Advanced Freshservice Mapping and Customization
This page covers advanced data mapping customization and XML file editing.
- For initial setup and installation, see Setting Up the Device42 Freshservice Integration.
- For usage and operations, see Using the Freshservice Integration.
Manage Customization with Newer Releases
The Device42-Freshservice integration ships with a default mapping file. Newer versions of the mapping file may include sending additional elements to Freshservice (such as assets, devices, CIs, and metadata). We share these new additions in the Freshservice mapping release notes.
If you make an adjustment and use a custom XML file, Device42 will not update the custom XML during updates.
If you want to incorporate updates, you need to do so manually: Download the current XML file, compare it to your customized XML file, and add in the new items as needed.
We recommend keeping track of your customizations so they can be added to the latest default mapping file.
Get Started with Custom Data Mapping
To get started, download the default mapping XML file and view the current mapping.
Download the mapping.xml File
-
From the Settings tab of the Configuration page, scroll down to the Schedule Synchronization section and click the Data Mapping button to reveal the custom mapping buttons.
-
Click the Download Default Mapping button to download the
mapping.xmlfile. Customize the mapping between fields in Device42 and Freshservice by downloading, editing, and reuploading themapping.xmlfile.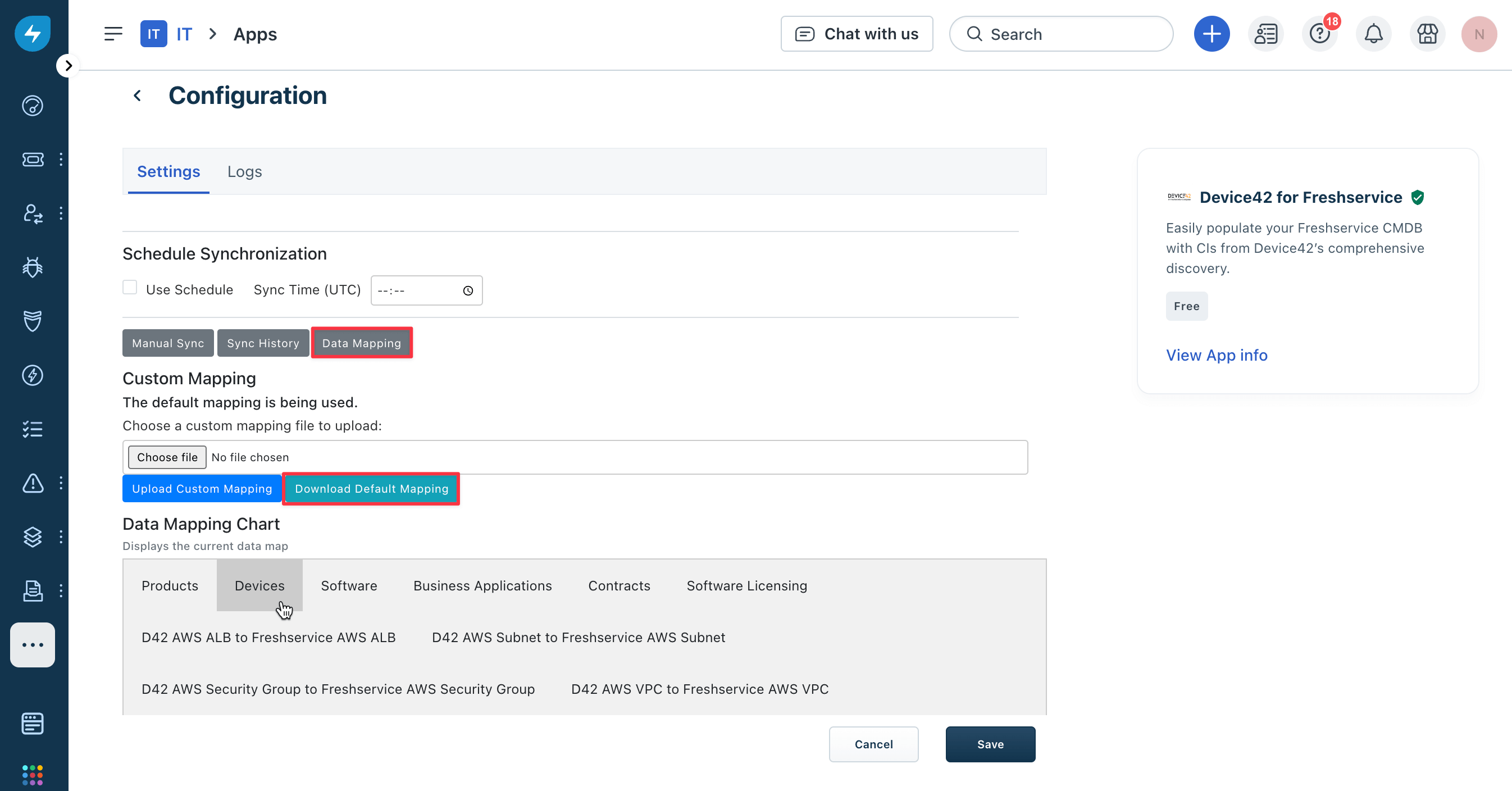
View the Current Mapping
-
Explore the mapped fields and their data types by selecting a type (for example, Devices) from the Data Mapping Chart. Scroll to the bottom of the page to view the mapping table.

The mapping.xml File Structure
Open the mapping.xml file in a text or code editor to view and edit the data mapping. Version 1.0 of the file has around 6010 lines. There are tasks for syncing data, tasks for syncing the relationships between Device42 CI types (by recreating them between the corresponding Freshservice types), and two cleanup tasks for deleting any assets or asset relationships from Freshservice that do not exist in Device42.

You can customize the data mapping between Device42 and Freshservice by modifying and adding to these tasks. Refer to The mapping.xml File Tasks table below for descriptions of the default mapping tasks, types, and their version requirements.
For example, the following <task> element copies product information from Device42 to Freshservice:
Click to expand the code block
<tasks>
<task enable="true" name="Products" type="product" description="Copy Product info from Device42 to Freshservice" d42_min_version="16.19.00">
<api>
<target asset-type="Hardware"/>
<resource
doql="
select distinct
view_vendor_v1.name as manufacturer,
<!-- ... -->
"
/>
</api>
<mapping key="name" doql-suffix=" where GREATEST(view_hardware_v2.last_changed, view_vendor_v1.last_changed, view_device_v2.last_changed) >'%s'">
<field resource="name" source-type="string" target="name" target-type="string" max-length="255" escape="true"/>
<field resource="manufacturer" source-type="string" target="manufacturer" target-type="string"
not-null="true" set-space="true" min-length="1" max-length="255"/>
</mapping>
</task>
Let's take a closer look at the attributes and elements of the <task> elements so you can understand what to adapt or emulate to suit your particular case.
The <task> Element Attributes
-
enable: You can turn off syncing for individual tasks by setting theenableattribute tofalse. For example:<task enable="false" name="Products" type="product" description="Copy Product info from Device42 to Freshservice" d42_min_version="16.19.00">Note that if you turn off a task that has
assetorasset_relationshipas its corresponding Freshservice type (for example, devices, business services, and resources in Device42), you'll need to find and remove its corresponding query snippet in theDeletecleanup tasks. For an example, see this answer in the FAQ section. -
name: You can edit the task name. Task names appear in the integration app's Data Mapping Chart. -
type: Holds the Freshservice classification of the data. The valid types are:productassetsoftwaresoftware_installationasset_relationshipcontractcontract_assetcomponentdeploymentservicedaemon_setstateful_set
-
description: You can write and edit a brief task description. -
d42_min_versionandd42_max_version: These attributes specify the minimum and maximum Device42 versions required to run a task. Tasks may have a maximum version, a minimum version, both, or neither. You can generally leave this out when creating new tasks.
The <task> Element Elements
The <api> and <mapping> elements are nested in each task. Think of the <api> element as relating to Device42 data and the <mapping> element as relating to the Freshservice fields.
The <api> element contains:
<target>: This holds any additionalasset-typeclassifications from Device42 and will be empty in most cases. For example,Hardwarerefers to the Hardware Model under which the details of physical devices are organized.<resource>: This is the DOQL query used to fetch data from Device42.
The <mapping> element contains:
key: This is used to look the item up in Freshservice. It usually hasnameas its value.doql-suffix: A query condition used to fetch data that has been updated since the last sync. Omitting this value results in a full data sync.
Typically, the first <field> represents the Device42 data returned from the query put in a field. The second <field> element describes the equivalent field in Freshservice.
resource: The same as thetargetvalue.source-type: Not functionally critical; this provides the data type displayed on the integration app's Data Mapping Chart.target: The Device42 field to be mapped to Freshservice. The Freshservice convention is to use the display name in snake case, occasionally with the ID of the asset type as a suffix. For example,memory_max_usageandmemory_reservation_used. The sync process determines the ID. Please look up which target field names to use in the Freshservice API documentation.escape: This is used on field elements wheretarget="name". Some characters used in Device42 names aren't supported in Freshservice and need to be substituted. When creating a new task, you can set this totrue, but disable it if mismatching issues occur.
Use our InsightsAI chat under Analytics > InsightsAI to interpret DOQL query snippets quickly in the context of the Device42 data tables.
Additional Matching Criteria for Updating Existing Items
Some <task> elements in mapping.xml have a helper <matching> element for updating synced data that currently exists in Freshservice but may have slightly different name formats. For example, asset-type syncing tasks include the <matching> element to determine which query fields are used to match which asset attributes when trying to find a match. For example:
Click to expand the code block
<task enable="true" name="Devices" type="asset" description="Copy Servers from Device42 to Freshservice ...">
<!-- Device42 query -->
<matching>
<source-1
device42-id="device42_id"
name="name"
serial-number="serial_no"
uuid="uuid"
item-id="instance_id"
mac-address="snmp_device_mac_address"
imei-number="imei"
/>
</matching>
<mapping ...>
<!-- and so on... -->
Reupload the mapping.xml File
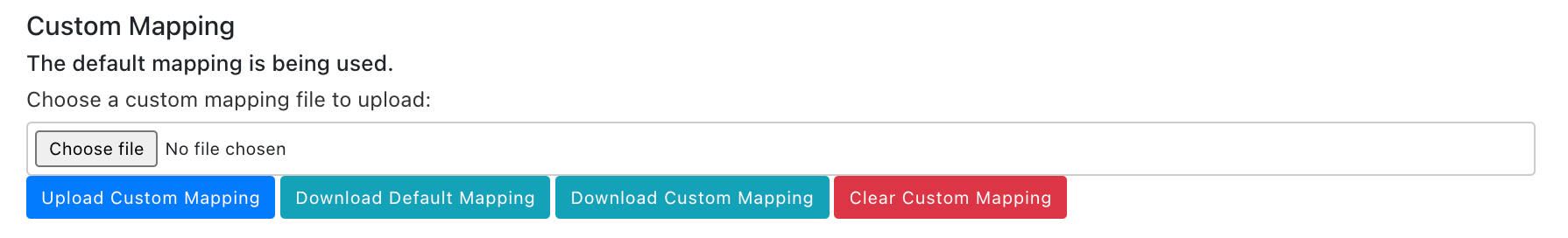
Save the file and reupload it to Freshservice, using the Upload Custom Mapping button in the Settings tab of the Configuration page.
The mapping.xml File Tasks
Use this table to look up the mapping tasks in the mapping.xml file.
Each <task> element has the following Freshservice type, description, and (d42_min_version and d42_max_version) version attributes.
For a quick look at all the valid Freshservice types, see the The <task> Element Attributes section above.
description= | type= | d42_min_version= | d42_max_version= |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copy Product info from Device42 to Freshservice | product | 16.19.00 | |
| Copy Product info from Device42 to Freshservice | product | 16.18.02 | |
| Copy Servers from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL v2 | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy Servers from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL v2 | asset | 16.19.00 | 19.03.99 |
| Copy Servers from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL v1 | asset | 16.18.02 | |
| Copy Softwares from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL | software | ||
| Create Software Install from Software In Use | software_installation | 16.19.00 | |
| Create Software Install from Software In Use | software_installation | 16.18.02 | |
| Create Relationship from Service Communication | asset_relationship | ||
| Create Relationship from Business Apps | asset_relationship | ||
| Copy Business Application from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 16.19.00 | |
| Copy Business Application from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 16.18.02 | |
| Create Relationship from Devices to Business Apps | asset_relationship | ||
| Copy contract info from Device42 to Freshservice | contract | ||
| Create association between asset and contract | contract_asset | ||
| Copy Software Licensing info from Device42 to Freshservice | contract | ||
| Create relationship between Host and Virtual Machine | asset_relationship | ||
| Create relationship between cluster and device | asset_relationship | ||
| Copy AWS ALB from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy AWS Subnet from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy AWS Security Group from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy AWS VPC from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy AWS RDS from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy AZURE Subnet from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy Azure Disk from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy Azure Security Group from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy Azure Subscription from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy Azure Application Gateway from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy AWS EBS from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy AWS Key Pair from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy AWS S3 from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy AWS Public IP from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy Azure VPC from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy GCP Subnet from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy GCP VPC from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy GCP Disk from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy GCP Firewall Rules from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy CPU Parts from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL | component | ||
| Copy RAM Parts from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL | component | ||
| Copy Network Adapter from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL | component | ||
| Copy Hard Disk Parts from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL | component | ||
| Copy Mount Point(Logical Drive) from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL | component | ||
| Copy Mount Point(Datastore) from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL | component | ||
| Copy Printer Input Parts from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL | component | ||
| Copy Printer Output Parts from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL | component | ||
| Copy Printer Marker Parts from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL | component | ||
| Copy Interface Component from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL | component | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy GCP LB from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy Azure Images from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy Azure Network Interface from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy AWS Network Interface from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy GCP Network Interface from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy Azure Resource Group from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy AWS Image from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy Azure Public IP from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | 19.04.99 |
| Copy Azure Public IP from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.05.00 | |
| Copy GCP Image from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy GCP BigQuery Table from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy Azure Key Vault from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.00 | |
| Copy VMware VCenter Resource Pool from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy VMware VCenter Network from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy VMware VCenter Disk from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy VMware VCenter Datastore from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy VMware VCenter Datacenter from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy AWS K8 Pod from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy AWS K8s Namespace from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy AWS K8s Deployment from Device42 to Deployment | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy AWS K8s Service from Device42 to Service | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy AWS K8s Daemon Set from Device42 to Daemon Set | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy AWS K8s Replica Set from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy AWS K8s Cron Job from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy GCP Public IP from Device42 to Freshservice | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy AWS K8s Config Map from Device42 to Config Map | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Copy AWS K8s Stateful Set from Device42 to Stateful Set | asset | 19.04.10 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Public IP to Azure Subscription | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Network Interface to Azure Subscription | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Subnet to Azure Subscription | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Public IP to Azure Resource Group | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Network Interface to Azure Resource Group | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Subnet to Azure Resource Group | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Resources to Azure Subscription | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Resources to Azure Resource Group | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Image to Azure VM | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Disk to Azure VM | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Network Interface to Azure VM | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Public IP to Azure VM | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure VM to Azure Subnet | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure VM to Azure Subscription | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure VM to Azure Resource Group | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure VM ( netport ) to Azure Security Group | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure VM ( subnet ) to Azure Security Group | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Network Interface to Azure Subnet | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from Azure Public IP to Azure Network Interface | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS VM to AWS Disk | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS VM to AWS Network | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS Network Interface to AWS Public IP | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS Public IP to AWS VM | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS VM to AWS Application LB | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS VM to AWS Key Pair | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS VM to AWS Subnet | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS VM to AWS Security Group | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS Subnet to AWS Network | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS RDS to AWS Subnet | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS Image to AWS VM | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS K8s Namespace To AWS K8s Pods | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS K8s Node To AWS K8s Pods | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS K8s Daemon Set To AWS K8s Config Map | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from AWS K8s Deployment To AWS K8s Replica Set | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from GCP Network Interface to GCP Public IP | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from GCP Network Interface to GCP VM | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from GCP Public IP to GCP VM | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from GCP Disk to GCP VM | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from GCP Image to GCP VM | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from GCP VM to GCP Security Group | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from GCP Subnet to GCP VM | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Create Relationship from GCP Subnet to GCP Network Interface | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Datacenter to Datastore relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Datacenter to Virtual Machine relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Datacenter to Host relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Datacenter to Network relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Datastore to Host relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Datastore to Virtual Machine relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Host to Virtual Machine relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Network to Host relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Network to Virtual Machine relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Resource Pool to Virtual Machine relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Resource Pool to Resource Pool relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Sync Device42 VMWare Virtual Machine to Disk relationship | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 | |
| Delete assets from Freshservice that do not exist in Device42 | asset | ||
| Delete asset relationships from Freshservice that do not exist in Device42 | asset_relationship | 19.04.99 | |
| Delete asset relationships from Freshservice that do not exist in Device42 | asset_relationship | 19.05.00 |
Syncing to Custom Field Names in Freshservice
When creating a custom field in Freshservice that corresponds with a Device42 field, you need to set the target field in the XML file to match Freshservice naming conventions. Verify the correct field names via the Freshservice API endpoint before running the sync.
Field names in Freshservice are automatically generated according to the following conventions:
- Using lowercase characters
- Replacing spaces with underscores
- Appending the asset type ID to the end of the field name (this suffix provides a means of verifying the field name, and is visible in the Freshservice interface but not required in the XML file)
For example, the custom field with the Used By label in Freshservice is represented internally as used_by_12345467, but you'll use used_by in the mapping.xml file.
Use the following steps to verify that the field name is correct:
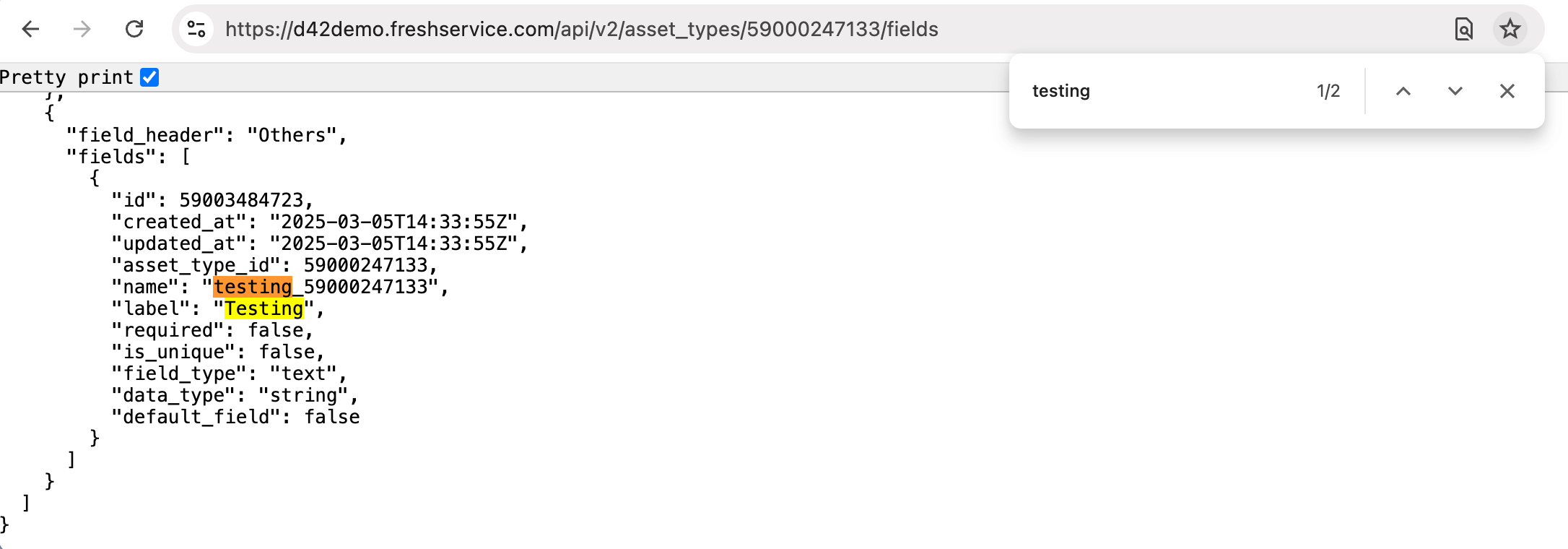
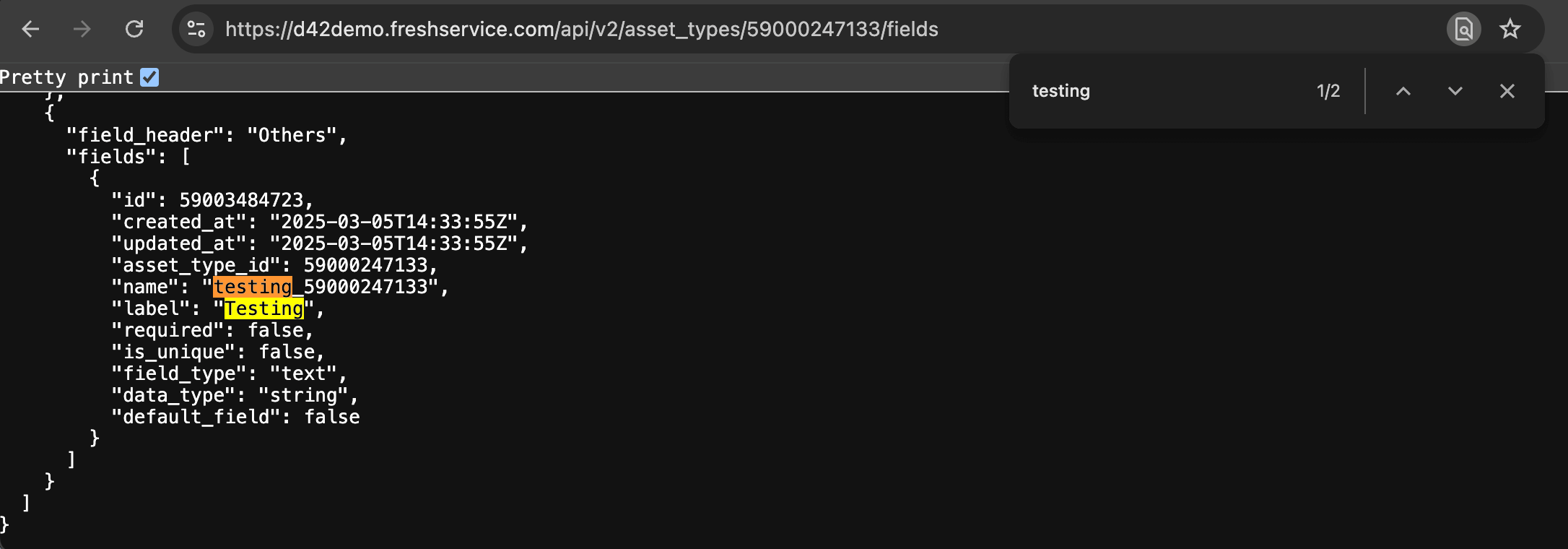
- Navigate to the edit page for the asset type under the Freshservice Settings (if you need help locating the asset type's edit page, consult the Freshservice Assets page). Copy the asset type ID, which appears in the URL of the edit page.
- Open your browser to access the API endpoint. Replace
<Freshservice-Instance>with your Freshservice instance and<Asset-Type-ID>with the asset type ID from the URL.
<Freshservice-Instance>/api/v2/asset_types/<Asset-Type-ID>/fields
-
Search the returned JSON for the field label you are interested in to verify the field name.
Control Updates
Control whether changes made to Device42 asset types and contracts will update the corresponding items in Freshservice during sync.
Control Asset Type Updates
When you customize asset type mappings in the mapping.xml file, you can control whether your changes update existing assets in Freshservice. See Asset-Type Update Behavior for more details about the Update asset type for existing assets setting.
Control Contract Updates
You can control whether Device42 contract updates sync to Freshservice. This applies to contract tasks with name="Contracts" and name="Software Licensing".
Add the skip-update attribute to the <task> element:
- If
skip-update="false", contract updates in Device42 will be updated in Freshservice (if the contract exists). - If
skip-update="true", the contracts are created in Freshservice but will not be updated after initial creation.
If the attribute is absent from the task element, the contracts in Freshservice will not be updated.
-
For example, add
skip-update="false"to enable contract updates in mapping.xml v4.0: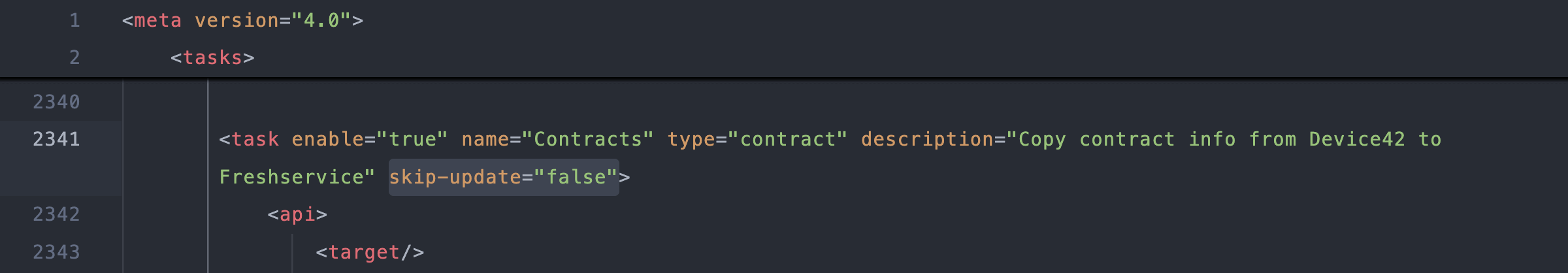
<task enable="true" name="Contracts" type="contract" description="Copy contract info from Device42 to Freshservice" skip-update="false"> -
For example, add
skip-update="false"to enable contract updates for software licensing in mapping.xml v4.0: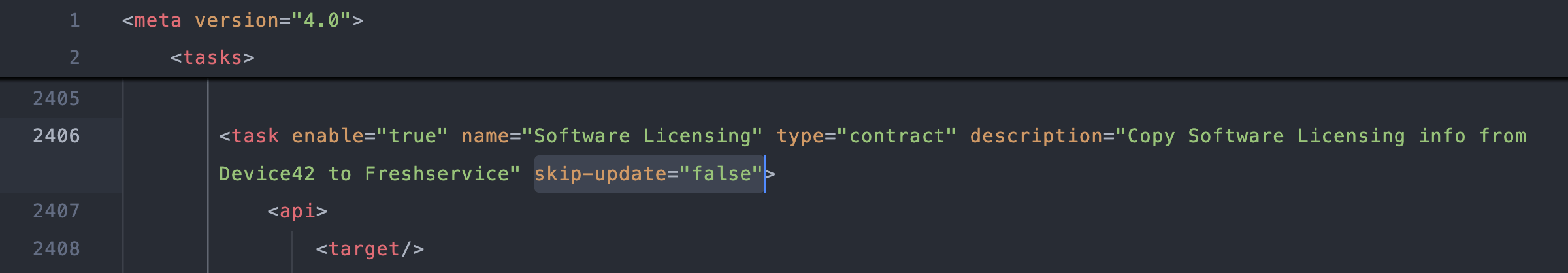
<task enable="true" name="Software Licensing" type="contract" description="Copy Software Licensing info from Device42 to Freshservice" skip-update="false">
Data Mapping FAQs
This section answers some common questions about data mapping between Device42 and Freshservice. We're actively improving the integration and this documentation. Please contact support if you have technical questions, and use the Page Feedback button at the top of this page to leave feedback about the documentation.
Syncing a Custom Device42 Field to Freshservice (Overview)
To add a custom field to Freshservice, modify the mapping.xml file and reupload it. You'll need to modify the <task> that's most closely related to the custom field you want to create.
Find an existing task with a query related to the field you want to map to Freshservice. For example, if you want to add a custom field about servers, inspect and modify the Copy Servers from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL v2 task. Add new <field> elements (one for Device42 and one for Freshservice) to the <mapping> element of the <task>.
Depending on the custom field you want to add, you may have to modify the DOQL query in the <resource> element to fetch that data from Device42. If needed, use the InsightsAI chat under Analytics > InsightsAI to help you find the tables and fields you need to query.
If you can't find a task related to your custom field, you can create a new <task> element in the mapping.xml file.
How Do I Sync a Device42 Custom Field to Freshservice? (Detailed Steps)
-
First, create and add the new custom field in Device42. You can create a custom field for any CI type using either the UI or the API. In this example, we'll use the UI to create a custom field called
Namein the Devices section of Custom Fields in the Main Appliance.
-
You should now see the custom field available for all device types. Navigate to the details page for one of your devices and set a value for the custom field. The example below shows the new Name field in the Custom Fields section for a Server device named
centos-884163.device42.testing.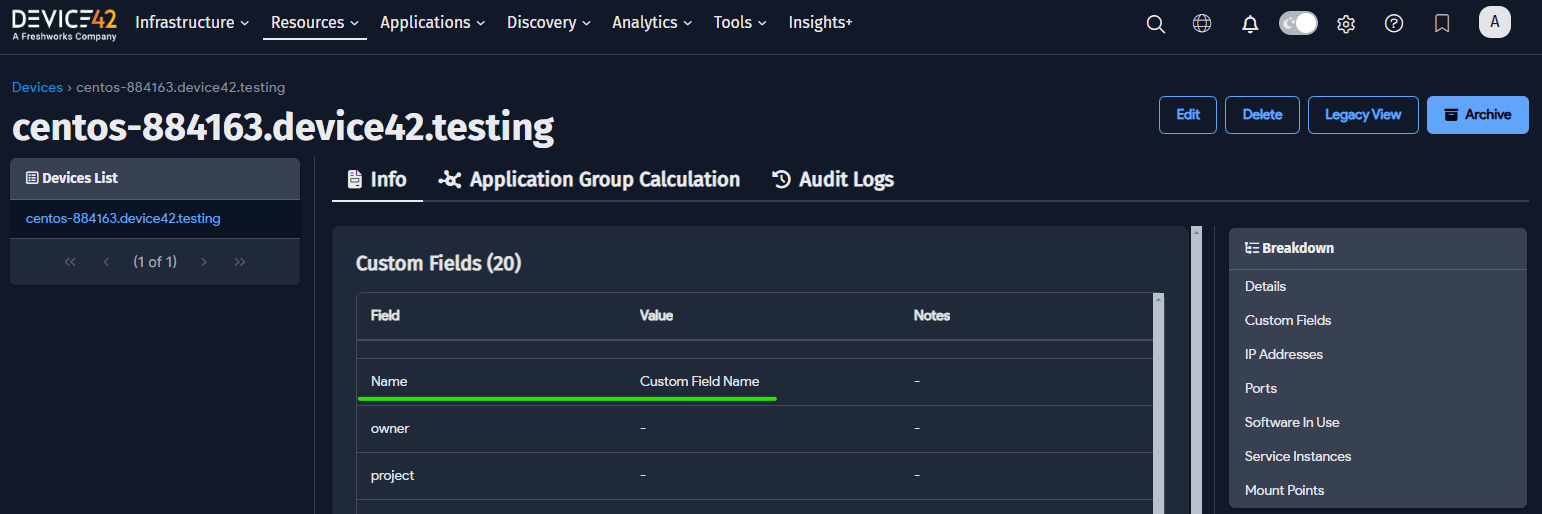
-
Next, add the new custom field to the
mapping.xmlfile. Change the DOQL query in theCopy Servers from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL v2task to map the new custom field to Freshservice. (There are normally three types of task with differentd42_min_versionparameters; update the DOQL for each task type, in case you're using older or different versions.)Click to expand the code block
-- The DOQL snippet pictured above:
SELECT
-- ... existing fields ...
view_device_v2.details->>'used by' AS used_by,
cf."Name" as cf_name
FROM
view_device_v2
LEFT JOIN
view_hardware_v2
ON view_device_v2.hardware_fk = view_hardware_v2.hardware_pk
LEFT JOIN
view_device_custom_fields_flat_v2 cf
ON view_device_v2.device_pk = cf.device_fk
LEFT JOIN
network_ip
ON view_device_v2.device_pk = network_ip.device_fk
LEFT JOIN
network_hw
ON view_device_v2.device_pk = network_hw.device_fkExplanation of the DOQL changes:
- The custom field
Nameis added to theSELECTstatement. Syntax notes: You need to escape the double quotes (") by using the"e;HTML entity. The greater-than (>) and less-than (<) symbols also need to be escaped. The equality operator works without special quotes. Please check existing DOQL for examples. - A
LEFT JOINis added because all custom fields in Device42 are stored in the{CI name}_custom_fieldsviews. For example, the Devices CI is stored inview_device_custom_fields_flat_v2.
- The custom field
-
Now it's time to map the custom field to Freshservice. Add a new
<field>element in the<mapping>tag section of the XML file. You'll need to keep Freshservice open and follow the next step to get the exact Freshservice values to use in the new<field>element below.<!-- Custom Fields -->
<field resource="cf_name" source-type="string" target="cf_name" target-type="string"
target-header="Server" not-null="true" set-space="true" min-length="1" max-length="255"/>
<!-- Custom Fields -->Explanation of the XML changes:
- The
resource=argument is set to the name of the custom field in Freshservice. The custom field name in this example iscf_name, which follows the Freshservice convention of using the display name (label) in snake case for the field name, occasionally with the ID of the asset type as a suffix. (See Syncing to Custom Field Names in Freshservice for more details). - The
target-header=argument is set to the name of the CI properties section of the heading name under which the custom field will appear in Freshservice. In this case,target-header="Server"refers to the "Server Properties" heading — there's no need to use "Properties", as it's automatically added to every asset type.
- The
-
In the Freshservice Asset Types & Fields section, find the asset field to which you are mapping the Device42 custom field. In this case, our example device is of the Server type, so we find it under Hardware > Computer > Server.
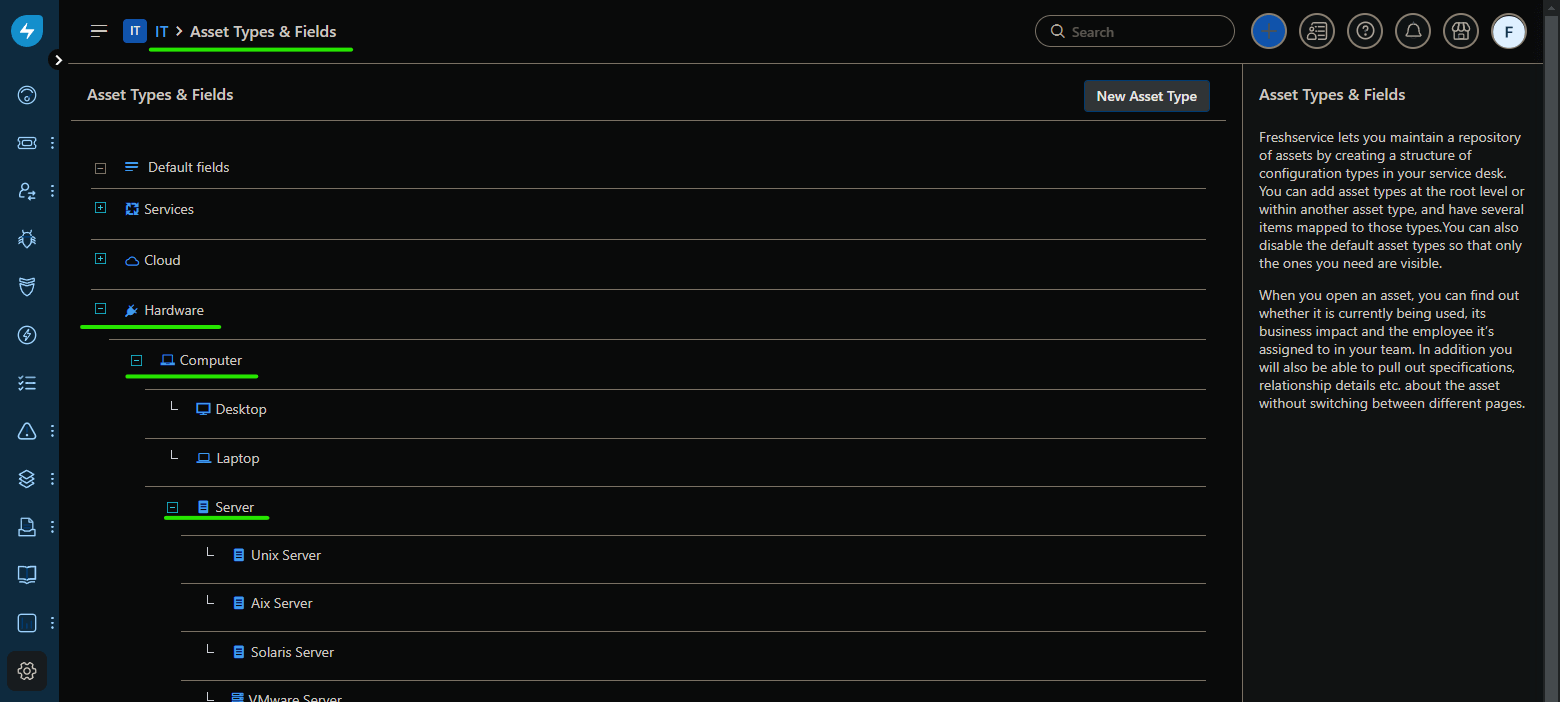
-
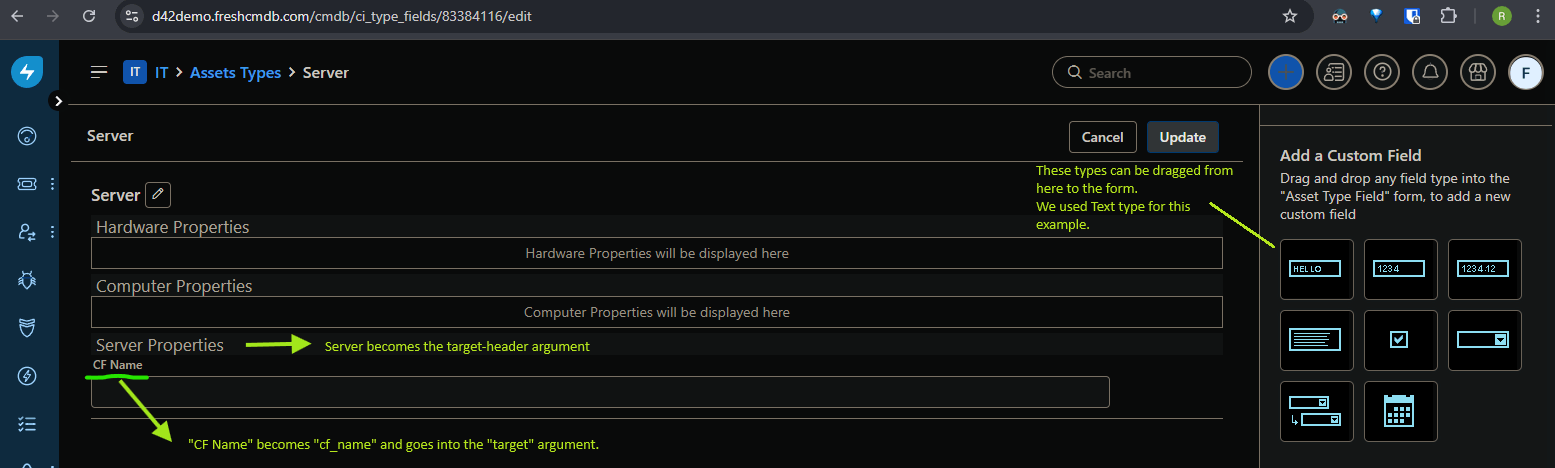
Now, edit the asset type by clicking on the pencil icon all the way on the right, as highlighted below in the screenshot of the Server asset type.
Set the 'target' directive to the Device42 field you are mapping to Freshservice.
-
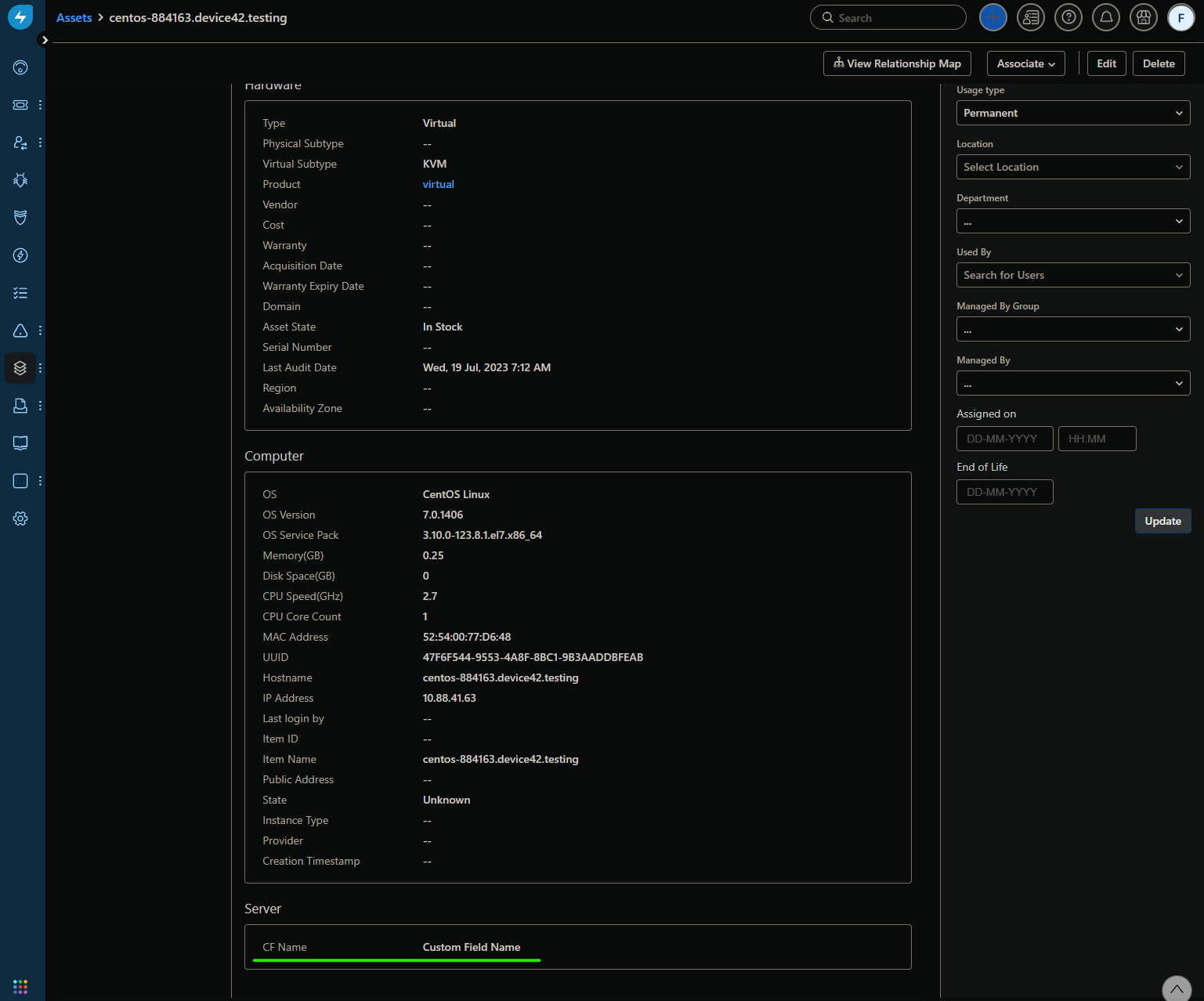
Finally, run the sync in Freshservice's Device42 integration app. You should end up with the custom field you created and set in Device42:
How Do I Sync a Device42 Field to a Custom Contract Field in Freshservice?
You can map existing Device42 contract data to custom fields in Freshservice contracts. This allows you to sync Device42 contract information (either standard fields or existing custom fields) to new custom fields you create in Freshservice.
Prerequisites:
- You need to upload a custom mapping file in Freshservice to make these changes.
- For updating contracts to work, you need to add
skip-update="false"to contract tasks. See Control Contract Updates for details.
In Freshservice:
-
Create custom fields. Go to Settings > Contract Types in Freshservice and add custom fields to receive the Device42 contract data.
-
Log in to your Freshservice instance.
-
Click the ellipsis menu (bottom of left panel) and select Admin.
-
In the search bar, type
contract type. -
Click the edit icon to the right of the contract type name.
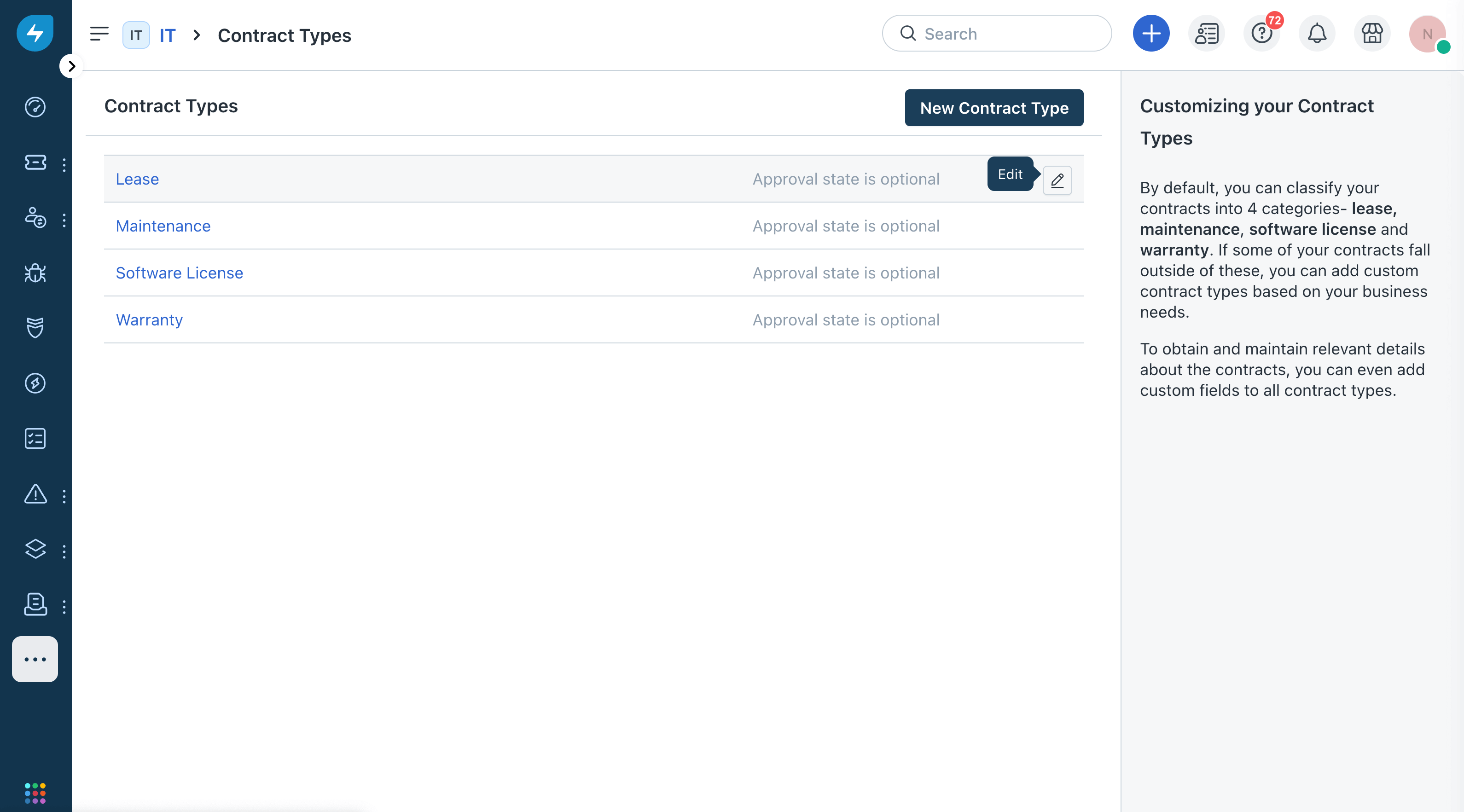
-
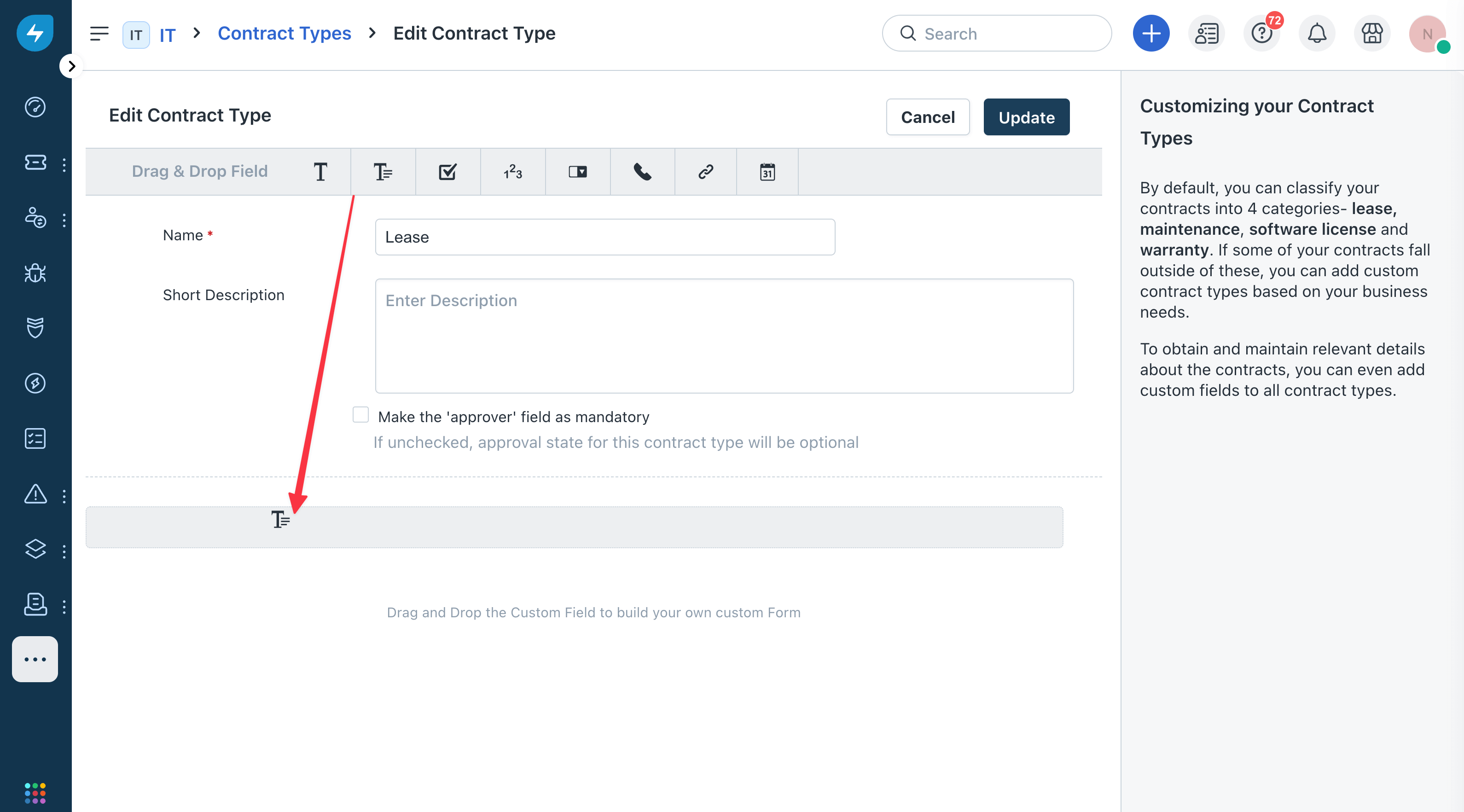
Drag one of the data type buttons below the last input on the form to add the custom field. Freshservice supports the following custom field types: Single Line Text, Multi Line Text, Checkbox, Number, Dropdown, Phone Number, URL, and Date.
-
Label the custom field and set whether a value is required and whether the field should appear on renewal forms. If you don't send a value to the required field, you will get an error.
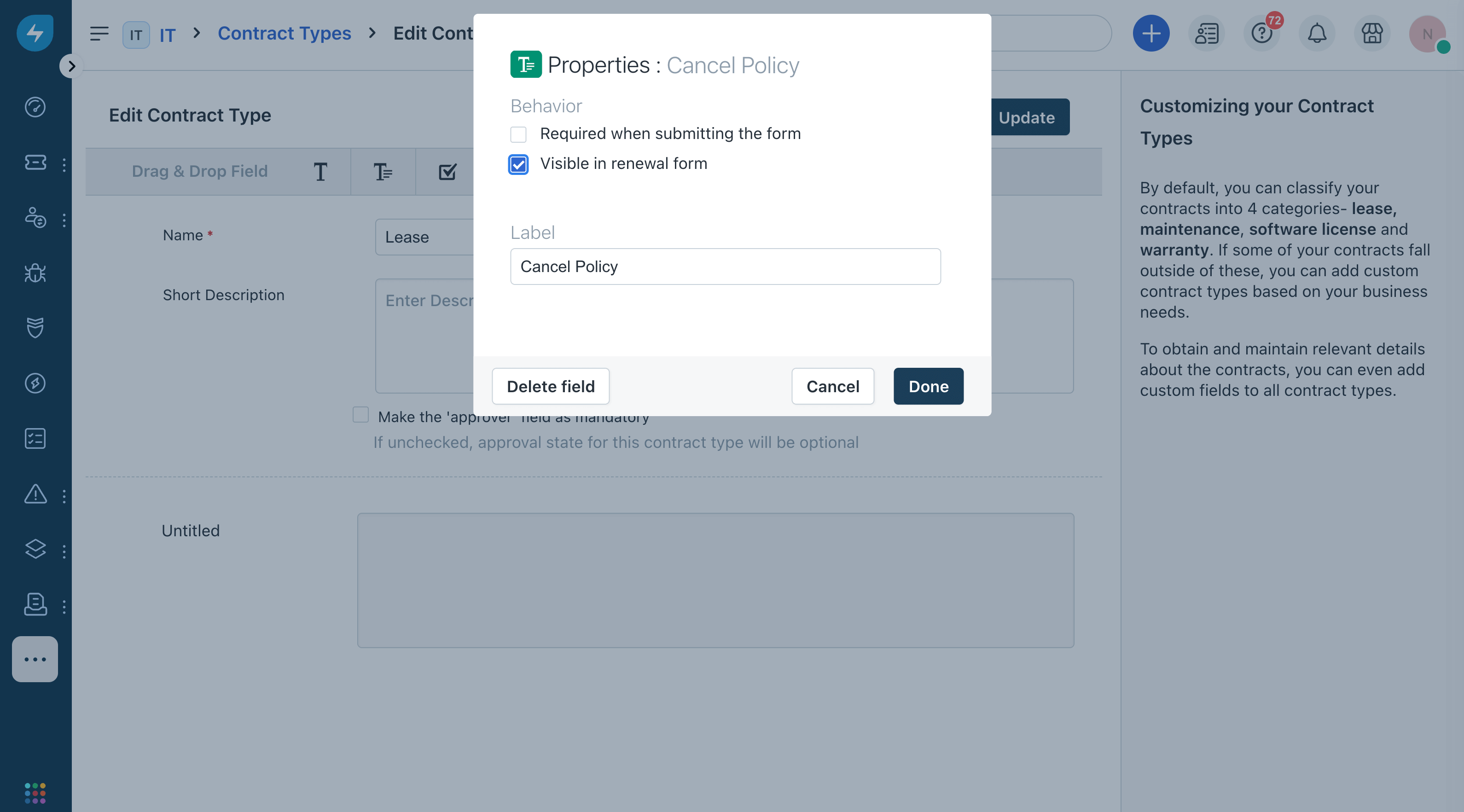
You can create custom fields that exist in one contract type but not others, allowing you to customize each contract type independently.
-
In mapping.xml:
-
Update the DOQL queries in the contract type tasks to select data that you will enter in the contract custom fields. For example, add the Cancel Policy field,
pli.cancel_policy, from the purchase line item:Click to expand the code block
<task enable="true" name="Contracts" type="contract" description="Copy contract info from Device42 to Freshservice" skip-update="false">
<api>
<target/>
<resource
doql="
select plid.device_name, v.name vendor_name,
v.name || '-' || p.order_no || '-' || pli.line_no as name,
case
WHEN lower(pli.contract_type_name) = 'warranty' THEN 'Warranty'
WHEN lower(pli.contract_type_name) in ('base', 'upgrade') and lower(v.name) in ('ibm', 'lenovo') THEN 'Warranty'
WHEN lower(pli.contract_type_name) = 'lease' THEN 'Lease'
ELSE 'Maintenance'
end as contract_type_name,
pli.contract_id, pli.cost, pli.start_date, pli.end_date, pli.cancel_policy
from view_purchaselineitems_to_devices_v1 plid
inner join view_purchaselineitem_v1 pli on plid.purchaselineitem_fk = pli.purchaselineitem_pk
inner join view_purchase_v1 p on pli.purchase_fk = p.purchase_pk
inner join view_vendor_v1 v on p.vendor_fk = v.vendor_pk
where lower(pli.line_type) = 'contract' and pli.start_date is not null and pli.end_date is not nulltipUse the ERD Diagram located under the question mark icon in Device42 to look up Device42 tables and fields for the DOQL query.
-
Add a field mapping to map the field from the DOQL query to the Freshservice contract custom field. For example:
<field resource="cancel_policy" source-type="string" target="cf_cancel_policy" target-type="string"/>The Freshservice custom field
targetiscf_cancel_policy, following this pattern:cf_[lowercase with underscores replacing spaces]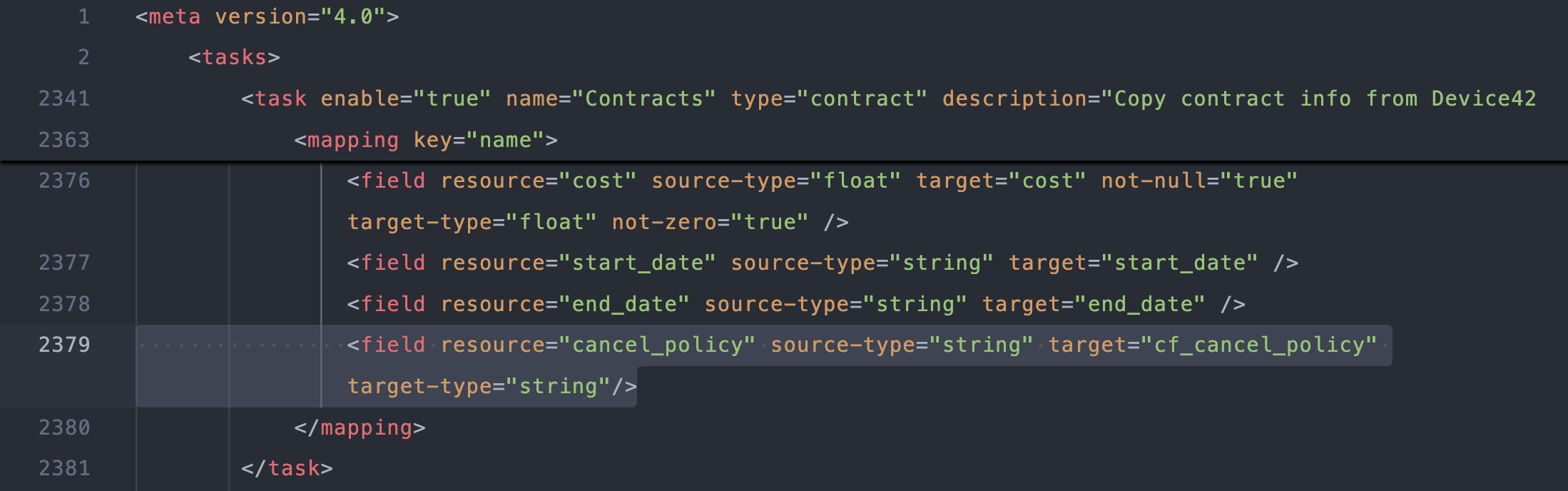
In Freshservice:
-
Reupload
mapping.xmlto Freshservice using the Upload Custom Mapping button. -
Verify that your custom field (
cf_cancel_policy) appears in the Data Mapping Chart table.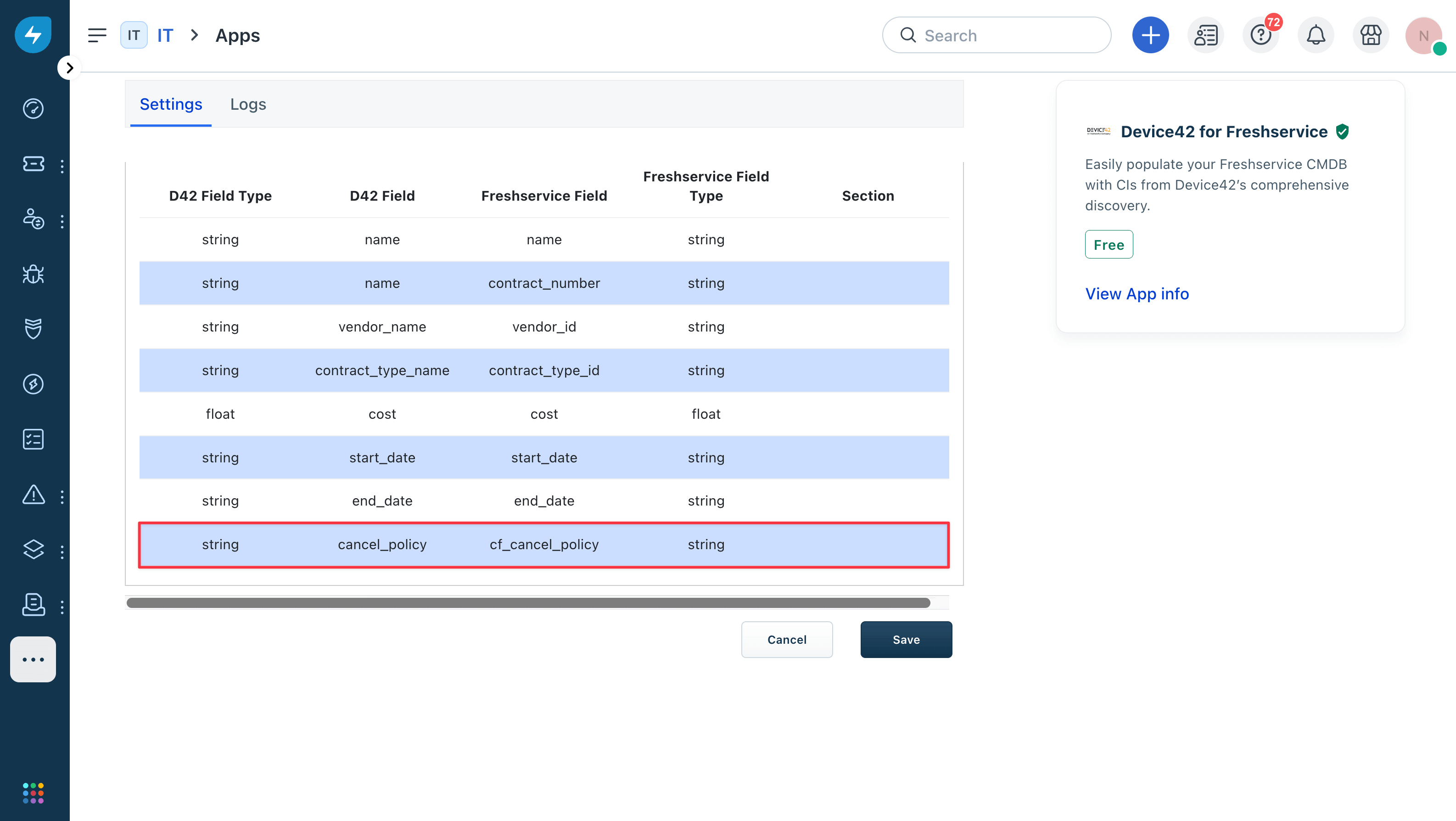
-
Run the sync.
How Do I Change an Existing Mapping to Pull From a Different Device42 Field?
In the <task> that corresponds with the Device42 field you want to pull from, change the resource and target attributes of the <field> elements in the <mapping> element.
Refer to The <task> Element Elements section for a description of the <field> element attributes.
How Do I Prevent a Relationship Between Two Device42 Asset Types From Syncing to Freshservice?
You need to modify two <task> elements within the mapping.xml file.
-
In your
mapping.xmlfile, find the<task>element that creates the relationship between the asset types you want to disable. Set theenableattribute fromtruetofalseto disable the relationship. For example:<task enable="false" name="Create relationship between cluster and device" type="asset_relationship" description="Create relationship between cluster and device"> -
Remove the corresponding relationship query from the last
<task>with the attribute<description="Delete asset relationships from Freshservice that do not exist in Device42">, which is nested in thedescription="D42 AWS ALB to Freshservice AWS ALB"><task>element.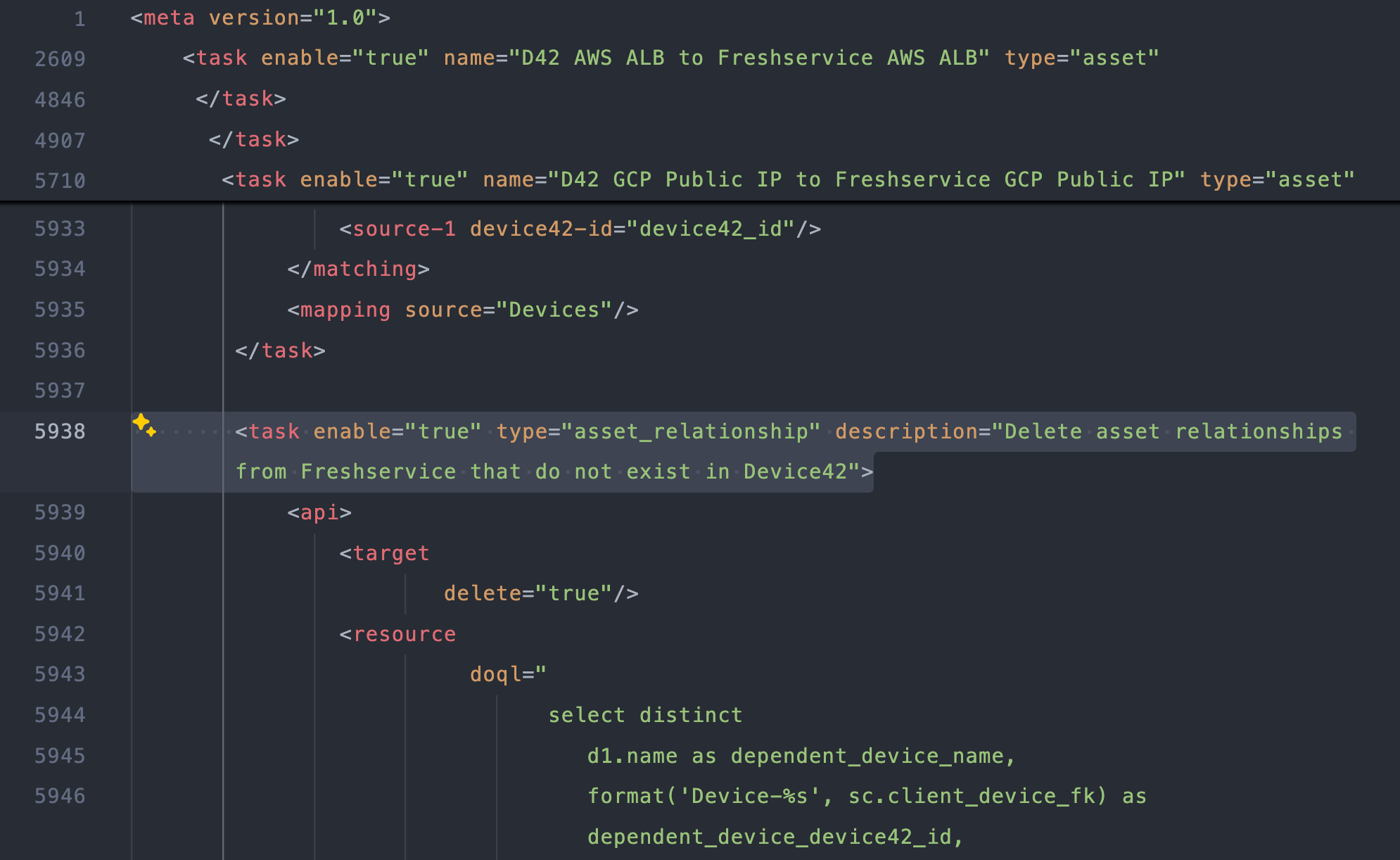
For example, if you want to disable the relationship between clusters and devices, remove the following query snippet from the
<resource doql="attribute:
Click to expand the code block
<task enable="true" type="asset_relationship" description="Delete asset relationships from Freshservice that do not exist in Device42">
<api>
<target
delete="true"/>
<resource
doql="
<!-- ... other queries -->
<!-- remove or comment out this cluster and device relationship query -->
select
dc.name as dependent_device_name,
format('Device-%s', dc.device_pk) as dependent_device_device42_id,
'Member of' as downstream_relationship,
dp.name as dependency_device_name,
format('Device-%s', dp.device_pk) as dependency_device_device42_id,
'Includes' as upstream_relationship
from view_devices_in_cluster_v1 dic
inner join view_device_v2 dp on dic.parent_device_fk = dp.device_pk
inner join view_device_v2 dc on dic.child_device_fk = dc.device_pk
where lower(dp.type) = 'cluster'
"
/>
</api>
- Save the file and reupload it to Freshservice with the Upload Custom Mapping button.
How Do I Troubleshoot Data Mapping and Syncing Issues?
From Freshservice, go to Admin, search for apps, and click Manage Apps. Find the Device42 for Freshservice app, open the Settings dropdown, and select Edit settings. Under the Schedule Synchronization, click the Sync History button and click on a row to view details of the errors.
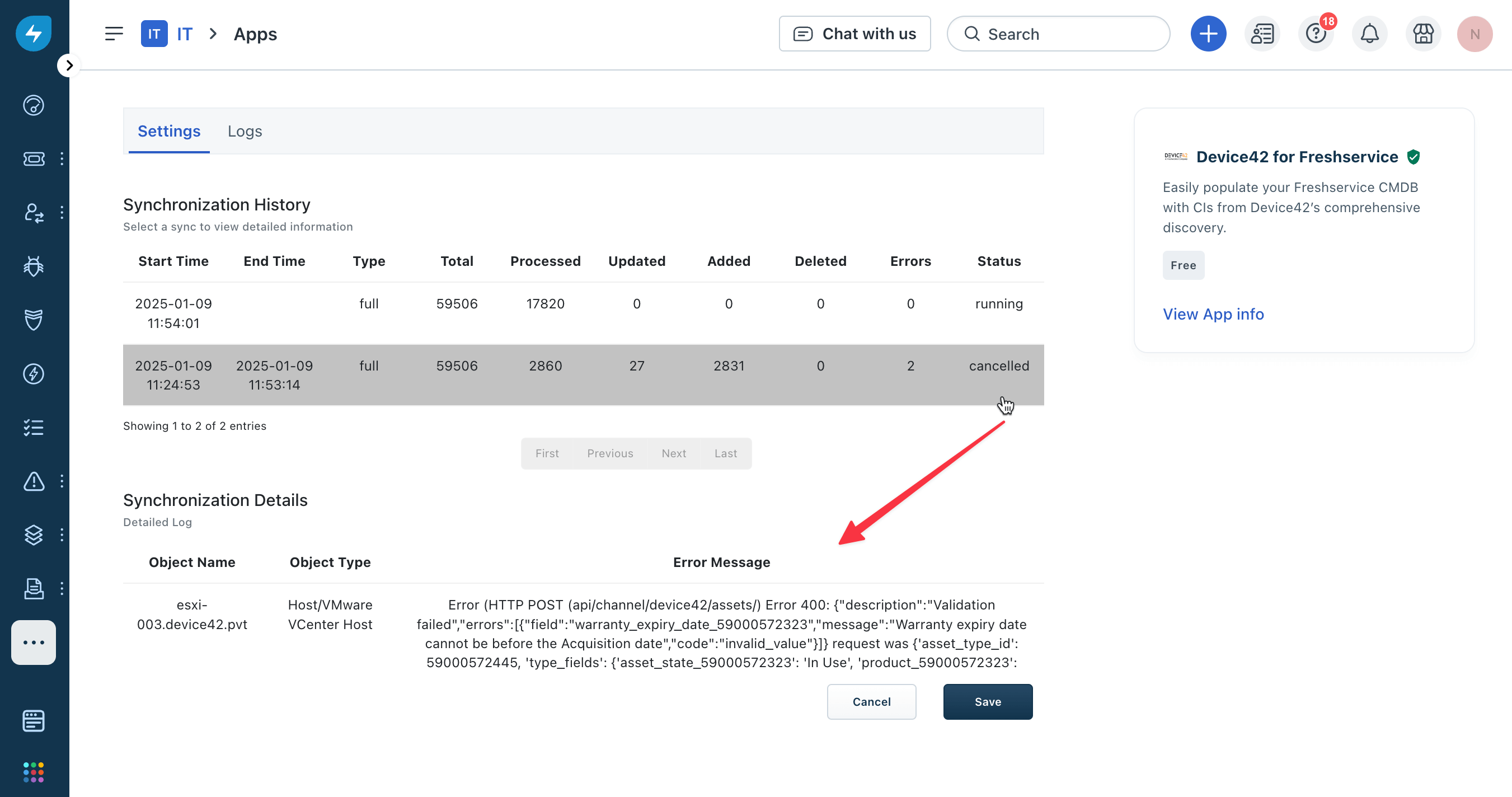
To download the full logs, scroll down and click the Download Full Log button in the lower-left corner of the text area.
Examples of Changing the mapping.xml File for Specific Use Cases
This section provides specific examples of how to edit the mapping.xml file to change the data synced from Device42 to Freshservice.
The line estimates in the examples are based on the default version 1.0 of the mapping.xml file and won't match your file exactly if you've customized the sync or used an updated version.
Example 1: How Can I Stop the Sync From Importing Contracts From Device42 to Freshservice?
In the mapping.xml file, do a text search for tasks containing the word contract in their description attribute. You can also search for contract-related tasks in The mapping.xml File Tasks table.
Set the enable attribute to false on those <task> elements:
-
Find the task with the description
Copy contract info from Device42 to Freshservice(around line2372):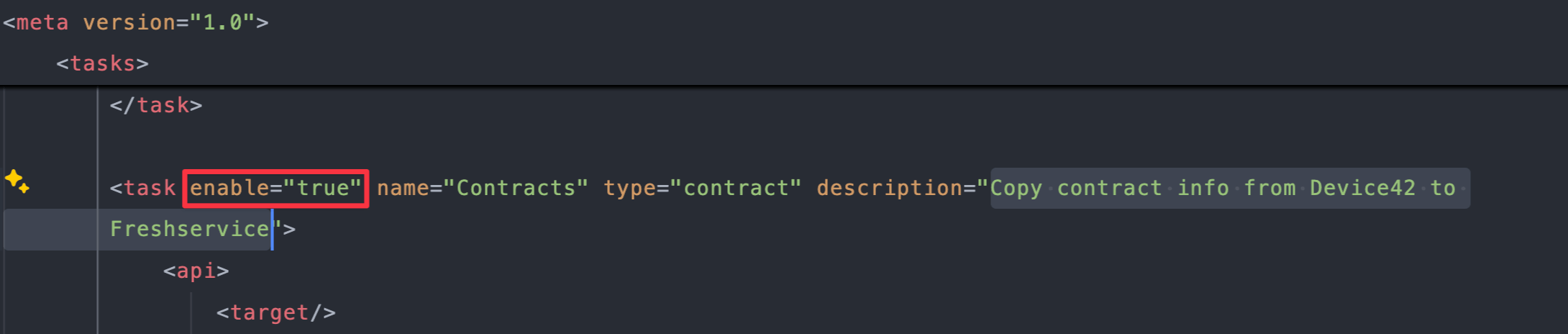
Change
enable="true"toenable="false":<task enable="false" name="Copy contract info from Device42 to Freshservice" type="contract" description="Copy contract info from Device42 to Freshservice"> -
Find the
Create association between asset and contracttask (around line2413):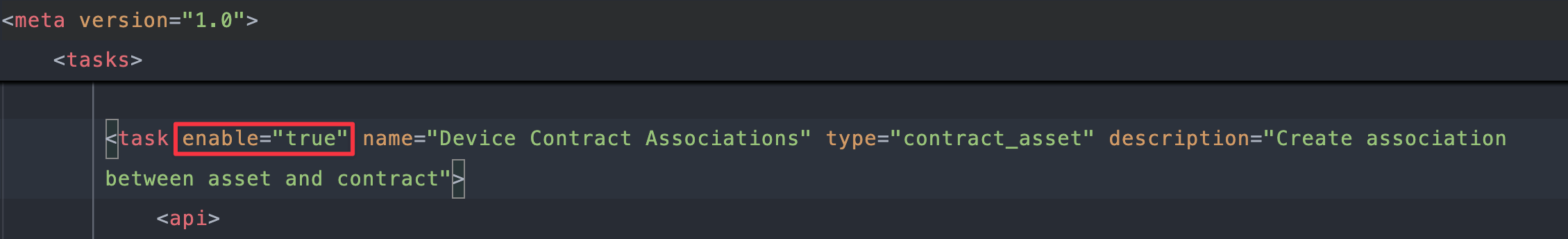
Change
enable="true"toenable="false":<task enable="false" name="Device Contract Associations" type="contract_asset" description="Create association between asset and contract"> -
If you want to prevent software licensing from being synced, find the
Copy Software Licensing info from Device42 to Freshservicetask (around line2437):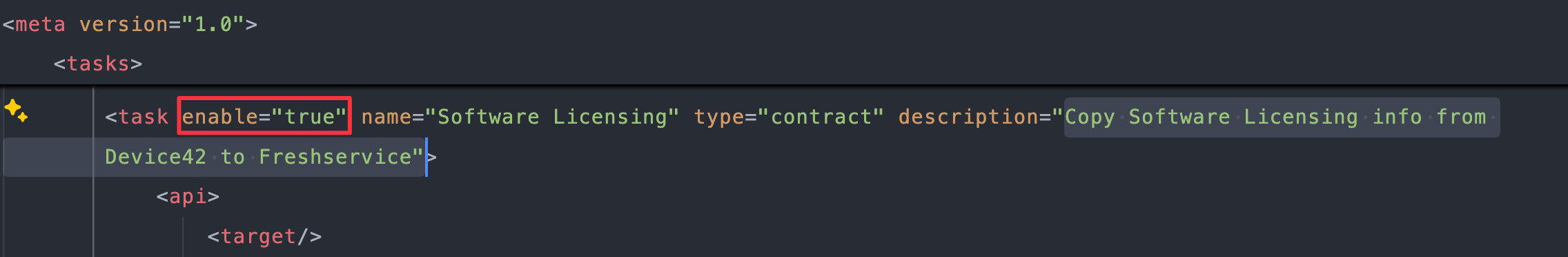
Change
enable="true"toenable="false":<task enable="false" name="Software Licensing" type="contract" description="Copy Software Licensing info from Device42 to Freshservice"> -
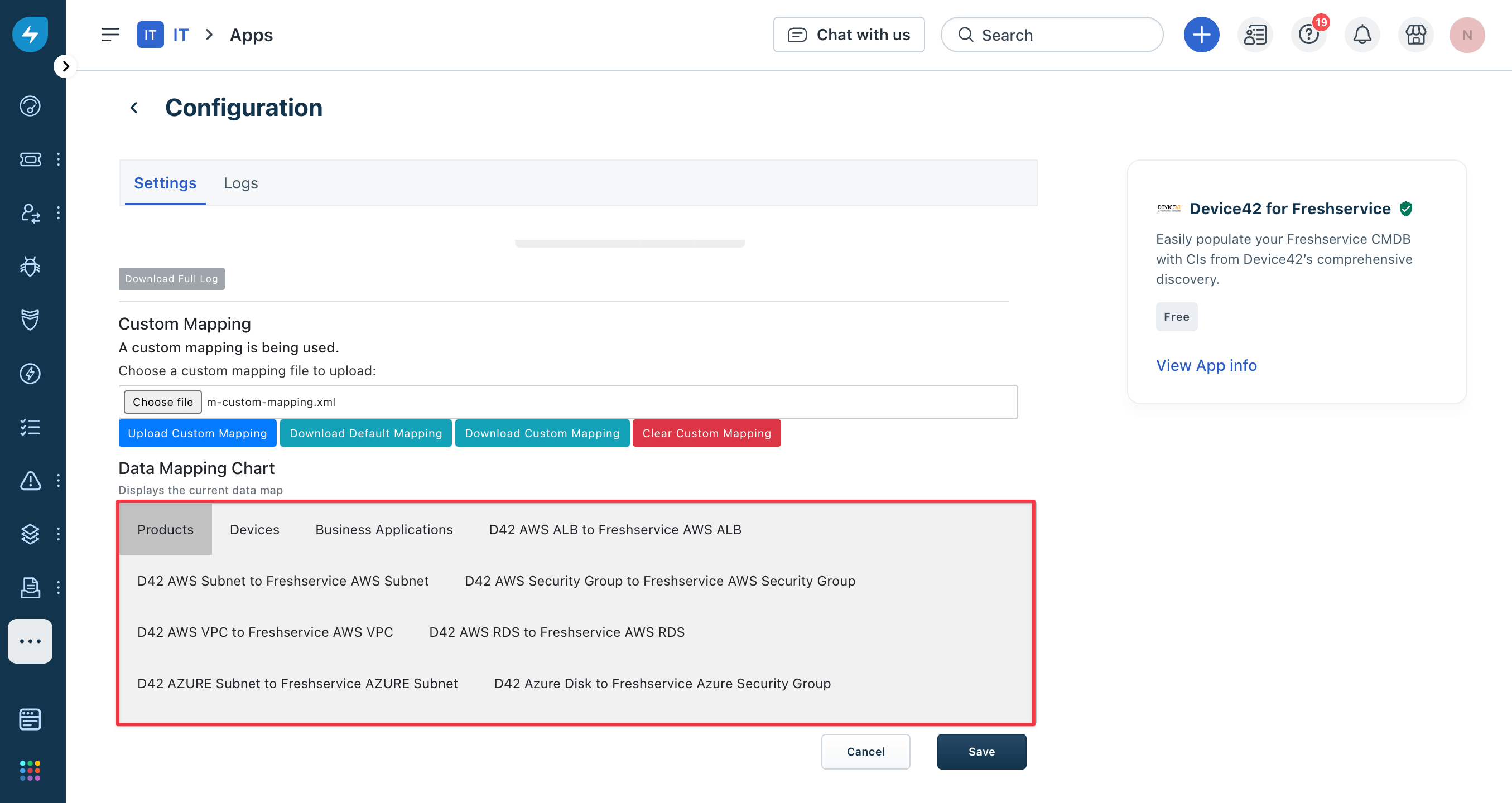
Save the file and reupload it to Freshservice using the Upload Custom Mapping button. The Contracts option will no longer appear in the Data Mapping Chart box
-
Run a partial sync to confirm that contract items are no longer being synced, or wait until the scheduled sync runs.
Example 2: How Do I Prevent Software Imports From Syncing to Freshservice?
In the mapping.xml file, do a text search for tasks that contain the word software in their description attribute. You can also search for contract-related tasks in the The mapping.xml File Tasks table.
Set the enable attribute to false on those <task> elements:
-
Find the task with the description
Copy Softwares from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL(around line2087).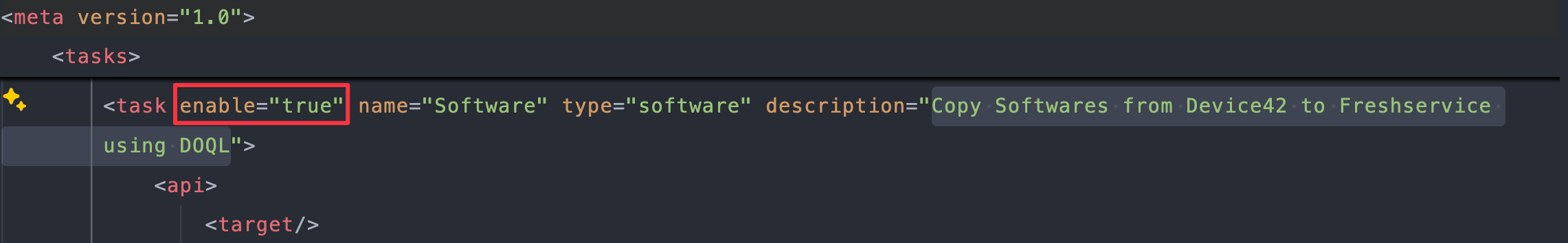
Change
enable="true"toenable="false":<task enable="false" name="Software" type="software" description="Copy Softwares from Device42 to Freshservice using DOQL"> -
There are two
Create Software Install from Software In Usetasks; one with ad42_min_versionattribute and one with ad42_max_version. Set theenableattribute tofalseon both of them:- The first task is around line
2102:
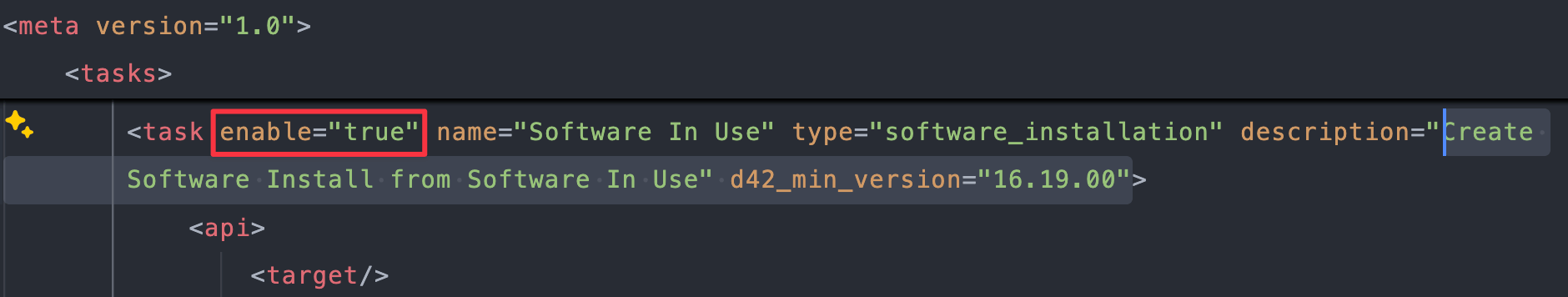
Change
enable="true"toenable="false":<task enable="false" name="Software In Use" type="software_installation" description="Create Software Install from Software In Use" d42_min_version="16.19.00">- The second task is around line
2172:
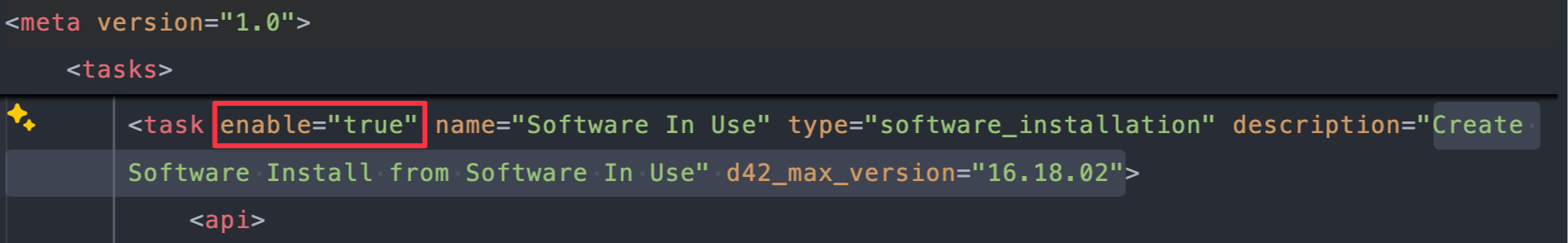
Change
enable="true"toenable="false":<task enable="false" name="Software In Use" type="software_installation" description="Create Software Install from Software In Use" d42_max_version="16.18.02"> - The first task is around line
-
Software licensing from Device42 syncs to
contractin Freshservice. Find and disable theCopy Software Licensing info from Device42 to Freshservicetask (around line2437):
Change
enable="true"toenable="false":<task enable="false" name="Software Licensing" type="contract" description="Copy Software Licensing info from Device42 to Freshservice"> -
Save the file and reupload it to Freshservice with the Upload Custom Mapping button.
-
Run a partial sync to confirm that software items are no longer being synced, or wait until the scheduled sync runs.
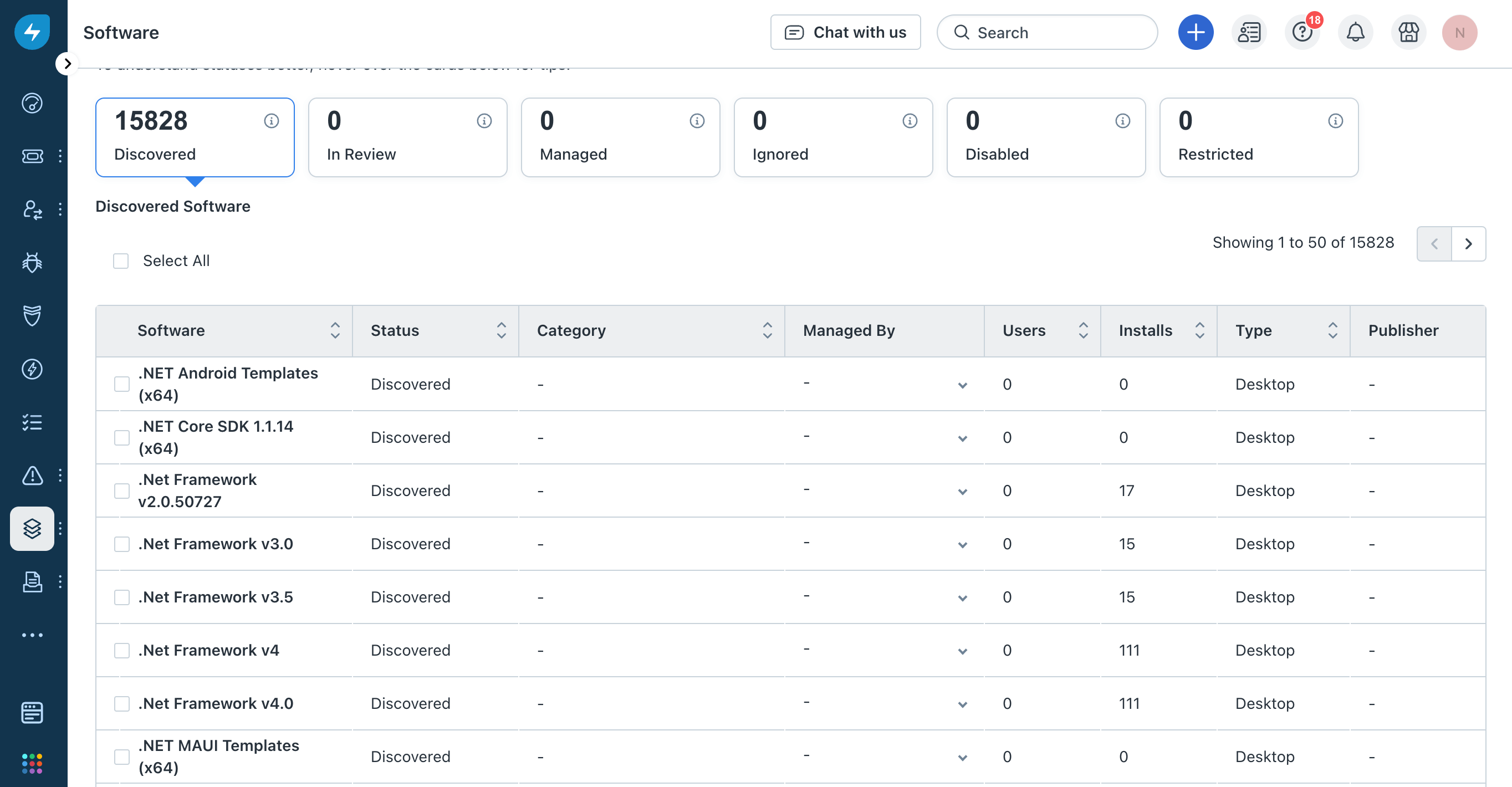
- Go to Assets > Software in the integration app. The page is populated before you disable software imports:
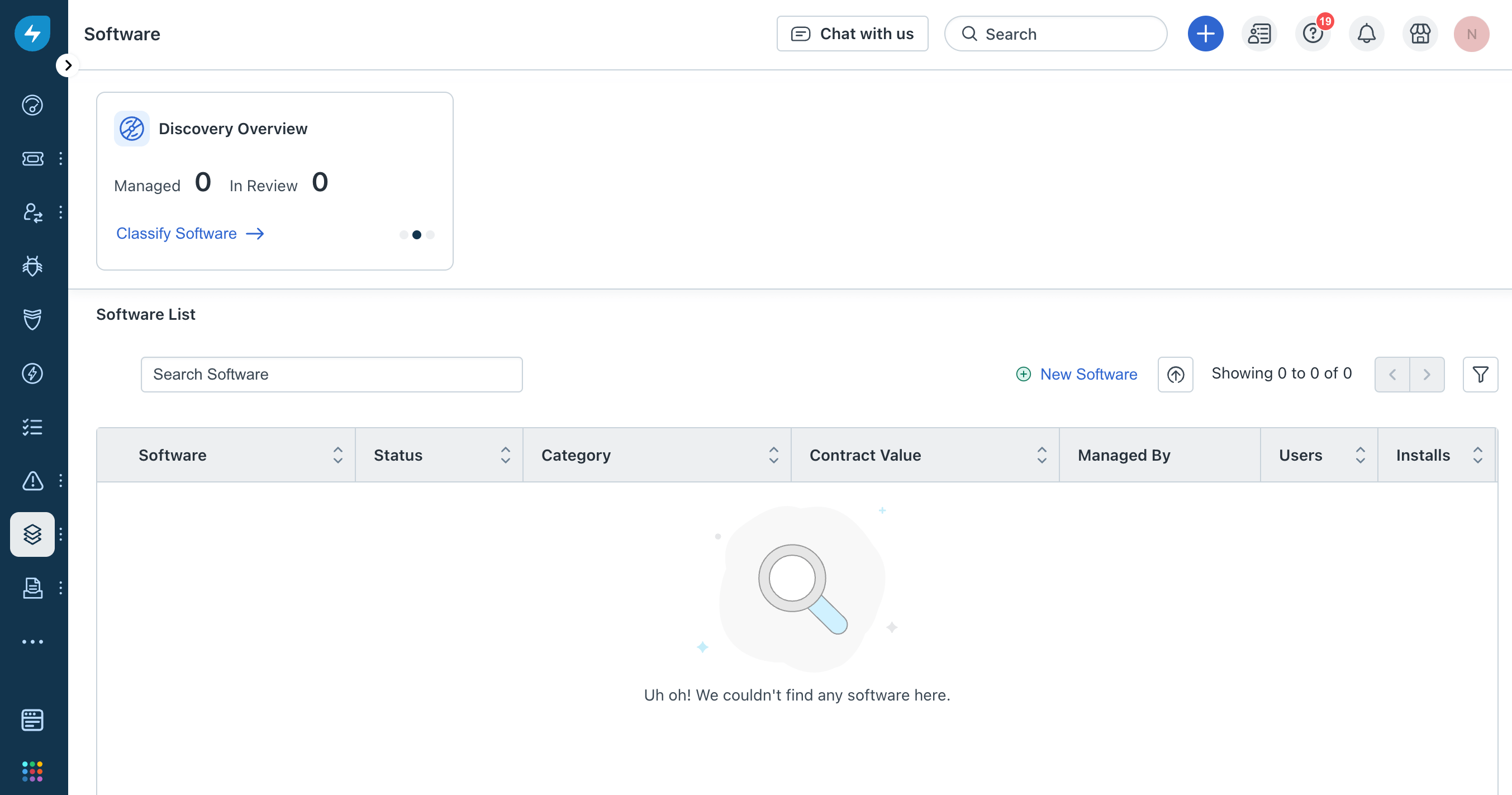
- After you've disabled software imports, the page will be empty:
Example 3: How To Ensure Device42 Correctly Updates the Hardware asset_state
By default, Device42 does not update asset_state values in Freshservice (in Device42, the field is called in_service).
The mapping file includes <field> elements with asset_state as the target. The skip-update attribute is set to "true" to prevent the overwriting of values that may trigger Freshservice workflow automations.
If you want Device42 to update asset_state values, set skip-update to "false". There are three <field> elements to update in version 2.0 of the default mapping.xml file:
-
Find the attribute on line 493 (for DOQL v2).
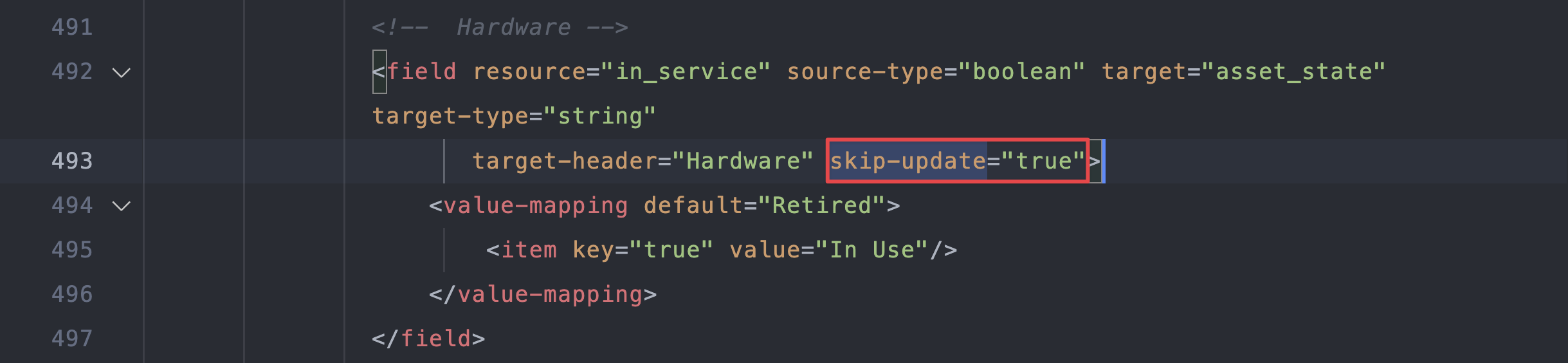
Change
skip-updateto"false":Click to expand the code block
<field resource="in_service" source-type="boolean" target="asset_state" target-type="string"
target-header="Hardware" skip-update="false">
<value-mapping default="Retired">
<item key="true" value="In Use"/>
</value-mapping>
</field> -
Find the attribute on line 1302 (also for DOQL v2).
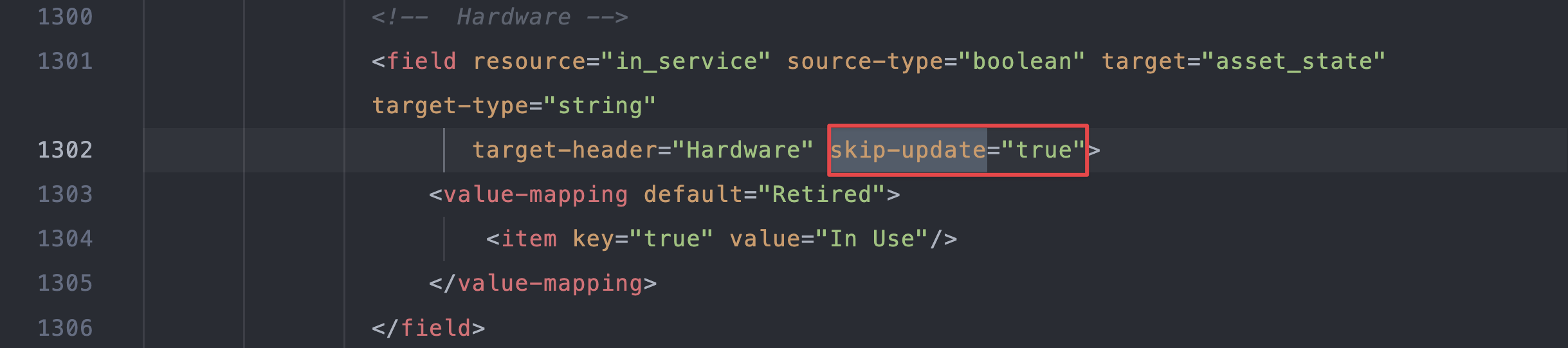
Change
skip-updateto"false":Click to expand the code block
<field resource="in_service" source-type="boolean" target="asset_state" target-type="string"
target-header="Hardware" skip-update="false">
<value-mapping default="Retired">
<item key="true" value="In Use"/>
</value-mapping>
</field> -
Find the attribute on line 1878 (for DOQL v1).
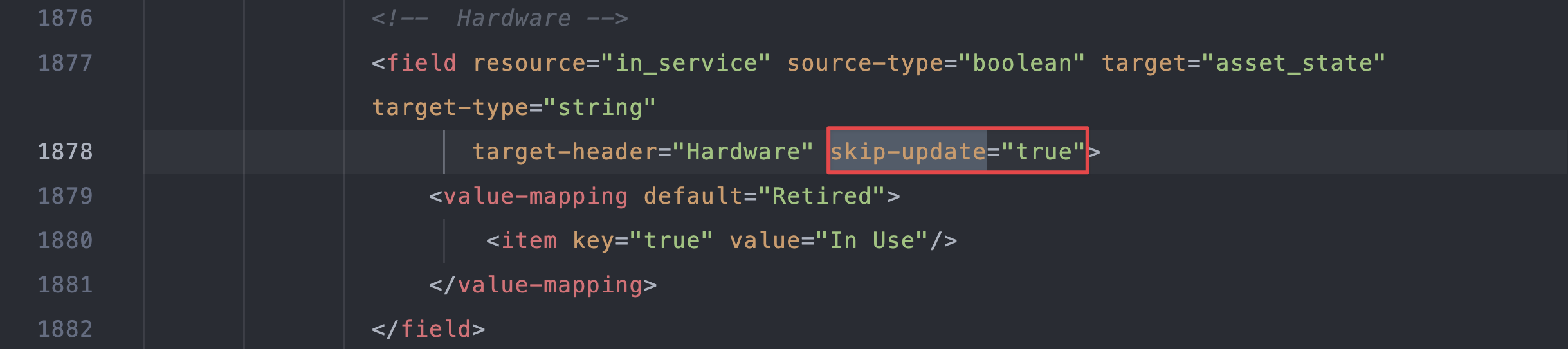
Change
skip-updateto"false":Click to expand the code block
<field resource="in_service" source-type="boolean" target="asset_state" target-type="string"
target-header="Hardware" skip-update="false">
<value-mapping default="Retired">
<item key="true" value="In Use"/>
</value-mapping>
</field>