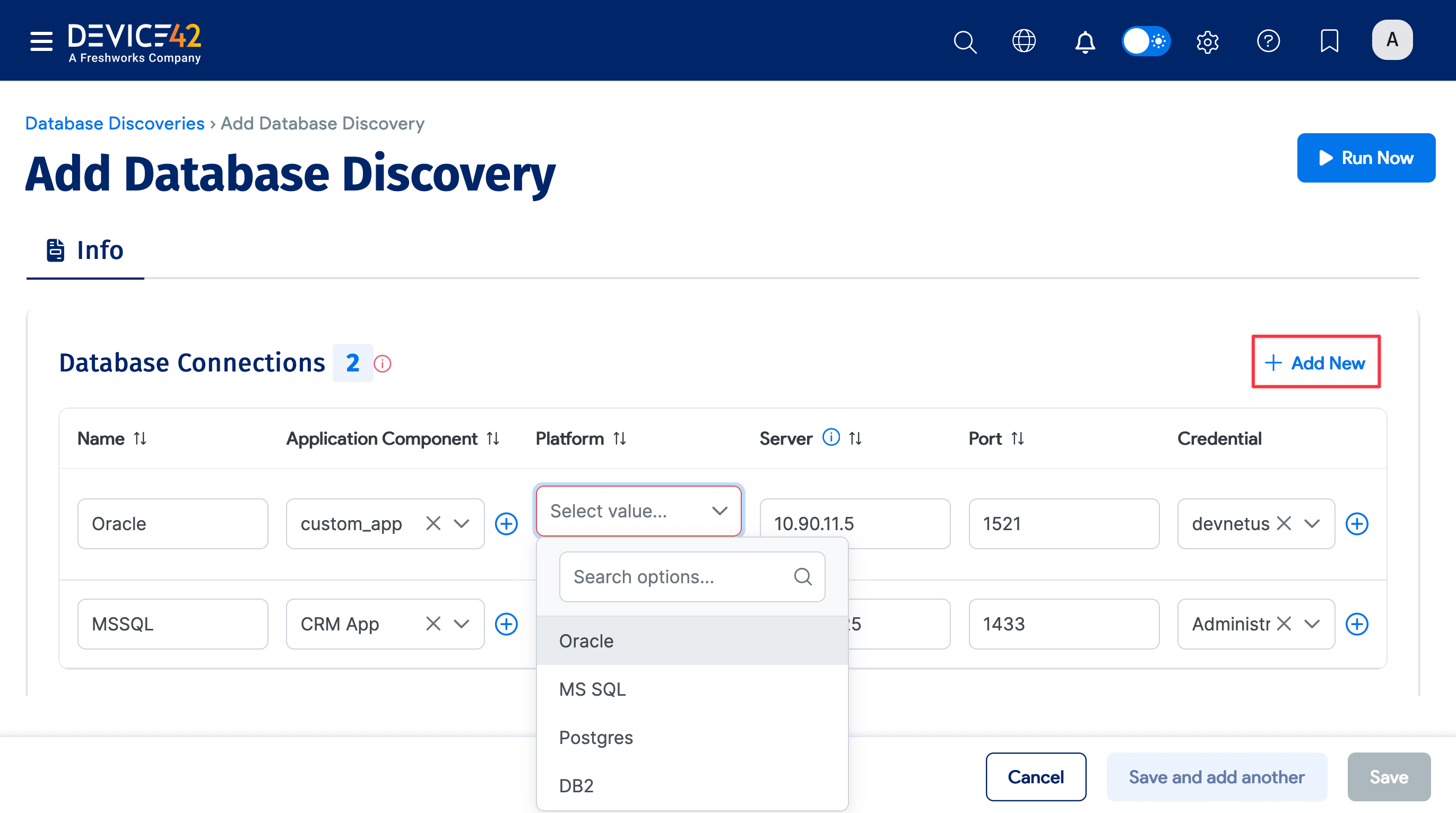
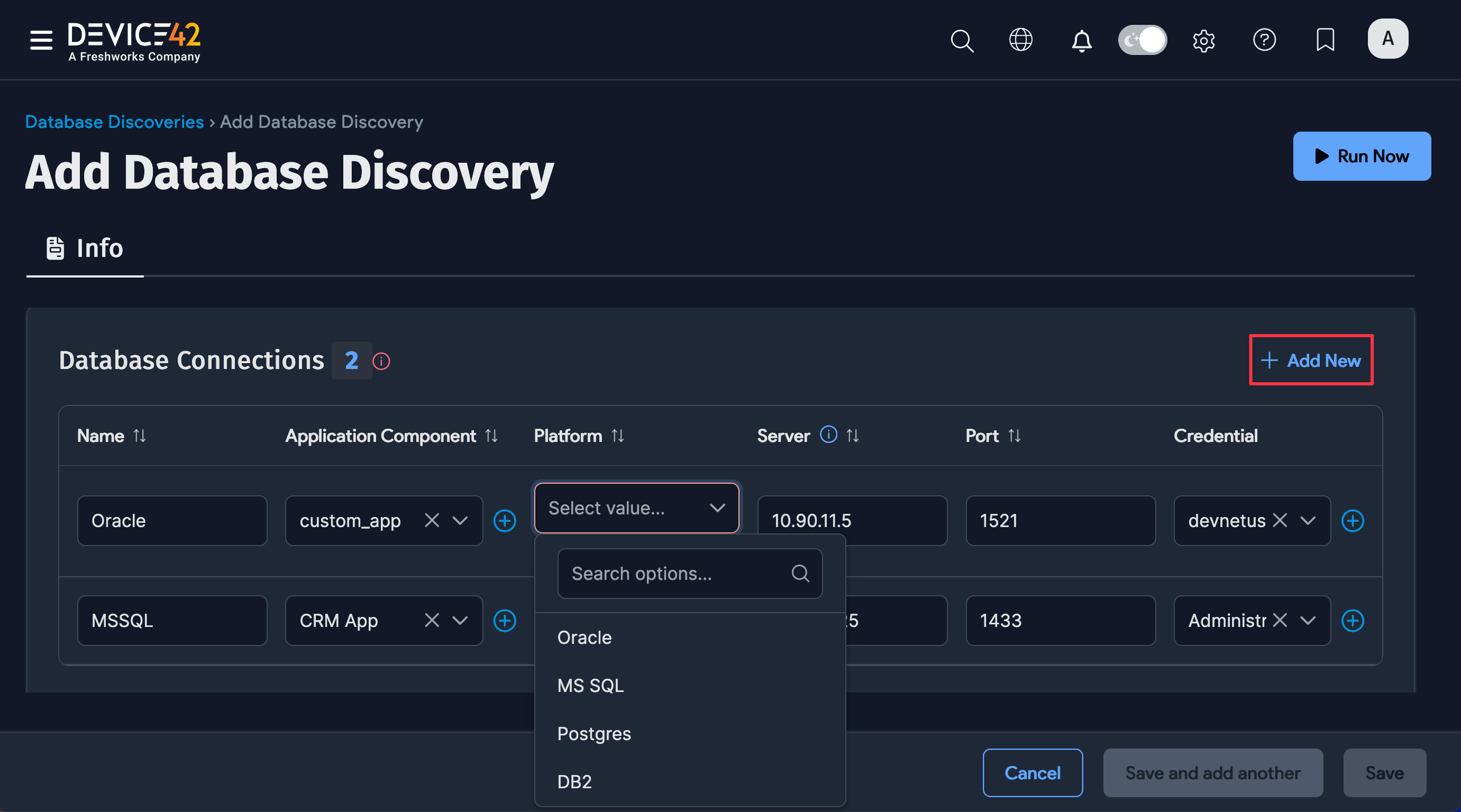
Click + Add New to add Database Connections.
-
Enter or select the Database Connections information:
-
Name: Connection name
-
Application Component: Application component to link to
-
Platform: Database type: Oracle, MS SQL, Postgres, or DB2
-
Server: IP address of the DB server
-
Port: DB server port
-
Credential: DB server access credentials
-
Extra: Enter a name specific to the database type:
- Enter an Instance: name for Oracle (required)
- Enter a Database: name for Postgres and DB2 (required)
- Not required for MS SQL
-
-
Use the trash can icon to remove a Database Connections line.
-
Scroll down the page to add or edit the Discovery Schedule for the job.
-
Click Save to save the job.
Database Discovery Job Scores
You can view Discovery Scores for the database jobs that have been run.
-
Navigate to Analytics > Discovery Status > Discovery Scores to display the Discovery Scores page.
-
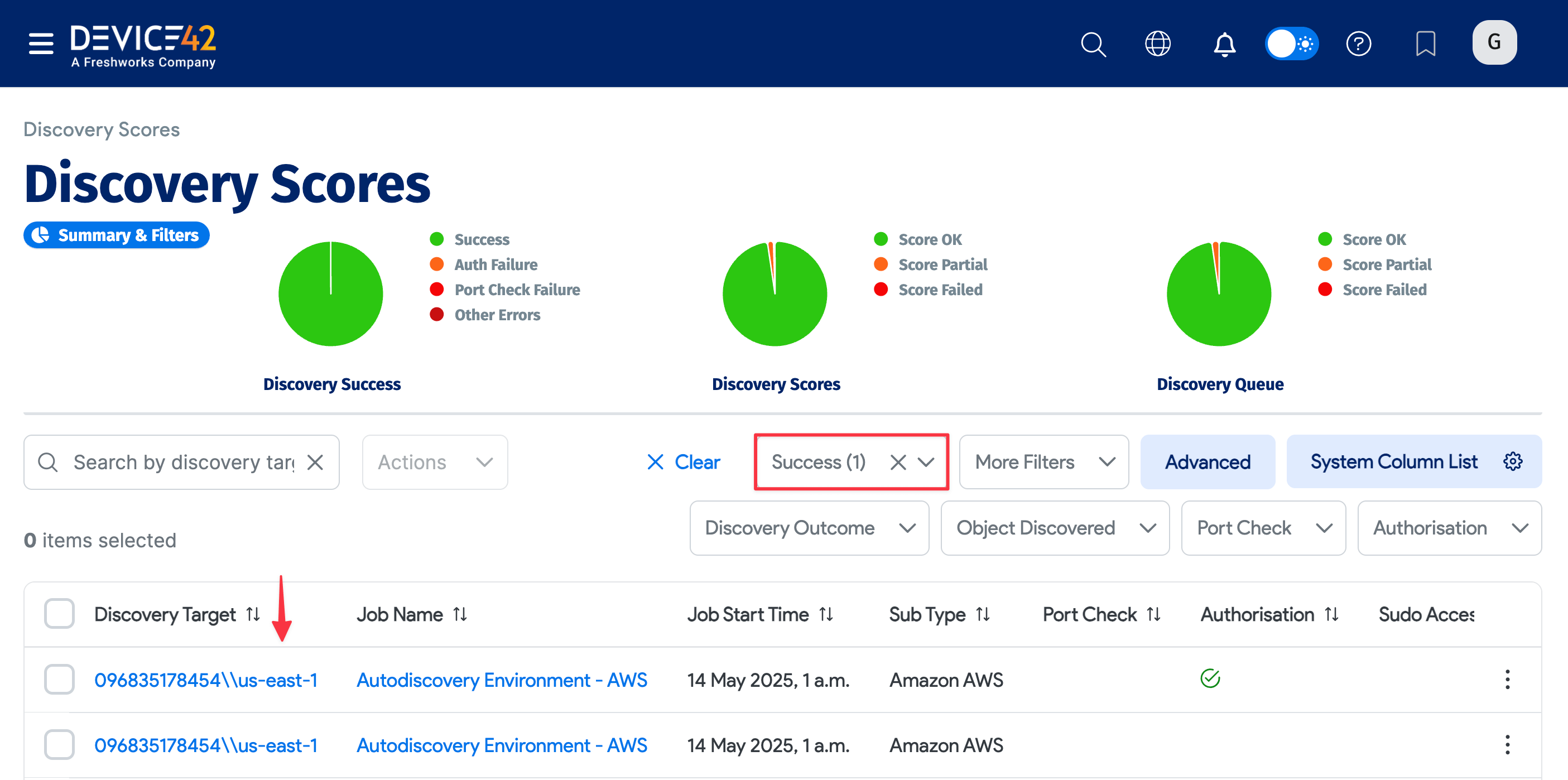
Click on the job you want to view in the Discovery Target column. You can use the search bar and filters to find a specific database or narrow down your results.
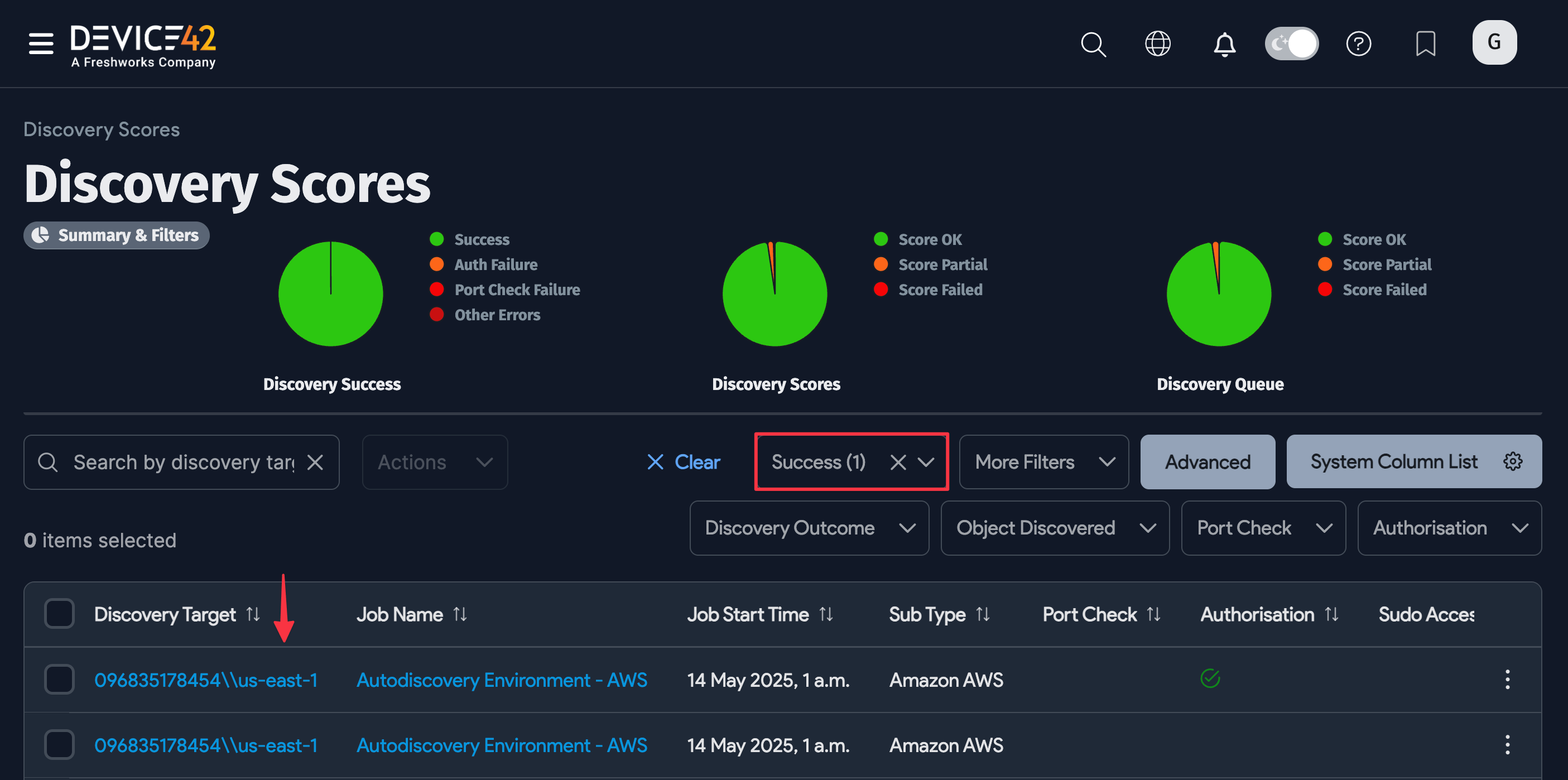
-
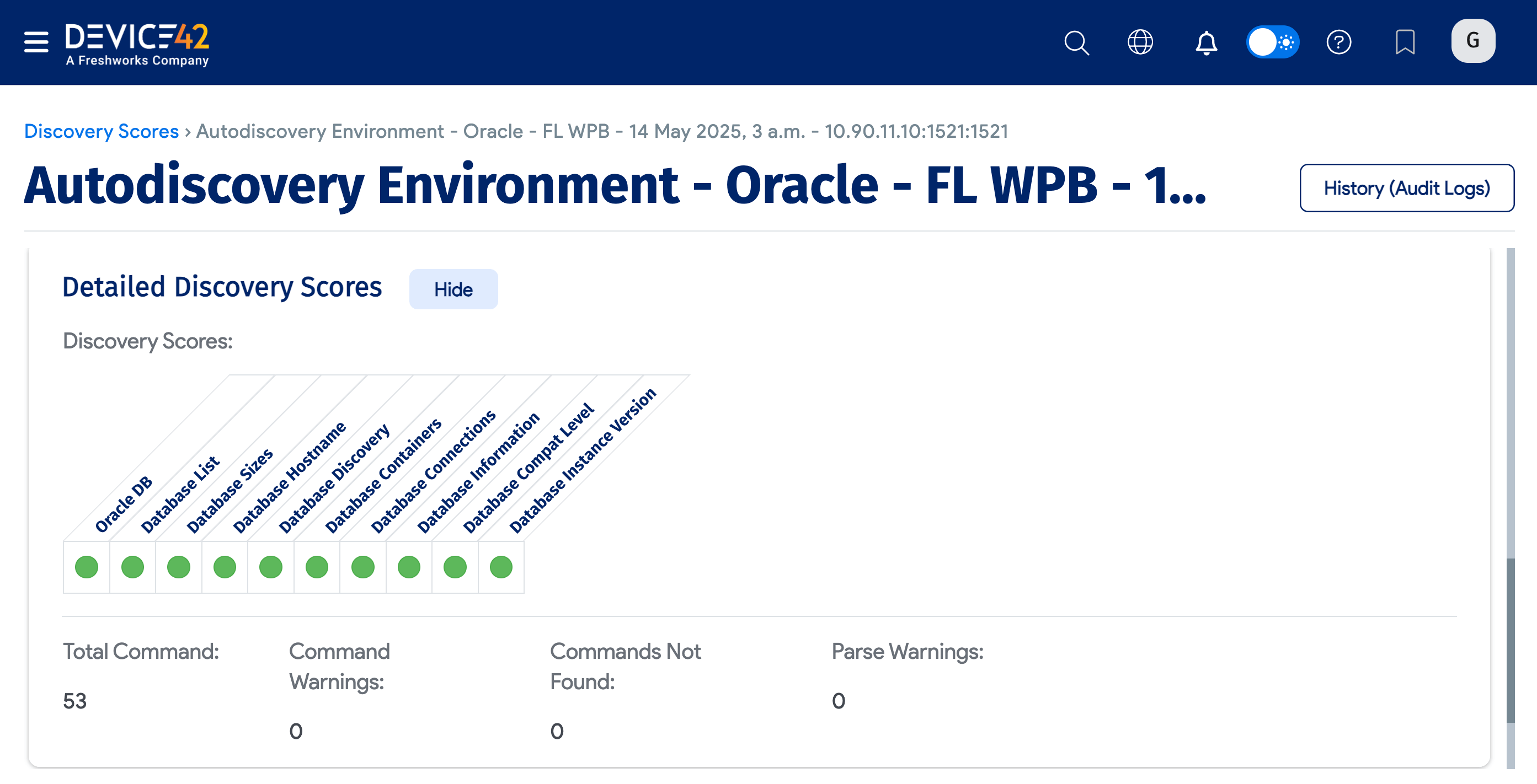
Click Detailed Discovery Scores to see additional information.
View Discovered Databases
Discovered databases are added to the On-Prem Databases list page.
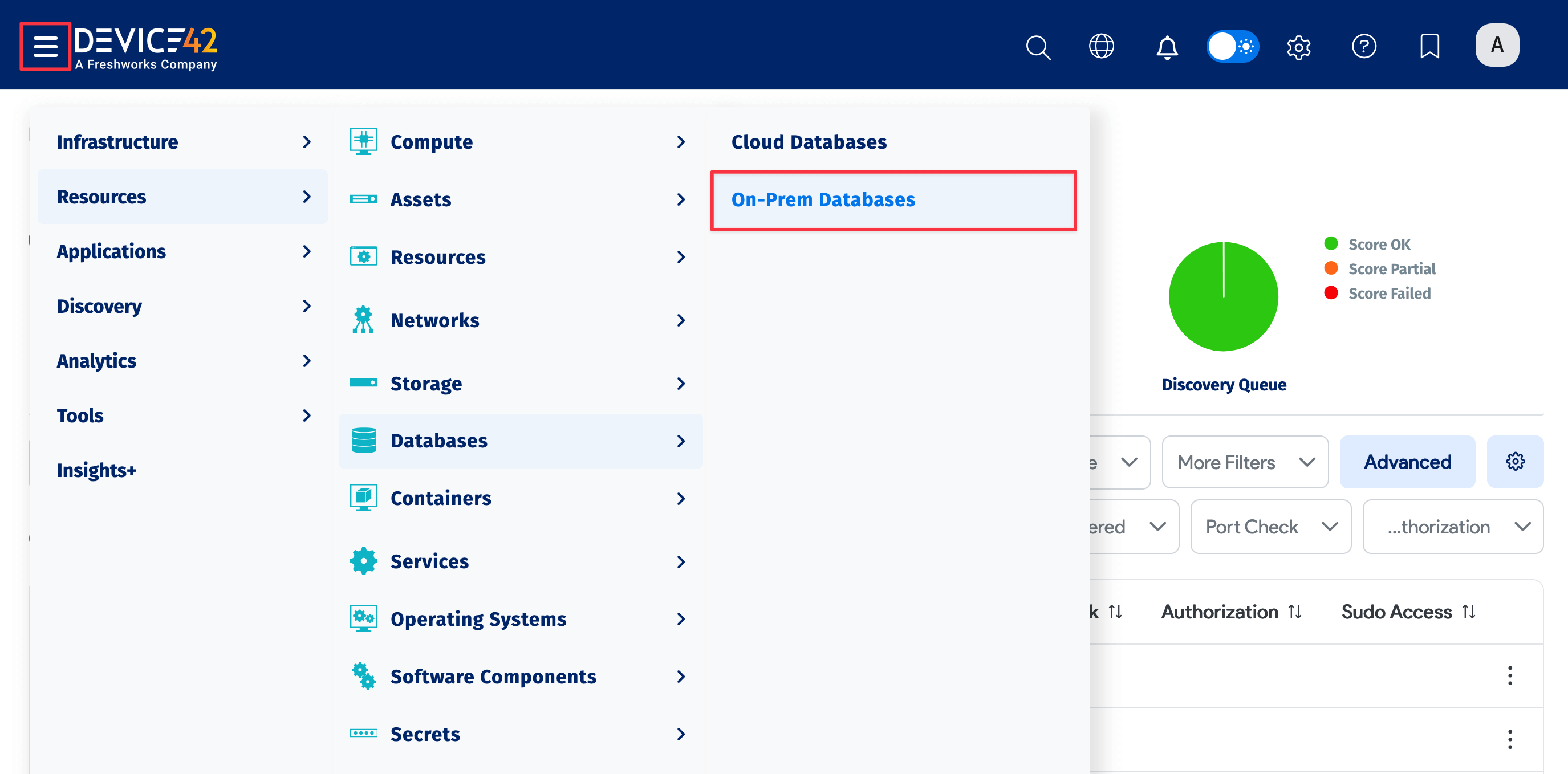
- Select Resources > Databases > On-Prem Databases to display the list page.
- Click on the name of the database you want to see in the Resource Name column.